Abstract
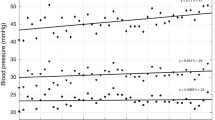
Systolic and diastolic blood pressures were evaluated in a cohort of 61 non-hypertensive premature [very low birth weight (VLBW),n=16; low birth weight (LBW),n=22] and full-term [normal birth weight (NBW),n=23] newborn infants admitted to a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) and followed to their 4-month age-adjusted outpatient examination. All were receiving routine postnatal care by 7 days of age. Blood pressure was measured at 7 days of age, at discharge from the NICU, and at the outpatient examination. Simple linear regression of blood pressure on weight was used to fit a straight line to the three measurements for each infant and the average regression line for each birth weight group was then obtained. There was a significant correlation between systolic blood pressure and both weight and length at each of the measurement points and also between the change in systolic, blood pressure and change in weight from the discharge to the 4-month examination. Diastolic blood pressure tended to follow this same pattern. Gestational age was correlated significantly with the 7-day blood pressure, but postnatal age at the outpatient examination was not correlated with either systolic or diastolic blood pressure. The average slopes of systolic and diastolic blood pressure on weight (mmHg/kg body weight) were virtually identical for the LBW and NBW groups; in constrast, the average slope of the VLBW group was greater than the other two groups, and the difference was statistically significant for diastolic blood pressure. These results show significant group differences in mean blood pressure prior to 4 months of age between VLBW, LBW, and NBW groups and, for the VLBW infants, a steeper slope of the estimated regression line of blood pressure on weight between birth and 4 months.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Task Force on Blood Pressure Control in Children (1987) Report of the Second Task Force on Blood Pressure Control in Children-1987. Pediatrics 79:1–25
Zinner SH, Rosner B, Oh W, Kass EH (1985) Significance of blood pressure in infancy: familial aggregation and predictive effect on later blood pressure. Hypertension 7:411–416
Swiet M de, Fayers P, Shinebourne EA (1980) Systolic blood pressure in a population of infants in the first year of life: the Brompton study. Pediatrics 65:1028–1035
Schacter J, Kuller LH, Perfetti C (1982) Blood pressure during the first two years of life. Am J Epidemiol 116:29–41
Versmold HT, Kitterman JA, Phibbs RH, Gregory GA, Tooley WH (1981) Aortic blood pressure during the first 12 hours of life in infants with birthweight 610 to 4220 grams. Pediatrics 67:607–613
Moscoso P, Goldberg RN, Jamieson J, Bancalari E (1983) Spontaneous elevation in arterial blood pressure during the first hours of life in the very-low-birth-weight infant. J Pediatr 103:114–117
Hulman S, Edwards R, Chen Y, Polansky M, Falkner B (1991) Blood pressure patterns in the first three days of life. J Perinatol XI:231–234
Hegyi T, Carbone MT, Anwar M, Ostfeld B, Hiatt M, Koons A, Pinto-Martin J, Paneth N (1994) Blood pressure ranges in premature infants. I. The first hours of life. J Pediatr 124:627–633
Tan KL (1988) Blood pressure in very low birth weight infants in the first 70 days of life. J Pediatr 112:266–270
Levine RS, Hennekens CH, Jesse MJ (1994) Blood pressure in prospective population based cohort of newborn and infant twins. BMJ 308:298–302
Greenough A, Emery EF (1993) Blood pressure levels of preterm infants in the first year of life. Acta Paediatr 82:528–529
Babson SG, Benda GI (1976) Growth graphs for the clinical assessment of infants of varying gestational age. J Pediatr 89:814–820
Kitterman JA, Phibbs RH, Tooley WH (1969) Aortic blood pressure in normal newborn infants during the first 12 hours of life. Pediatrics 44:959–968
Elliott SJ, Hansen TN (1990) Neonatal hypertension. In: Long WA (ed) Fetal and neonatal cardiology. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 492–498
Law CM, Robinson DJP (1994) Fetal influences on blood pressure. J Hypertens 12:1329–1332
Lever AF, Harrap SB (1992) Essential hypertension: a disorder of growth with origins in childhood. J Hypertens 10:101–120
Spinazzola R, Harper R, Soler M de, Lesser M (1991) Blood pressure values in 500- to 750-gram birthweight infants in the first week of life. J Perinatol 11:147–151
Swiet M de, Fayers P, Shinebourne EA (1992) Blood pressure in first 10 years of life: the Brompton study. BMJ 304:23–26
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Georgieff, M.K., Mills, M.M., Gómez-Marín, O. et al. Rate of change of blood pressure in premature and full term infants from birth to 4 months. Pediatr Nephrol 10, 152–155 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00862059
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00862059