Abstract
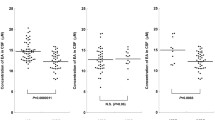
Clinical effects, levels of 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA) and homovanillic acid (HVA) in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and lithium levels in serum were examined in 13 manic depressive patients acutely admitted because of a manic or hypomanic episode. Patients were examined before and 12 days after the beginning of lithium treatment. Manic scores were significantly reduced during treatment. The levels of 5-HIAA as well as HVA increased significantly during treatment. The HVA to 5-HIAA ratio was significantly reduced, indicating a more pronounced change in 5-HIAA than in HVA. The 5-HIAA and HVA levels before as well as after 12 days of treatment were significantly correlated. No significant correlation was found between manic scores and monoamine metabolites in CSF or between lithium level in serum and reduction of manic scores or elevation of monoamine metabolites in CSF in the relative small number of patients studied.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
åsberg, M., Bertilsson, L., Tuck, D., Cronholm, B., Sjöqvist, F.: Indoleamine metabolites in the cerebrospinal fluid of depressed patients before and during treatment with nortriptyline. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 14, 277–286 (1973)
Bertilsson, L., åsberg, M., Thorén, P.: Differential effect of chlorimipramine and nortriptyline on metabolites of serotonin and noradrenaline in the cerebrospinal fluid of depressed patients. Europ. J. clin. Pharmacol. 7, 365–368 (1974)
Bliss, E. L., Ailion, J.: The effect of lithium upon brain neuroamines. Brain Res. 24, 305–310 (1970)
Bockar, J., Roth, R., Heninger, G.: Increased human platelet monoamine oxidase activity during lithium carbonate therapy. Life Sci. 15, 2109–2118 (1975)
Bowers, M. B., Jr., Henninger, G. R., Gerbode, F.: Cerebrospinal fluid 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid and homovanillic acid in psychiatric patients. Int. J. Neuropharmacol. 8, 255–262 (1969)
Bowers, M. B., Jr.: Amitriptyline in man: Decreased function of central 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 15, 167–170 (1974)
Bruinvels, J.: Inhibition of the biosynthesis of 5-hydroxytryptamine in rat brain by imipramine. Europ. J. Pharmacol. 20, 231–237 (1972)
Bulat, M., Zivkovic, B.: Origin of 5-HIAA in the spinal fluid. Science 173, 738–740 (1971)
Curzon, G., Gumpert, E. J. W., Sharpe, D. M.: Amine metabolites in the lumbar CSF of humans with restricted flow of CSF. Nature (Lond.) 231, 189–191 (1971)
Fri, C.-G., Wiesel, F.-A., Sedvall, G.: Simultaneous quantification of homovanillic acid and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in cerebrospinal fluid by mass fragmentography. Life Sci. 14, 2469–2480 (1974)
Fuxe, K., Hökfelt, T., Ungerstedt, U.: Distribution of monoamines in the mammalian central nervous system by histochemical studies. In: Metabolism of amines in the brain. G. Hooper, ed. London: MacMillan 1969
Klerman, G. L., Cole, J. O.: Clinical pharmacology of imipramine and related anti-depressant compounds. Pharmacol. Rev. 17, 101–141 (1965)
Lapin, I. P., Oxenkrug, G. F.: Intensification of the central serotoninergic processes as a possible determinant of the thymoleptic effect. Lancet 1969 I, 132–136
Mendels, J.: Relationship between depression and mania. Lancet 1971 I, 342
Pearson, K.: Tables of statisticians and biometricians. 3rd ed. London: Cambridge Univ. Press 1930
Perez-Cruet, J., Tagliamonte, A., Tagliamonte, P., Gessa, G. L.: Stimulation of serotonin synthesis by lithium. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 178, 325–330 (1971)
Petterson, U., Fyrö, B., Sedvall, G.: A new scale for the longitudinal rating of manic states. Acta psychiat. scand. 49, 248–256 (1973)
Post, R. M., Goodwin, F. K., Gordon, E., Watkin, D. M.: Amine metabolites in human cerebrospinal fluid: Effect of cord transection and spinal fluid block. Science 179, 897–899 (1973a)
Post, R. M., Kotin, J., Goodwin, F. K., Gordon, E. K.: Psychomotor activity and cerebrospinal fluid amine metabolites in affective illness. Amer. J. Psychiat. 130, 67–72 (1973b)
Schildkraut, J. J.: The catecholamine hypothesis of affective disorders. A review of supporting evidence. Amer. J. Psychiat. 122, 509–522 (1965)
Schildkraut, J. J., Logue, M. A., Dodge, G. A.: The effects of lithium salts on the turnover and metabolism of nor-epinephrine in rat brain. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 14, 135–141 (1969)
Schubert, J.: Effect of chronic lithium treatment on monoamine metabolism in rat brain. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 32, 301–311 (1973)
Schou, M: Special review. Lithium in psychiatric therapy and prophylaxis. J. Psychiat. Res. 6, 67–95 (1968)
Schou, M., Amdisen, A., Baastrup, P. C.: The practical management of lithium treatment. Brit. J. Hosp. Med. 6, 53–60 (1971)
Sedvall, G., Petterson, U., Fyrö, B.: Individual differences in serum levels of lithium in human subjects receiving fixed doses of lithium carbonate. Relation to renal lithium clearance and body weight. Pharmacol. Clin. 2, 231–235 (1970)
Sheard, M. H., Aghajanian, G. K.: Neuronally activated metabolism of brain serotonin: Effect of lithium. Life Sci. 9, 285–290 (1970)
Sjöqvist, F.: A pharmacokinetic approach to the treatment of depression. Int. J. Pharmacopsychiat. 6, 147–169 (1971)
Sjöström, R., Roos, B.-E.: 5-Hydroxyindoleacetic acid and homovanillic acid in cerebrospinal fluid in manic-depressive psychosis. Europ. J. clin. Pharmacol. 4, 170–176 (1972)
Snedecor, G. W., Cochran, W. G.: Statistical methods. Ames, Iowa: Iowa State University Press 1967
Sourkes, T. L.: On the origin of homovanillic acid (HVA) in the cerebrospinal fluid. J. Neurol. Trans. 34, 153 (1973)
Wilk, S., Shopsin, B., Gershon, S., Suhl, M.: Cerebrospinal fluid levels of MHPG in affective disorders. Nature (Lond.) 235, 440–441 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fyrö, B., Petterson, U. & Sedvall, G. The effect of lithium treatment on manic symptoms and levels of monoamine metabolites in cerebrospinal fluid of manic depressive patients. Psychopharmacologia 44, 99–103 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421192
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421192