Abstract
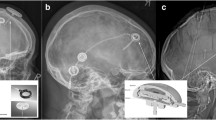
Several intracranial pressure monitoring devices have been developed in the past several years. We have recently adopted the Camino fiberoptic device that permits subdural, intraparenchymal, and intraventricular monitoring. In this report we compare experiences in monitoring a group of pediatric patients with severe craniocerebral trauma and coma, grouped according to severity of Glasgow Coma Scale score. Patient age ranged from 2 to 16 years. Twelve patients were monitored by a ventricular catheter and 37, treated more recently, by a Camino fiberoptic device. The study demonstrated that the fiberoptic device and the ventricular catheter have the same accuracy and reliability. The fiberoptic method correlates very closely with the ventriculostomy method, but the pressure values are always 3±2 mmHg lower than those obtained with the conventional pressure transducer system, especially in more critically ill patients. This new technique is also easier to implant, safer to use, has minimal drift, and is minimally invasive, which particularly speaks for its use in pediatric patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen R (1986) Intracranial pressure: a review of clinical problems, measurement techniques and monitoring methods. J Med Eng Technol 10:299–320
Aucoin PJ, Kotilainen HR, Gantz NM, et al (1986) Intracranial pressure monitors. Epidemiologic study of risk factors and infections. Am J Med 80:369–376
Barlow P, Mendelow AD, Lawrence AE, et al (1985) Clinical evaluation of two methods of subdural pressure monitoring. J Neurosurg 63:578–582
Choux M (1986) Incidence, diagnosis and management of skull fractures. In: Raimondi A, Choux M, Di Rocco C (eds) Head injury in the newborn and infant. Springer, New York Berlin Heidelberg, pp 163–182
Coroneos NJ, McDoxald DG, Gibson RM, et al (1973) Measurement of extradural pressure and its relationship to other intracranial pressure. An experimental and clinical study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 36:514–522
Crutchfield JS, Narayan RK, Robertson CS, Michael LH (1990) Evaluation of fiberoptic intracranial pressure monitor. J Neurosurg 72:482–487
Dearden NM, McDowal DG, Gibson RM et al (1984) Assessment of Leeds device for monitoring intracranial pressure. J Neurosurg 60:123–129
Gambardella G, D'Avella D, Staropoli C, Toscano S, Tomasello F (1991) Bilateral intraparenchymal pressure in patients with unilateral supratentorial mass lesions. VIII International Symposium on Intracranial Pressure, 16–20 June 1991, Rotterdam (abstract no 39)
Gentleman D, Mendelow AD (1986) Intracranial rupture of a pressure monitoring transducer: technical note. Neurosurgery 19:91–92
Guillaume J, Janny P (1951) Monometrie intracrânienne continue; interêt physio-pathologique et clinique de la methode. Presse Med 59:953–955
Lundberg N (1960) Continuous recording and control of ventricular fluid pressure in neurosurgical practice. Acta Psychiatr Neurol Scand [Suppl] 149:1–193
Marshall LF (1986) Intracranial pressure monitoring: theory and practice. In: McLaurin RL, et al (eds) Extracerebral collections. (Advances in neurotraumatology, vol 1) Springer, Wien New York, pp 209–228
Mendelow AD, Rowan JO, Murray L, et al (1983) A clinical comparison of subdural screw pressure measurements with ventricular pressure. J Neurosurg 58:45–50
Miller JD, Bobo H, Kapp JP (1986) Inaccurate pressure readings for subarachnoid bolts. Neurosurgery 19:253–255
North B, Reilly P (1986) Comparison among three methods of intracranial pressure recording. Neurosurgery 18:730–732
Ostrup RC, Luerssen TG, Marchall LF, et al (1987) Continuous monitoring of intracranial pressure with a miniaturized fiberoptic device. J Neurosurg 67:206–209
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gambardella, G., Zaccone, C., Cardia, E. et al. Intracranial pressure monitoring in children: comparison of external ventricular device with the fiberoptic system. Child's Nerv Syst 9, 470–473 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00393552
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00393552