Summary
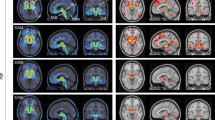
Regional cerebral glucose metabolism was studied in nine patients with progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP). (18F)-2-fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET) revealed general cerebral hypometabolism in all PSP patients in comparison with an age-matched reference group. When comparing the degree of regional metabolic deterioration, a consistent pattern of the most affected brain regions became obvious: the strongest significant alteration of cerebral glucose metabolism was observed in subcortical regions, e.g. in caudate nucleus, lentiform nucleus and upper mid-brain, which showed nerve cell loss in previous pathological studies. Less severe, but still significant hypometabolism was observed in frontal cortex. This pattern of hypometabolism was distinctly different from that typically seen in dementias of Alzheimer's type. The present data show that PET findings agree with histopathological studies: PSP is a primarily subcortical disease with secondary inactivation of cortical, especially of frontal brain regions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Behrman S, Carroll JD, Janota I, Matthews WB (1969) Progressive supranuclear palsy. Clinico-pathological study of four cases. Brain 92:663–678
Blin J, Baron JC, Dubois B, Pillon B, Cambon H, Cambier J, Agid Y (1990) Positron emission tomography study in progressive supranuclear palsy. Brain hypometabolic pattern and clinico-metabolic correlations. Arch Neurol 47:747–752
Bokobza B, Ruberg M, Scatton B, Javoy-Agid F, Agid Y (1984) (3H)spiperone binding, dopamine and HVA concentration in Parkinson disease and progressive supranuclear palsy. Eur J Pharmacol 99:167–175
D'Antona R, Baron JC, Samson Y, Serdaru M, Viader F, Agid Y, Cambier J (1985) Subcortical dementia. Frontal cortex hypometabolism detected by positron emission tomography in patients with progressive supranuclear palsy. Brain 108:785–799
David NJ, MacKey EA, Smith JL (1968) Further observations in progressive supranuclear palsy. Neurology 18:349–356
Foster NL, Gilman S, Berent S, Morin EM, Brown MB, Koeppe RA (1988) Cerebral hypometabolism in progressive supranuclear palsy studied with positron emission tomography. Ann Neurol 24:399–406
Goffinet AM, Volder AG de, Gillain C, Rectem D, Bol A, Michel C, Cogneau M, Labar D, Laterre C (1989) Positron tomography demonstrates frontal lobe hypometabolism in progressive supranuclear palsy. Ann Neurol 25:131–139
Grafman J, Litvan I, Gomez C, Chase TN (1990) Frontal lobe function in progressive supranuclear palsy. Arch Neurol 47:553–558
Heiss W-D, Pawlik G, Herholz K, Wagner R, Göldner H, Wienhard K (1984) Regional kinetic constants and CMRglu in normal human volunteers determined by dynamic positron emission tomography of (18F)-2-fluoro-deoxy-d-glucose. Cereb Blood Flow Metab 4:212–223
Herholz K, Pawlik G, Wienhard K, Heiss W-D (1985) Computer assisted mapping in quantitative analysis of cerebral positron emission tomograms. J Comput Assist Tomogr 9:154–161
Herholz K, Adams R, Kessler J, Szelies B, Grond M, Heiss W-D (1990) Criteria for diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease with positron emission tomography. Dementia 1:156–164
Jankovic J (1984) Progressive supranuclear palsy. Clinical and pharmacologic update. Neurol Clin 2:473–486
Jellinger K (1971) Progressive supranuclear palsy (subcortical argyrophilic dystrophy). Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 19:347–352
Kimura D, Barnett HJM, Burkhart G (1981) The psychological test pattern in progressive supranuclear palsy. Neuropsychologia 19:301–306
Kish SJ, Chang LJ, Mirchandain L, Shannak K, Hornykiewicz O (1985) Progressive supranuclear palsy: relationship between extrapyramidal disturbances, dementia, and brain neurotransmitter markers. Ann Neurol 18:530–536
Kristensen MO (1985) Progressive supranuclear palsy — 20 years later. Acta Neurol Scand 71:177–189
Leenders KL, Frackowiak RSJ, Lees AJ (1988) Steele-Richardson-Olszewski syndrome. Brain energy metabolism, blood flow, and fluorodopa uptake measured by positron emission tomography. Brain 111:615–630
Lees AJ (1987) The Steele-Richardson-Olszewski syndrome (progressive supranuclear palsy). In: Marsden CD, Fahn S (eds) Movement disorders 2. Butterworths, London, pp 272–287
Maher ER, Lees AJ (1986) The clinical features and natural history of Steele-Richardson-Olszewski syndrome (progressive supranuclear palsy). Neurology 36:1005–1008
Marsden CD, Schachter M (1981) Assessment of extrapyramidal disorders. Br J Clin Pharmacol 11:129–151
Masucci EF, Borts F, Smirmotopoulos JG, Kurtzke JF, Schellinger D (1985) Thin-section CT of midbrain abnormalities in progressive supranuclear palsy. AJNR 6:767–772
McGeer PL, Kamo H, Harrop R, McGeer EG, Martin WRW, Pate BD, Li DKB (1986) Comparison of PET, MRI and CT with pathology in a proven case of Alzheimer's disease. Neurology 36:1569–1574
Pawlik G, Herholz K, Wienhard K, Beil C, Heiss WD (1986) Some maximum likelihood methods useful for the regional analysis of dynamic PET data on brain glucose metabolism. In: Bacharach SL (ed) Information processing in medical imaging. Nijhoff, Dordrecht Boston Lancaster, pp 298–309
Posey WC (1904) Paralysis of the upward movement of the eyes. Ann Ophthal 13:523–529
Reisberg B (1983) The brief cognitive rating scale and global deterioration scale. In: Crook T, Ferris S, Bartus R (eds) Assessment in geriatric psychopharmacology. Marc Powley Association, New Canaan, pp 19–35
Reivich M, Kuhl D, Wolf A, Greenberg J, Phelps M, Ido T, Casella V, Fowler J, Hoffman E, Alavi A, Som P, Sokoloff P (1979) The (18F)fluorodeoxyglucose method for the measurement of local cerebral glucose utilization in man. Circ Res 44:127–137
Rougemont D, Baron JC, Collard P, Bustany P, Comar D, Agid Y (1984) Local cerebral glucose utilization in treated and untreated patients with Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 47:824–830
Ruberg M, Javoy-Agid F, Hirsch E, Scatton B, Lheureux R, Hauw JJ, Duyckaerts C, Gray F, Morel-Maroger A, Rascol A, Serdaru M, Agid Y (1985) Dopaminergic and cholinergic lesions in progressive supranuclear palsy. Ann Neurol 18:523–529
Savoiardo M, Strada L, Girotti F, D'Incerti L, Sberna M, Soliveri P, Balzarini L (1989) MR imaging in progressive supranuclear palsy and Shy-Drager syndrome. J Comput Assist Tomogr 13:555–560
Steele JC, Richardson JC, Olszewski J (1964) Progressive supranuclear palsy. A heterogenous degeneration involving the brainstem, basal ganglia and cerebellum with vertical gaze and pseudobulbar palsy, nuchal dystonia and dementia. Arch Neurol 10:333–359
Wienhard K, Pawlik G, Herholz K, Wagner R, Heiss W-D (1985) Estimation of local cerebral glucose utilization by positron emission tomography of (18F)-2-fluoro-deoxy-d-glucose: a critical appraisal of optimization procedures. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 5:115–125
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karbe, H., Grond, M., Huber, M. et al. Subcortical damage and cortical dysfunction in progressive supranuclear palsy demonstrated by positron emission tomography. J Neurol 239, 98–102 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00862982
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00862982