Summary
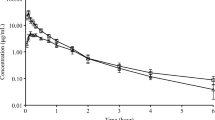
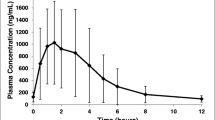
Subjects were each given either a 25, 50 or 100 mg intravenous loading dose of oxpentifylline followed by an intravenous infusion at a constant rate of 1.5 mg/min for 3 h. Plasma levels of oxpentifylline were measured to obtain information on its pharmacokinetics and to establish which of the loading doses gave the most rapid attainment of the steady state plasma levels of intact drug. Oxpentifylline kinetics were best described by a two compartment model giving a characteristic dip in the plasma level versus time curves before steady state was reached when either the 50 or 100 mg loading doses, followed by the constant intravenous infusion, were given. The terminal half-life of oxpentifylline was 1.02±0.86 h, reflecting a very high clearance of the drug (approx. 3 000 to 6 000 ml/min). The high clearance could be attributed to extrahepatic metabolism occurring in blood which was observed in vitro using whole blood but not plasma. The clearance of a reduced metabolite of oxpentifylline was less than that of the intact drug, although the half-life was similar (0.83±0.18 h). Of the three loading doses tested, only the highest showed any side effects, these being transient and occurring within a 5 to 10 min period after dosing and appeared to correlate with the high initial plasma levels of the drug. The 25 mg loading dose gave initial plasma levels generally below the final steady state levels, whilst the 50 mg loading was the closest to giving immediate steady state plasma levels of oxpentifylline.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aranda JV, Grondin D, Sasyniuk BJ (1981) Pharmacologic considerations in the Therapy of Neonatal apnea. Pediat Clin North Am 28: 113–133
Bryce TA, Burrows JL (1980) Determination of oxpentifylline and a metabolite, 1-(5′-hydroxyhexyl)-3,7-dimethylxanthine, by gasliquid chromatography using a nitrogen-selective detector. J Chromatogr 181: 355–361
Cohen GM, Flockhart IR (1975) The partial purification and properties of a human erythrocyte 4-nitroacetophenone reductase. Xenobiotica 5: 213–222
Dixon WJ, Massey FJ (1969) In: Introduction to statistical analysis. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 150–187
Gibaldi M, Perrier D (1975) In: Swarbrick J (ed) Pharmacokinetics. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 69–80
Grebe B (1977) Klinisch-experimentelle Untersuchungen zur Beeinflussung der Hormonsekretion beim Menschen. Doctoral thesis, University of Ulm, Fed. Rep. Germany
Hinze HJ, Bedessem G, Söder A (1972) Structure of excretion products of BL 191 in man. Arzneim-Forsch. 22: 1144
Ogilvie RI (1978) Clinical Pharmacokinetics of theophylline. Clin Pharmacokinet 3: 267–293
Pang KS, Gillette JR (1980) Metabolite pharmacokinetics: methods for simultaneous estimates of elimination rate constants of a drug and its metabolite. Drug Metab Dispos 8: 39–43
Shapiro SS, Wilk MB (1965) The joint assessment of normality of several independent samples. Biometrics 52: 591–611
Walpole RE (1972) In: Introduction to statistics. Collier-Macmillan International, London, pp 301–303
Yeh KC, Kwan KC (1978) A comparison of numerical integrating algorithms by Trapezoidal, Lagrange and Spline approximation. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 6: 79–98
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Also known as PENTOXIFYLLINE
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ings, R.M.J., Nüdemberg, F., Burrows, J.L. et al. The pharmacokinetics of oxpentifylline in man when administered by constant intravenous infusion. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 23, 539–543 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00637503
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00637503