Summary
Three groups of non-smoking epileptic patients without liver disease receiving antiepileptic monotherapy have been compared with 10 healthy non-smoking volunteers. Group 1 received phenytoin (n=10), Group 2 carbamazepine (n=10) and Group 3 valproic acid (n=6). Cytochrome P-450 activity was monitored by measuring urinary 6-β-hydroxycortisol output and systemic antipyrine clearance.
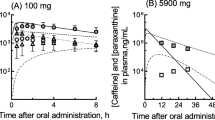
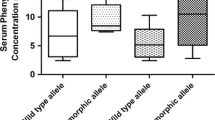
Both, 6-β-hydroxycortisol output and antipyrine clearance were significantly enhanced in patients on phenytoin and carbamazepine, but not in those on valproic acid. On the other hand, phenytoin alone increased the clearance of caffeine from 1.5 (controls) to 3.6 ml · min−1 · kg−1, and reduced its half life from 4.8 to 2.4 h. Carbamazepine and valproic acid had no effect on caffeine metabolism. The results are in keeping with the well known heterogeneity of the hepatic monooxygenase system, as phenytoin and carbamazepine induce different panels of cytochrome P-450 isoenzymes. Phenytoin treatment may impair the validity of the caffeine liver function test.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lauterburg B, Bircher J (1973) Hepatic microsomal drug metabolizing capacity measured in vivo by breath analysis. Gastroenterology 65: 556 (abstract)
Andreasen PB, Ranek L, Statland BE, Tygstrup N (1974) Clearance of antipyrine — dependence of quantitative liver function. Eur J Clin Invest 4: 129–134
Wietholtz H, Vögelin M, Arnaud MJ, Bircher J, Preisig R (1981) Assessment of the cytochrome P-448 dependent liver enzyme system by a caffeine breath test. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 21: 53–59
Campbell ME, Grant DM, Inaba T, Kalow W (1987) Biotransformation of caffeine, paraxanthine, theophylline, and theobromine by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-inducible cytochrome(s) P-450 in human liver microsomes. Drug Metab Dispos 15: 237–249
Bircher J, Küpfer A, Gikalov J, Preisig R (1976) Aminopyrine demethylation measured by breath analysis in cirrhosis. Clin Pharmacol Ther 20: 484–492
Desmond P, Patwardhan RH, Johnson RF, Schenker S (1980) Impaired elimination of caffeine in cirrhosis. Dig Dis Sci 25: 193–197
Renner E, Wietholtz H, Huguenin P, Arnaud MJ, Preisig R (1984) Caffeine: A model compound for measuring liver function. Hepatology 1: 38–46
Zysset T, Wietholtz H (1988) Differential effect of type I and type II diabetes on antipyrine disposition in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 34: 369–375
Knutti R, Rothweiler H, Schlatter C (1981) Effect of pregnancy on the pharmacokinetics of caffeine. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 21: 121–126
Röllinghoff W, Paumgartner G (1982) Inhibition of drug metabolism by cimetidine in man: Dependence on pretreatment microsomal liver function. Eur J Clin Invest 12: 429–432
Broughton LJ, Roger HJ (1981) Decreased systemic clearance of caffeine due to cimetidine. Br J Clin Pharmacol 12: 155–159
Patwardhan RV, Desmond PV, Johnson RF, Schenker S (1980) Impaired elimination of caffeine by oral contraceptive steroids. J Lab Clin Med 4: 603–608
Beach C, Mays D, Guiler R, Jacober C, Gerber N (1986) Inhibition of elimination of caffeine by disulfiram in normal subjects and recovering alcoholics. Clin Pharmacol Ther 39: 265–270
Park BK, Beckenridge AM (1981) Clinical implications of enzyme induction and inhibition. Clin Pharmacokinet 6: 1–24
Stevenson JH, O'Malley K, Shepherd AM (1976) Relative induction potency of anticonvulsant drugs. In: Richens A, Woodford FP (eds) Anticonvulsant drugs and enzyme induction. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 37–46
Aldrige A, Neims AH (1979) The effect of phenobarbital and β-naphtoflavone on the elimination kinetics and metabolic pattern of caffeine in the beagle dog. Drug Metab Dispos 7: 378–382
Parsons WD, Neims AH (1978) Effect of smoking on caffeine clearance. Clin Pharmacol Ther 24: 40–45
Marquis FJ, Carruthers SG, Spence D, Brownstone Y, Toogood J (1983) Phenytoin-theophylline interaction. N Engl J Med 19: 1189–1190
Rosenberry KR, Defusco CJ, Mansmann HC, McGeady SJ (1983) Reduced theophylline half-life induced by carbamazepine therapy. J Pediatrics 3: 472–474
Jost G, Wahlländer A, v. Mandach U, Preisig R (1987) Overnight salivary caffeine clearance: A liver function test suitable for routine use. Hepatology 7: 338–344
Zysset T, Wahlländer A, Preisig R (1984) Evaluation of caffeine plasma levels by an automated enzyme immunoassay (EMIT) in comparison with a high-performance liquid chromatographic method. Ther Drug Monit 6: 348–354
Park BK (1978) A direct radioimmunoassay for 6-β-hydroxycortisol in human urine. J Steroid Biochem 9: 963–966
Zylber-Katz E, Granit L, Levy M (1984) Relationship between caffeine concentration in plasma and saliva. Clin Pharmacol Ther 36: 133–137
v. Mandach U, Jost G, Preisig R (1985) Quantifizierung des arzneimittelabbauenden Enzymsystems bei Leberekrankungen: Vergleiche zwischen Antipyrin Speichelclearance und Aminopyrin Atemtest. Schweiz Med Wochenschr 115: 651–658
Harper JH (1984) Peritz` F-test. Basic program of a multiple comparison test for statistical analysis of all differences among group means. Comput Biol Med 14: 437–445
Wietholtz H, Colombo JP (1976) Das Verhalten der Gamma-Glutamyltranspeptidase und anderer Leberenzyme während der Alkoholentziehungskur. Schweiz Med Wochenschr 106: 981–987
Park BK (1981) Assessment of urinary 6-β-hydroxycortisol as an in vivo index of mixed function oxygenase activity. Br J Clin Pharmacol 12: 97–102
Vesell ES (1979) The antipyrine test in clinical pharmacology: conceptions and misconceptions. Clin Pharmacol Ther 26: 275–286
Schnegg M, Lauterburg B (1986) Quantitative liver function in the elderly assessed by galactose elimination capacity, aminopyrine demethylation and caffeine clearance. J Hepatol 3: 164–171
Moreland TA, Park BK, Rylance GW (1982) Microsomal enzyme induction in children: The influence of carbamazepine treatment on antipyrine kinetics, 6-β-hydroxycortisol excretion and plasma gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase activity. Br J Clin Pharmacol 14: 861–865
Perucca E, Hedges A, Makki KA, Ruprah M, Wilson JF, Richens A (1984) A comparative study of the relative enzyme inducing properties of anticonvulsant drugs in epileptic patients. Br J Clin Pharmacol 18: 401–410
Levy RH, Koch KM (1982) Drug interactions with valproic acid. Drugs 24: 543–556
Bresnick E, Foldes R, Hines RN (1984) Induction of cytochrome P-450 by xenobiotics. Pharmacol Rev 36: 43 S-51 S
Nebert DW, Negishi M (1982) Multiple forms of cytochrome P-450 and the importance of molecular biology and evolution. Biochem Pharmacol 31: 2311–2317
Lu AYH, West SB (1980) Multiplicity of mammalian microsomal cytochromes P-450. Pharmacol Rev 31: 277–295
Ioannides C, Lum PY, Parke DV (1984) Cytochrome p-448 and the activation of toxical chemicals and carcinogens. Xenobiotica 14: 119–137
Wahlländer A, Renner E, Preisig R (1985) Fasting plasma caffeine concentration. A guide to severity of chronic liver disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 20: 1133–1141
Joeres R, Klinker H, Heusler H, Epping J, Zilly W, Richter E (1988) Influence of smoking on caffeine elimination in healthy volunteers and in patients with alcoholic liver cirrhosis. Hepatology 8: 575–579
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wietholtz, H., Zysset, T., Kreiten, K. et al. Effect of phenytoin, carbamazepine, and valproic acid on caffeine metabolism. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 36, 401–406 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00558303
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00558303