Summary
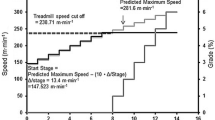
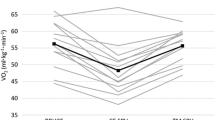
The purpose of this study was to measure the VO2max of trained cyclists on the treadmill (X ± SD=54.7±6.3 ml kg−1 min−1), while riding a bicycle on a velodrome track at 100 rpm (53.7±7.8) and on the bicycle ergometer at 60 rpm (62.4±8.1): VO2max beeing the highest in the latter case (p<0.05). The highest maximal HR, 188±6 beats min−1, was observed during the treadmill test, while estimates of 184±6 and 179±7 were obtained for the velodrome and the bicycle ergometer tests, respectively. No significant differences were observed in the blood lactate concentrations (treadmill: 10.35±4.01 bicycle ergometer: 10.25±2.29 velodrome: 10.95±1.51 mmol L−1. In conclusion, bicycle ergometer tests might not be specific enough to evaluate the ability of trained cyclists to perform an endurance or aerobic task on the track. Trained cyclists, as opposed to untrained ones, appear to achieve higher VO2max on the bicycle ergometer as compared to the treadmill.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
åstrand PO, Rodahl K (1970) Textbook of work physiology. McGraw Hill, New York
Davies CTM (1980) Effect of air resistance on the metabolic cost and performance of cycling. Eur J Appl Physiol 45: 245–254
di Prampero PE, Cortili G, Mognoni P, Saibene F (1976) Energy cost of speed skating and efficiency of work against air resistance. J Appl Physiol 40: 584–591
di Prampero PE, Cortili G, Mognoni P, Saibene F (1979) Equation motion of a cyclist. J Appl Physiol 47: 201–206
Faulkner JA, Roberts DE, Elk RL, Conway J (1971) Cardiovascular response to submaximum and maximum effort cycling and running. J Appl Physiol 30: 457–461
Froelicher VF, Brammell H, Davis G, Noguera I, Stewart A, Lancaster MC (1974) A comparison of the reproducibility and physiologic response to three maximal treadmill exercise protocols. Chest 65: 512–517
Hagberg JM, Giese MD, Schneider RB (1978) Comparison of three procedures for measuring VO2max in competitive cyclists. Eur J Appl Physiol 39: 47–52
Hartung H, McMillen J (1978) Specificity of aerobic testing in competitive cyclists compared with runners. In: Landry F, Orban WAR (eds) Exercise physiology book 4. Symposia Specialties Publ, Miami, pp 615–622
Hermansen L, Saltin B (1969) Oxygen uptake during maximal treadmill and bicycle exercise. J Appl Physiol 26: 31–37
Lavoie NF, Mahoney MD, Marnelic LS (1978) Maximal oxygen uptake on a bicycle ergometer without toe stirrups and with toe stirrups versus a treadmill. Can J Appl Sport Sci 3: 99–102
Léger LA, Seliger V, Brassard L (1980) Backward extrapolation of VO2max from oxygen recovery curve in humans. Med Sci Sports Exercise 12: 24–27
Matsui H, Kitamura K, Miyamura M (1978) Oxygen uptake and blood flow of the lower limb in maximal treadmill and bicycle exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 40: 57–62
Miyamura M, Kitamura K, Yamada A, Matsui H (1978) Cardiorespiratory responses to maximal treadmill and bicycle exercise in trained and untrained subjects. J Sports Med 18: 25–32
Niemela K, Palatsi I, Linnaluoto M, Takhunen J (1980) Criteria for maximum oxygen uptake in progressive bicycle tests. Eur J Appl Physiol 44: 51–59
Pannier JL, Vrijens J, VanCanter C (1980) Cardiorespiratory response to treadmill and bicycle exercise in runners. Eur J Appl Physiol 43: 243–251
Pechar GS, McArdle WD, Katch FI, Magel JR, De Luca J (1974) Specificity of Cardiorespiratory adaptation to bicycle and treadmill training. J Appl Physiol 36: 753–756
Pugh LGCE (1974) The relation of oxygen intake and speed in competition cycling and comparative observations on the bicycle ergometer. J Physiol 241: 795–808
Stromme SB, Ingjer F, Meen HD (1977) Assessment of maximal aerobic power in specifically trained athletes. J Appl Physiol 42: 833–837
Whitt FR (1971) A note on the estimation of the energy expenditure of sporting cyclists. Ergonomics 14: 419–424
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by the Fonds de développement pour la recherche de l'Université de Montréal
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ricci, J., Léger, L.A. VO2max of cyclists from treadmill, bicycle ergometer and velodrome tests. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 50, 283–289 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00422167
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00422167