Summary
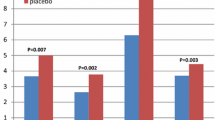
The skin reactivity to histamine was measured in 10 healthy and 10 atopic subjects after the ingestion of single doses of loratadine 10 mg, cetirizine diHCl 10 mg and placebo, in a double-blind cross-over randomized study.
The anti-H1 effect of cetirizine diHCl proved to be significantly more rapid, more pronounced and longer lasting than that of loratadine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rihoux JP, Dupont P (1987) Comparative study of the peripheral and central effects of terfenadine and cetirizine diHCl. Ann Allergy 59: 235–238
Pechadre JC, Trolese JF, Bloom M, Dupont P, Rihoux JP (1987) Compared central and peripheral effects of terfenadine and cetirizine diHCl. Allergol Immunol Clin 2: 83
Snyder S, Snowman A (1987) Receptor effects of cetirizine. Ann Allergy 59 (Part II): 4–8
Fadel R, Herpin-Richard N, Rihoux JP, Henocq E (1987) Inhibitory effect of cetirizine diHCl on eosinophil migration in vivo. Clin Allergy 17: 373–379
Charlesworth EN, Kagey-Sobotka A, Norman PS, Lichtenstein LM (1988) Effects of cetirizine on mast cell mediator release and cellular traffic during the cutaneous late phase response. J Allergy Clin Immunol Allergy Abstracts 81: 212 (abstract 176)
Kreutzner W, Chapman RW, Gulbenkian A, Siegel MI (1987) Antiallergic activity of loratadine, a non-sedative antihistamine. Allergy 42: 57–63
Barnet A, Iorio LC, Kreutner W, Tozzi S, Ano HS, Gulbenkian A (1984) Evaluation of the CNS properties of SCH 29851, a potential non-sedative antihistamine. Agents Actions 14: 590–597
Sheldon GM, Lovell RG, Mathews KP (1967) A manual of clinical allergy. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 56–59
Harvey RP, Schocket AL (1980) The effect of H1- and H2-blockade on cutaneous histamine response in man. J Allergy Clin Immunol 65: 1356
Sidiropoulos J, Volonakis M, Kontou-Filik (1988) Inhibition of histamine-induced wheal and flare reactions by cetirizine diHCl and mequitazine both in healthy and atopic subjects. A comparative double-blind placebo-controlled study. Rev Clin Pharmacol Pharmacokinet 2: 110–119
Roman IJ, Kassem N, Gural RP, Herron J (1986) Suppression of histamine-induced wheal response by loratidine over 28 days in man. Ann Allergy 57: 253–256
Kassem N, Roman I, Gural RP, Dyer JG, Robillard N (1987) Effects of loratadine (SCH 29851) in suppression of histamine-induced skin wheals. Ann Allergy 60: 505–507
Poppa VT (1980) Effect of an H1-blocker, chlorpheniramine, on inhalation tests with histamine and allergen in allergic asthma. Chest 78: 442
Howarth PH, Holgate ST (1985) Astemizole, an H1-antagonist in allergic asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 75: (Part 2): 166 (Abst 248)
Tashkin DP, Brik A, Gong Jr H (1987) Cetirizine inhibition of histamine-induced bronchospasm. Ann Allergy 59 (Part 2): 49–52
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kontou-Fili, K., Paleologos, G. & Herakleous, M. Suppression of histamine-induced skin reactions by loratadine and cetirizine diHCl. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 36, 617–619 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00637746
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00637746