Abstract
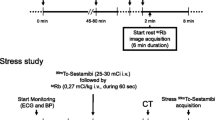
The purpose of this study was to determine the blood clearance, myocardial uptake and heart/lung and heart/liver ratios of technetium 99m methoxyisobutylisonitrile (99mTc-SESTAMIBI) following 3 different types of cardiac stimulation in normal subjects: treadmill stress (STRESS), intravenous administration of dipyridamole (DIP) and trans-oesophageal atrial pacing (TAP). Ten normal volunteers were submitted to 3 injections of 99mTc-SESTAMIBI (10 mCi/70 kg, separated by an interval of 7 days) following STRESS (standard Bruce protocol), DIP (0.142 mg/kg·min during 4 min) and TAP procedures. Blood samples were collected from 1 to 60 min after each 99mTc-SESTAMIBI injection. Planar imaging was performed at 5, 30 and 60 min. Blood retention (percentage of injected dose at 1 min) was 56% ± 4%, 24% ± 4% and 38% ± 6% for STRESS, DIP and TAP, respectively (P<0.001). Myocardial uptake was similar for the 3 procedures while the heart/lung ratio at 60 min was 3.1 ± 0.5, 3.8 ± 0.6 and 3.2 ± 0.5 for STRESS, DIP and TAP, respectively. Heart/liver ratio at 60 min was 1.9±0.5, 1.3±0.3 and 1.1±0.2 for STRESS, DIP and TAP, respectively (P<0.001). These results demonstrated that the 3 types of cardiac stimulation show good imaging parameters with 99mTc-SESTAMIBI.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benson WD (1987) Transesophageal electrocardiography and cardiac pacing: state of the art. Circulation 75:III 86-III 90
Boucher CA, Brewster DC, Darling C et al. (1985) Determination of cardiac risk by dipyridamole-thallium imaging before peripheral vascular surgery. N Engl J Med 312:389–394
Brown KA, Boucher CA, Okada RD et al. (1983) Prognostic value of exercise thallium-201 imaging in patients presenting for evaluation of chest pain. J Am Coll Cardiol 1(4):994–1001
Gibson RS, Watson DD, Craddock GB et al. (1983) Prediction of cardiac events after uncomplicated myocardial infarction: a prospective study comparing predischarge exercise thallium-201 scintigraphy and coronary angiography. Circulation 68(2):321–336
Heller GV, Aroesty JM, Partner JA, et al. (1984) The pacing stress test: thallium-201 myocardial imaging after atrial pacing. Diagnostic value in detecting coronary artery disease compared with exercise testing. J Am Coll Cardiol 3(5):1197–1204
Holman BL, Sporn V, Jones AG, et al. (1987) Myocardial imaging with technetium-99m CPI: initial experience in the human. J Nucl Med 28:13–18
Jones AG, Abrams MJ, Davison A, et al. (1984) Biological studies of a new class of technetium complexes: the hexakis (alkylisonitrile) technetium (I) cations. Int J Nucl Med Biol 11(3–4):225–234
Karcher G, Bertrand A, Amor M, et al. (1987) Qualitative and quantitative comparison of 201-T1 and Tc-99m isonitrile by SPECT in coronary artery disease. J Nucl Med 28:654–655
Kiat H, Maddahi J, Roy L, et al. (1989) Comparison of technetium 99m-methoxy isobutyl isonitrile and thallium-201 for evaluation of coronary artery disease by planar and tomographic methods. Am Heart J 117(1):1–11
Leppo J, Boucher CA, Okada RD, et al. (1982) Serial thallium-201 myocardial imaging after dipyridamole infusion: diagnostic utility in detecting coronary stenoses and relationship to regional wall motion. Circulation 66(3):649–657
Leppo J, O'Brien J, Rothendler JA, et al. (1984) Dipyridamole thallium scintigraphy in the prediction of future cardiac events after acute myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med 310:1014–1018
Maddahi J, Merz R, Wantrain KF, et al. (1987) Tc-99m-MIBI (RP-30) and Tl-201 myocardial perfusion scintigraphy in patients with coronary artery disease: quantitative comparison of planar and tomographic techniques for perfusion defect intensity and defect reversibility. J Nucl Med 28:654–655
McKusick KA, Holman BL, Jones AG, et al. (1986) Comparison of 3 Tc-99m isonitriles for detection of ischemic heart disease in humans (abstract). J Nucl Med 27:878
Okada RD, Boucher CA, Strauss HW, et al. (1980) Exercise radionuclide imaging approaches to coronary artery disease. Am J Cardio1 46:1188–1204
Picard M, Dupras G, Taillefer R, et al. (1987) Myocardial perfusion agents: compared biodistribution of 201-thallium, Tc-99m-tertiary butyl isonitrile (TBI) and Tc-99m-methoxy isobutyl isonitrile (MIBI). J Nucl Med 28:654–655
Pohost GM, Zir LM, Moore RM, et al. (1979) Differentiation of transiently ischemic from infarcted myocardium by serial imaging after a single dose of thallium-201. Circulation 55:294–302
Rothendler JA, Okada RD, Wilson RA (1985) Effect of a delay in commencing imaging on the ability to detect transient thallium defects. J Nucl Med 26:880–883
Sia STB, Holman BL, McKusick KA, et al. (1986) The utilization of Tc-99m-TBI as a myocardial perfusion agent in exercise studies: comparison with TL-201 thallous chloride and examination of its biodistribution in humans. Eur J Nucl Med 12:333–336
Stratmann HG, Mark AL, Walter KE, et al. (1989) Diagnostic value of atrial pacing and thallium-201 scintigraphy for the assessment of patients with chest pain. Clin Cardiol 12:193–201
Taillefer R, Gagnon A, Laflamme L, et al. (1989) Same day injections of Tc-99m methoxy isobutyl isonitrile (hexamibi) for myocardial transgraphic imaging: comparison between rest-stress and stress-rest injection sequences. Eur J Nucl Med 15:113–117
Taillefer R, Lambert R, Dupras G, et al. (1989b) Clinical comparison between thallium-201 and Tc-99m-methoxy isobutyl isonitrile (hexamibi) myocardial perfusion imaging for detection of coronary artery disease. Eur J Nucl Med 15:280–286
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Offprint requests to: R. Taillefer
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Primeau, M., Taillefer, R., Essiambre, R. et al. Technetium 99m SESTAMIBI myocardial perfusion imaging: comparison between treadmill, dipyridamole and trans-oesophageal atrial pacing “stress” tests in normal subjects. Eur J Nucl Med 18, 247–251 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00186648
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00186648