Summary
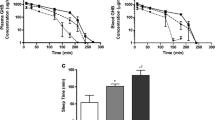
Gamma-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) is effective in treatment of the alcohol and opiate withdrawal syndromes. Its absorption and disposition kinetics have been studied in 8 healthy male volunteers following oral administration of single doses of 12.5, 25 and 50 mg kg−1.
The AUC increased disproportionately with the dose and so the apparent oral clearance decreased significantly as the dose was increased, whereas the terminal half-life and mean residence time increased. The peak plasma concentrations normalised to the lowest dose fell significantly with increasing doses, whilst the corresponding peak times increased.
These findings suggest that both the oral absorption and the elimination of GHB are capacity-limited processes. GHB did not bind to significant extent to plasma proteins over the therapeutic concentration range.
The pharmacokinetic parameters in healthy volunteers were not significantly different from those previously observed in alcohol-dependent patients with compensated alcoholic liver disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roth RH, Giarman NJ (1969) Conversion in vivo of gamma-aminobutyric to gamma-hydroxybutyric acid in the rat. Biochem Pharmacol 18: 247–250
Snead OC, Morley BJ (1981) Ontogeny of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid. Regional concentration in developing rat, monkey and human brain. Brain Res 227: 579–589
Vayer P, Mandel P, Maitre M (1987) Gamma-hydroxybutyrate, a possible neurotransmitter. Life Sci 41: 1547–1557
Laborit H, Jovany JM, Gerard J, Fabiani F (1960) Sur un substrat metabolique à action centrale inibitrice. Le 4-hydroxybutyrate de Na. Press Med 50: 1867–1869
Mamelak M, Scharf MB, Woods M (1986) Treatment of narcolepsy with gamma-hydroxybutyrate. A review of clinical and sleep laboratory findings. Sleep 9: 285–289
Gallimberti L, Canton G, Gentile N, Ferri M, Cibin M, Ferrara SD, Fadda F, Gessa GL (1989) Gamma-hydroxybutyric acid for treatment of alcohol withdrawal syndrome. Lancet 2: 787–789
Gallimberti G, Ferri M, Ferrara SD, Fadda F, Gessa GL (1992) Gamma-hydroxybutyric acid in the treatment of alcohol dependence: a double blind study. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 16: 673–676
Ferrara SD, Zotti S, Tedeschi L, Frison G, Castagna F, Gallimberti L, Gessa GL, Palatini P (1992) Pharmacokinetics of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid in alcohol dependent patients after single and repeated oral doses. Br J Clin Pharmacol 34: 231–235
Hoyumpa AM, Schenker S (1982) Major drug interactions: effect of liver disease, alcohol and malnutrition. Ann Rev Med 33: 113–149
Gallimberti L, Cibin M, Pagnin P, Sabbion R, Pani PP, Pirastu R, Ferrara SD, Gessa GL (1993) Gamma-hydroxybutyric acid for treatment of opiate withdrawal syndrome. Neuropsychopharmacology 9: 77–82
Ferrara SD, Tedeschi L, Frison G, Castagna F, Gallimberti L, Giorgetti R, Gessa GL, Palatini P (1993) Therapeutic gamma-hydroxybutyric acid monitoring in plasma and urine by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. J Pharmaceut Biomed Anal 11: 483–487
Huang J-D (1983) Errors in estimating the unbound fraction of drugs due to the volume shift in equilibrium dialysis. J Pharm Sci 72: 1368–1369
Gibaldi M, Perrier R (1982) Pharmacokinetics. Dekker, New York
Deleted
van der Pol W, van der Kleijn E, Lauw M (1975) Gas chromatographic determination and pharmacokinetics of 4-hydroxybutyrate in dog and mouse. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 3: 99–113
Shumate JS, Snead OC (1979) Plasma and central nervous system kinetics of gamma-hydroxybutyrate. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol 25: 241–256
Lettieri JT, Fung HL (1979) Dose-dependent pharmacokinetics and hypnotic effects of sodium gamma-hydroxybutyrate in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 208: 7–11
Arena C, Fung HL (1980) Absorption of sodium gamma-hydroxybutyrate and its prodrug gamma-butyrolactone: relationship between in vitro transport and in vivo absorption. J Pharm Sci 69: 356–358
van Ginneken CAM, van Rossum JM, Fleuren HLJM (1974) Linear and nonlinear kinetics of drug elimination. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 2: 395–415
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Palatini, P., Tedeschi, L., Frison, G. et al. Dose-dependent absorption and elimination of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid in healthy volunteers. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 45, 353–356 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00265954
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00265954