Summary
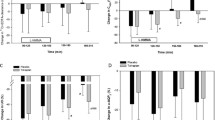
Renal plasma flow (RPF), glomerular filtration rate (GFR), arginine vasopressin in plasma (AVP), free water clearance (\({\text{C}}_{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}} {\text{O}}}\)) and blood pressure (BP) were determined in 11 patients with essential hypertension at the end of 3 consecutive periods of observation each of 6 of weeks duration; indapamide 2.5 mg daily was given in period 2 and placebo in periods 1 and 3. RPF and GFR were reduced by 9% and BP by 9%/14% supine and 14%/12% standing during indapamide treatment. Changes in renal haemodynamics were not correlated with those in BP. AVP was not significantly altered by indapamide and was not correlated with BP. Indapamide reduced \({\text{C}}_{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}} {\text{O}}}\) possibly due to the reduction in GFR. It is concluded that indapamide evidently induces redistribution of the cardiac output, with enhanced muscle blood flow and reduced renal perfussion, and that AVP does not seem to be involved in blood pressure regulation in mild to moderate essential hypertension under basal conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartter FC (1981) Vasopressin and blood pressure. N Engl J Med 304: 1097–1098
Bradley JV (1968) Distribution-free statistical tests. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA
Burgess CD, McKee CEL, Wilson CA, Warren DJ (1981) The effect of indapamide on muscle blood flow in hypertensive patients. Postgrad Med J 57 [Suppl 2]: 23–25
Campbell DB, Moore RA (1981) The pharmacology and clinical pharmacology of indapamide. Postgrad Med J 57 [Suppl 2]: 7–17
Cowley AW, Jr, Cushman WC, Quillen EW Jr, Skelton MM, Langford HG (1981) Vasopressin elevation in essential hypertension and increased responsiveness to sodium intake. Hypertension 3 [Suppl 1]: 93–100
Dunn FG, Hellis WS, Tweddel A, Rae AP, Lorimer AR (1981) Non-invasive cardiovascular assessment of indapamide in patients with essential hypertension. Postgrad Med J 57 [Suppl 2]: 19–22
Epstein M, Oster JR (1982) Beta-blockers and the kidney. Mineral Electrolyte Metab 8: 237–254
Finch L, Hicks PE, Moore RA (1977) The effects of indapamide on vascular reactivity in experimental hypertension. Curr Med Res Opin 5 [Suppl 1]: 44–54
Grimm M, Weidmann P, Meier A, Keusch G, Ziegler W, Glück Z, Beretta-Piccoli C (1981) Correction of altered noradrenaline reactivity in essential hypertension by indapamide. Br Heart J 46: 404–409
Horgan JH, O'Donovan A, Teo KK (1981) Ecchocardiographic evaluation of left ventricular function in patients showing an antihypertensive and biochemical response to indapamide. Postgrad Med J 57 [Suppl 2]: 64–67
Isaac R, Witchitz S, Kamoun A, Bagattini JC (1977) A long-term study of the influence of indapamide on the exchangeable potassium and sodium pools in hypertensive patients. Curr Med Res Opin 5 [Suppl 1]: 64–70
Johnston CI, Newman M, Woods R (1981) Role of vasopressin in cardiovascular homeostasis and hypertension. Clin Sci 61 [Suppl 7]: 129s-139s
Khokar AM, Slater JDH (1976) Increased renal excretion of arginine-vasopressin during mild hydropenia in young men with mild essential benign hypertension. Clin Sci 51 [Suppl 3]: 691s-694s
Laubie M, Schmitt H (1981) Comparison of the haemodynamic and autonomic effects of furosemide and indapamide, and localization of the natriuretic action of indapamide. Curr Med Res Opin 5 [Suppl 1]: 89–100
Mogensen, CE (1971) Glomerular filtration rate and renal plasma flow in short-term juvenile diabetes mellitus. Scand J Clin Invest 28: 91–100
Möhring J, Möhring B, Petri M, Haack D (1977) Vasopressor role of ADH in the pathogenesis of malignant DOC hypertension. Am J Physiol 232: F260–269
Onesti G, Pitone J, Lowenthal DL, Kim KE, Affrime M, Bronstein BJ, Shirk J, Valvo E, Martinez E, Fernandes M, Swartz C (1977) Studies on the natriuretic effect and site of action of indapamide. Curr Med Res Opin 5 [Suppl 1]: 83–88
Padfield PL, Brown JJ, Lever AF, Morton JJ, Robertson JIS (1976) Changes in vasopressin in hypertension: cause or effect? Lancet 1: 1255–1257
Pedersen EB (1978) Abnormal renal haemodynamics during exercise in young patients with mild essential hypertension without treatment and during long-term propranolol therapy. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 38: 567–571
Pedersen EB (1979) Som aspects of kidney function, the reninaldosterone system and sympathetic activity in essential hypertension. Acta Med Scand 636 [Suppl]: 1–66
Robertsen GL, Mahr EA, Athar S, Sinha T (1973) Development and clinical application of a new method for the radioimmunoassay of arginine vasopressin in human plasma. J Clin Invest 52: 2340–2353
Schlesinger P, Oignam W, Tabet FF, Benchimol AB (1977) The treatment of hypertension with indapamide: A controlled trial. Curr Med Res Opin 5 [Suppl 1]: 159–163
Share L, Crofton JT (1982) Contribution of vasopressin to hypertension. Hypertension 4 [Suppl 3]: 85–92
Skov PE, Hansen HE (1974) Glomerular filtration rate, renal plasma flow and filtration fraction in living donors before and after nephrectomy. Acta Med Scand 195: 97–103
Thibonnier M, Aldigier JC, Soto ME, Sassano P, Menard J, Corvol P (1981) Abnormalities and drug-induced alterations of vasopressin in human hypertension. Clin Sci 61 [Suppl 7]: 149s-152s
Uhlich E, Tröger C, Knoll W (1977) Effects of indapamide in hypertensive patients and on experimental vascular reactivity. Curr Med Res Opin 5 [Suppl 1]: 71–78
Warren SE, O'Connor DT, Cohen IM, Mitas JA (1981) Renal hemodynamic changes during long-term antihypertensive therapy. Clin Pharmacol Ther 29: 310–317
Weidman P, Keusch G, Meier A, Glück Z, Grimm M, Beretta-Piccoli C (1980) Effects of indapamide on the body sodium-volume state, plasma renin, aldosterone and catecholamines, and cardiovascular pressor sensitivity in normal and borderline hypertensive man. Proceedings of the Second International Symposium on Arterial Hypertension, Caracas 1979. Velasco M (ed) Int Congr Ser 496: pp 169–181, Excerpta Medica Amsterdam Oxford Princeton
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pedersen, E.B., Danielsen, H. & Spencer, E.S. Effect of indapamide on renal plasma flow, glomerular filtration rate and arginine vasopressin in plasma in essential hypertension. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 26, 543–547 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00543482
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00543482