Abstract
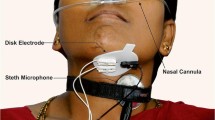
Many children with cerebral palsy (CP) suffer from feeding disorders. Twenty children with spastic CP and 20 neurologically normal children (age range 6.2–12.9 years) were monitored with ultrasound imaging of the oral cavity synchronized with surface electromyographic (EMG) recordings of masseter and infrahyoid museles and respiratory inductance plethysmograph (RIP) recordings during feeding tasks. A lip-cup contact detector signaled contact of the drinking cup on the lip during liquid tasks. Children with CP required more time than normals for collection and organization of 5 ml and 75 ml liquid boluses for swallowing. The ventilatory preparation phase, recovery to baseline resting ventilatory pattern after swallowing, and total time for task completion were longer in children with CP for 5-ml and 75-ml tasks. The interval from lip-cup contact until alteration of ventilation from baseline resting ventilatory pattern was longer for children with CP during 75-ml tasks but not for 5-ml tasks. The interval from completion of the task-related cookie swallow until initiation of the next swallow was longer in children with CP than in normal children. These data provide evidence than children with CP manage solid boluses more easily than liquid boluses and small liquid boluses more easily than large liquid boluses. This investigation statistically confirms empirically based recommendations that children with CP be allowed more time to complete feeding tasks and consume small volume drinks rather than large volume drinks.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Freeman JM, Nelson KB: Intrapartum asphyxia and cerebral palsy. Pediatrics 82:240–249, 1988
Blair E, Stanley F: Interobserver agreement in the classification of cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol 27:615–622, 1985
Bjure J, Berge K: Dynamic and static lung volumes of school children with cerebral palsy. Acta Paed Scand (Suppl) 204:5–39, 1970
Miyasaka K, Hoffman HJ, Froese AB: The influence of chronic cerebellar stimulation on respiratory muscle coordination in a patient with cerebral palsy. Neurosurgery 2(3):217–224, 1979
Wong PKH, Hoffman HJ, Froese AB, Platt LJ, Blacha S, Gear J: Cerebellar stimulation in the management of cerebral palsy: clinical and physiological studies. Neurosurgery 5:217–224, 1979
Storey AT: Laryngeal initiation of swallowing. Exp Neurol 20:359–365, 1968
Mueller H: Feeding. In: Handling the Young Cerebral Palsied Child at Home. London: William Heinemann Medical Books Ltd, 1974, pp 111–130
Helfrich-Miller KR, Rector KL, Straka JA: Dysphagia: its treatment in the profoundly retarded cerebral palsied patient. Arch Phys Med Rehab 67:520–525, 1986
Griggs C, Jones P, Lee R: Videofluoroscopic investigation of children with multiple handicaps. Dev Med Child Neurol 31:303–308, 1989
McPherson KA, Kenny DJ, Koheil R, Bablich K, Sochaniwskyj A, Milner M: Ventilation/swallowing interactions in normal children and children with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol (in press)
Woods GE: The handicapped child. Assessment and management. In: Cerebral Palsy—Types of Movement Defect. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1975, pp 108–138
Shawker TH, Sonies B, Stone M, Baum BJ: Real-time ultrasound visualization of tongue movement during swallowing. J Clin Utrasound 11:485–490, 1983
Shawker TH, Sonies B, Hall TE, Baum BF: Ultrasound analysis of tongue, hyoid and larynx activity during swallowing. Invest Radiol 19:82–86, 1984
Smith WL, Erenberg A, Nowak A, Franken EA: Physiology of sucking in the normal term infant using real-time US. Radiology 156:379–381, 1985
Stone M, Shawker TH: An ultrasound examination of tongue movement during swallowing. Dysphagia 1:78–83, 1986
Weber F, Woolridge MW, Baum JD: An ultrasonographic study of the organization of sucking and swallowing by newborn infants. Dev Med Child Neurol 28:19–24, 1986
Sonies B, Parent L, Morrish K, Baum B: Durational aspects of the oral-pharyngeal phase of swallow in normal adults. Dysphagia 3:1–10, 1988
Bosma JF, Hepburn LG, Josell SD, Baker K: Ultrasound demonstration of tongue motions during suckle feeding. Dev Med Child Neurol 23:223–229, 1990
Wein B, Böcler R, Klajman S: Temporal reconstruction of sonographic imaging of disturbed tongue movements. Dysphagia 6:135–139, 1991
Zagzebski JA: Bioeffects and safety considerations. In: Textbook of Diagnostic ultrasonography. Toronto: The C.V. Mosby Co, 1983
Kenny DJ, Casas MJ, McPherson KA: Correlation of ultrasound imaging of oral swallow with ventilatory alterations in cerebral palsied and normal children: preliminary observations. Dysphagia 4:112–117, 1989
Loveridge B, West P, Anthonisen NR, Kryger MH: Singleposition calibration of the respiratory inductance plethysmograph. J Appl Phys 55:1031–1034, 1983
Casas MJ: Ultrasound investigation of ventilation/swallowing interactions during the oral phase of swallow. Thesis, Toronto: University of Toronto, 1992
Wilson S, Thach BT, Brouillette RT, Abu-Osba YK: Coordination of breathing and swallowing in human infants. J Appl Phys 50:851–859, 1981
Nishino T, Yonezawa T, Honda Y: Effects of swallowing on the pattern of continuous respiration in human adults. Am Rev Resp Dis 132:1219–1222, 1985
Sochaniwskyj AE, Koheil RM, Bablich K, Kenny DJ: Oral motor functioning, frequency of swallowing and drooling in normal children and cerebral palsy children. Arch Phys Med Rehab 67:866–874, 1986
Selley W, Flack F, Ellis R, Brooks W: Respiratory patterns associated with swallowing: part 1. The normal adult pattern and changes with age. Age Ageing 18:169–172, 1989
Widdicombe J: Nasal and pharyngeal reflexes. In: Respiratory Function of the Upper Airway. New York: Marcel Dekker, 1988, pp 137–144
Coster ST, Schwarz WH: Rheology and the swallow=safe bolus. Dysphagia 1:113–118, 1987
Patrick J, Boland M, Stoski D, Murray GE: Rapid correction of wasting in children with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol 28:734–739, 1986
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Casas, M.J., Kenny, D.J. & McPherson, K.A. Swallowing/ventilation interactions during oral swallow in normal children and children with cerebral palsy. Dysphagia 9, 40–46 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00262758
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00262758