Summary
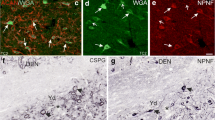
Immunofluorescent staining techniques were performed on a series of cryostat sections of the vestibular ganglion taken during ganglionectomy from a patient with Menière's disease. The direct technique using FITC-labelled antiserum proved the presence of immunoglobulins in the patient's blood vessels and endoneural connective tissue. Preincubation with unlabelled antiserum blocked this reaction. An additional positive reaction of ganglion cells was demonstrated by incubating tissue with the patient's serum. These findings prove antibodies in the patient's serum against the autologous ganglion cells. The vestibular ganglion from a patient with dizziness following a skull base fracture served as a control specimen. No autoimmune reaction was found in the ganglion cells when incubation was carried out with the patient's serum. A positive reaction in the blood vessels and connective tissue was less pronounced. The findings of the present study underline the occurrence of immunological reactions in the vestibular ganglion of patients with Menière's disease. A subsequent degeneration of ganglion cells could provoke clinical Menière's attacks.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold W (1984) Möglichkeiten der immunfluoreszenzmikroskopischen Diagnostik am entkalkten menschlichen Felsenbein. Laryngol Rhinol Otol 63:230–265
Arnold W (1985) Experimental and clinical approach to autoimmune diseases of the inner ear. In: Veldman JE, McCabe BF, Huizing EH, Mygind N (eds) Immunobiology, autoimmunity, transplantation in otorhinolaryngology. Kugler, Amsterdam, pp 131–136
Elies W (1983) Beiträge zur Ätiologie und Pathogenese ein-und doppelseitiger cochlea-vestibulärer Störungen. Habilitationsschrift, Aachen
Elies W, Plester D (1985) Sensorineural hearing loss and immunity. In: Veldman JE, McCabe BF, Huizing EH and Mygind N (eds) Immunobiology, autoimmunity, transplantation in otorhinolaryngology. Kugler, Amsterdam, pp 111–117
Galic M (1987) Klinische Bedeutung der elektromikroskopischen Pathologie des Ganglion scarpae bei Morbus Meniere. Acta Fac Mod Zagreb [Suppl] 28:189–204
Galic M, Helms J (1977) Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen fiber die Häufigkeit, Verteilung und Struktur des Lipofuszins im Ganglion vestibuli bei Morbus Menièdre. INSERM 68:243–262
Galic M, Helms J (1982) Elektronenmikroskopische Befunde am Bindegewebe von Nervus und Ganglion vestibuli bei Morbus Meniere. Arch Otorhinolaryngol 236:67–79
Galic M, Schmelzer A (1987) The lipofuscin content of Scarpa's ganglion of normal and Menière's disease patients related to age: a histological and morphometric study. Clin Neuropathol 6:88–92
Gebbers JO, Altermatt HJ, Arnold W, Laissue JA, Pfaltz CR (1987) Bindung von Serum-Immunglobulinen an menschlichen Innenohrgewebe bei Innenohrschwerhörigkeit. Methodische Grenzen. HNO 35:487–491
Giebel W (1987) Immunological studies in inner ear diseases. Acta Med Fac Zagreb [Suppl] 28:224–234
Giebel W, Kirsch H, Lang B, Voigt P (1986) Qualitative und quantitative Beurteilung der Antikörperkonzentration im Serum bei Innenohrerkrankungen. Arch Otorhinolaryngol 243 [Suppl II]:167–170
Kaupp H (1984) Diskussionsbemerkungen zu den Referaten Lehnhardt B, Klinik der Innenohrschwerhörigkeiten. Arch Otorhinolaryngol 241 [Suppl II]:11–13
Kempf HG, Hörnig T (1987) Immunologische Befunde und Therapieergebnisse bei chronisch-progredienter Innenohrschwerhörigkeit. HNO 35:38–42
McCabe BF (1979) Autoimmune sensorineural hearing loss. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 88:585–589
Wei NR, Giebel W (1988) Spezifische und unspezifische Fluoreszenz bei Verwendung von Gefrierschnitten der Cochlea. Rhinol Otol Laryngol 67:512–516
Wei NR, Giebel W, Kaupp H, Plester D (1985) The application of human and animal tissue for testing Immoral antibodies in inner ear disease. In: Meyer E (ed) New dimensions in otorhinolaryngology, head and neck surgery, vol 2. Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam, pp 935–937
Wei NR, Giebel W, Plester D, Schrader M (1986) Zur Verwendung von Cochleagewebe von Goldhamster und Mensch zur Auswertung humoraler Antikörper bei Innenohrerkrankungen. Arch Otorhinolaryngol 243 [Suppl II]:165–167
Zanetti F, Klein R, Berg P (1987) Progressive Innenohrerkrankungen — Folge eines sekundären autoimmunen Prozesses? HNO 35:34–37
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, N.R., Helms, J. & Giebel, W. Immunohistochemical findings in the vestibular ganglion from a patient with Menière's disease. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 247, 340–344 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00179002
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00179002