Abstract
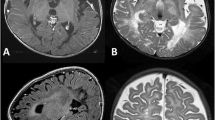
Two siblings presented with macrocephaly, psychomotor delay, and progressive dystonia. The initial diagnosis was of hydrocephalus and bilateral temporal cerebrospinal fluid collections. Following ventriculoperitoneal shunting, the patients showed only modest neurological improvement. Metabolic investigations performed later in the course of the disease disclosed increased levels of glutaric acid in the urine and decreased levels of serum carnitine, which were confirmatory of glutaric aciduria type 1. The association of macrocephaly, dystonia, and bilateral temporal arachnoid cysts, shown either by computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, seems to be diagnostic of glutaric aciduria type 1. The authors report these two cases as they think they might be of interest to neurosurgeons.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altman NR, Rovira MJ, Bauer M (1991) Glutaric aciduria type 1: MR findings in two cases. AJNR 12:966–968
Amir N, El Peleg O, Shalev RS, Christensen E (1987) Glutaric aciduria type I: clinical heterogeneity and neuroradiologic features. Neurology 37:1654–1657
Amir N, El Peleg ON, Shalev RS, Christensen E (1989) Glutaric aciduria type I: enzymatic and neuroradiologic investigation of two kindreds. J Pediatr 114:983–989
Bennet MJ, Marlow M, Pollitt RJ, Wales JKH (1986) Glutaric aciduria type 1: biochemical investigations and postmortem findings. Eur J Pediatr 145:403–405
Bergman I, Finegold D, Gartner JC Jr, Zitelli BJ, Claassen D, Scarano J, Roe CR, Stanley C, Goodman SI (1989) Acute profound dystonia in infants with glutaric acidemia. Pediatrics 83:228–234
Chalmers RA, Cheng KN, English NR, Jones MA, Savage W (1989) Glutaric aciduria type I: prenatal exclusion using GC-MS analysis of amniotic fluid and enzymology with oxidation of [6–14C]lysine. J Inherited Metab Dis 12:335–336
Christensen E (1989) First trimester prenatal exclusion of glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency (glutaric aciduria type 1). J Inherited Metab Dis 12 [Suppl 2]:227–229
Francois B, Jafken J, Gillis P (1990) Vigabatrim in the treatment of glutaric aciduria type I. J Inherited Metab Dis 13:352–354
Goodman SI, Markey SP, Moe PG, Miles BS, Teng CC (1975) Glutaric aciduria: a “new” disorder to amino-acid emtabolism. Biochem Med 12:12–21
Goodman SI, Norenberg MD, Skikes RH, Breslich DJ, Moe PG (1977) Glutaric aciduria: biochemical and morphologic considerations. J Pediatr 90:746–750
Gregersen N, Brandt NJ, Christensen E (1977) Glutaric aciduria: clinical and laboratory findings in two brothers. J Pediatr 90:740–745
Hald JK, Nakstad PH, Skieldal OH, Stromme P (1991) Bilateral arachnoid cysts of the temporal fossa in four children with glutaric aciduria type I. AJNR 12:407–409
Harworth JC, Booth FA, Chudley AE, Degroot GW, Dilling LA, Goodman SI, Greenberg CR, Mallory CJ, McClarty BM, Seshia SS (1991) Phenotypic variability in glutaric aciduria type I: report of fourteen cases in five Canadian Indian kindreds. J Pediatr 118:52–58
Hoffman GF, Tretfz FK, Barth PG, Böhles HJ, Biggemann B, Bremer HJ, Christensen E, Frosh M, Hanefeld F, Hunneman DH, Jacobi K, Kurleman G, Laurenz-Wolf B, Rating D, Roe CR, Schutgens BH, Ullrich K, Weisser J, Wendel U, Lehnert W (1991) Glutaryl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency. A distinct encephalopathy. Pediatrics 88:1194–1203
Iafolla AK, Kahler SG (1989) Megalencephaly in the neonatal period as the initial manifestation of glutaric aciduria type I. J Pediatr 114:1004–1006
Kidouchi K, Sugiyama N, Morishita H, Kobayashi M, Wada Y, Nagay S, Sakakibara J (1987) Identification of glutaryl-carnitine in glutaric aciduria type I. J Inherited Metab Dis 10 [Suppl 2]:279–281
Lipkin PH, Roe CR, Goodman SI, Batshaw ML (1988) A case of glutaric aciduria type I: effect of riboflavin and carnitine. J Pediatr 112:62–65
Morton DH, Bennet MJ, Seargeant LE, Nichter CA, Kelley RI (1991) Glutaric aciduria type I: a common cause of episodic encephalopathy and spastic paralysis in the Amish of Lancaster County, Pennsylvania. Am J Med Genet 41:89–95
Naidu SB, Moser HV (1991) Value of neuroimaging in metabolic diseases affecting the CNS. Commentary. AJNR 12:413–416
Orzand PT, Gascon GG (1991) Organic acidurias. A review. Part 1. J Child Neurol 6:196–219
Orzand PT, Gascon GG (1991) Organic acidurias. A review. Part 2. J Child Neurol 6:288–303
Valk J, Knaap MS van der (1989) Magnetic resonance of myelin, myelination, and myelin disorders. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 141–147
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martínez-Lage, J.F., Casas, C., Fernández, M.A. et al. Macrocephaly, dystonia, and bilateral temporal arachnoid cysts: glutaric aciduria type 1. Child's Nerv Syst 10, 198–203 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00301092
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00301092