Abstract
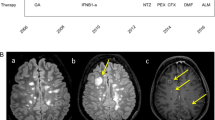
In this study we assessed the subclinical disease activity in 45 patients with primary progressive, secondary progressive or relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (MS). The patients had gadolinium-enhanced brain MRI scans, which were analysed using a semiquantitative method both for lesion load and for degree of enhancement. At the same time cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and serum samples were collected and, from these, cytokine levels were measured in most cases by enzyme-linked immunoassay using commercially available kits. Enhancing lesions on MRI were found in 73% of the patients. The sensitivity of this test was greatly increased by our method of analysis as far as the primary progressive patients are concerned (70% vs 40% for conventional evaluation). CSF interleukin-1 β (IL-1 β) levels were above the normal range in 22% and IL-6 levels in 13% of patients, while tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) was undetectable or below the upper normal limits in all the samples tested. Serum IL-1 β was above the normal limits in 40%, IL-6 in 42% and TNF-α in 7% of patients. No significant differences in cytokine profiles were found between the clinical subgroups. This study confirms the high sensitivity of gadolinium-enhanced MRI in detecting MS activity, which was further increased by our method of analysis. Longitudinal studies performed with more sensitive immunological techniques are needed to define better the relationship between cytokine, clinical and MRI data in MS patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi K, Kumamoto T, Araki S (1990) Elevated soluble interleukin-2 receptor levels in patients with active multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 28:687–691
Baumhefner RW, Tourtellotte WW, Syndulko K, Waluch V, Ellison GW, Meyers LW, Cohen SN, Osborne M, Shapshak P (1990) Quantitative multiple sclerosis plaque assessment with magnetic resonance imaging. Its correlation with clinical parameters, evoked potentials and intrablood-brain-barrier IgG synthesis. Arch Neurol 47:19–26
Benvenuto R, Paroli M, Buttinelli C, Franco A, Barnaba V, Fieschi C, Balsano F (1991) Tumour necrosis factora synthesis by cerebrospinal-fluid-derived T cell clones from patients with multiple sclerosis. Clin Exp Immunol 84:97–102
Capra R, Marciano N, Cotti-Cometti V, Vignolo LA, Bettinzioli M, Airo P, Cattaneo R, Gasparotti R, Moretti R (1992) Immunological and gadolinium-DTPA MRI evaluation of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurol Scand 86:342–345
Comi G, Martinelli V, Medaglini S, Locatelli T, Filippi M, Canal N, Triulzi F, Del Maschio A (1989) Correlations between multimodal evoked potentials and magnetic resonance imaging in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol 236:4–8
Corti A, Fassina G, Marcucci F, Barbanti E, Cassani G (1992) Oligometric tumour necrosis factor α slowly converts into inactive forms at bioactive levels. Biochem J 284:905–910
Corti A, Poiesi C, Merli S, Cassani G (1994) Tumor necrosis factor a quantification by ELISA and bioassay: effects of TNF-α soluble receptor (p55) complex dissociation during assay incubations. J Immunol Methods 177:191–198
Fesenmeier JT, Whitaker JT, Herman PK, Walker DP (1991) Cerebrospinal fluid levels of myelin protein-like material and soluble interleukin-2 receptor in multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 34:77–80
Filippi M, Horsfield MA, Morrissey SP, MacManus DG, Rudge P, McDonald WI, Miller DH (1994) Quantitative brain MRI lesion load predicts the course of clinically isolated syndromes suggestive of multiple sclerosis. Neurology 44:635–641
Filippi M, Campi A, Martinelli V, Colombo B, Yousry T, Canal N, Scotti G, Comi G (in press) Comparison of triple dose vs standard dose gadolinium-DTPA for detection of MRI enhancing lesions in patients with primary progressive multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry
Franciotta DM, Grimaldi LME, Martino GV, Piccolo G, Bergamaschi R, Citterio A, Melzi d'Eril GV (1989) Tumour necrosis factor in serum and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 26:787–789
Frei K, Fredrikson S, Fontana A, Link H (1991) Interleukin-6 is elevated in plasma in multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 31:147–153
Gallo P, Piccinno MG, Pagni S, Argentiero V, Giometto B, Bozza F, Tavolato B (1989) Immune activation in multiple sclerosis: study of IL-2, sIL-2R and γ-IFN levels in serum and cerebrospinal fluid. J Neurol Sci 92:915
Hartung HP, Reiners K, Archelos JJ, Michels M, Seeldrayers P, Heidenreich F, Pflughaupt KW, Toyka KV (1995) Circulating adhesion molecules and tumor necrosis factor receptor in multiple sclerosis: correlation with magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol 38:186–193
Hauser SL, Doolittle TH, Lincoln R, Brown RH, Dinarello CA (1990) Cytokine accumulations in CSF of multiple sclerosis patients: frequent detection of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor but not interleukin-6. Neurology 40:1735–1739
Hawkins CP, Munro PMG, MacKenzie F, Kesselring G, Tofts PS, duBoulay EPGH, Landon DN, McDonald WI (1990) Duration and selectivity of blood-brain barrier breakdown in chronic relapsing experimental encephalomyelitis studied by gadolinium-DTPA and protein markers. Brain 113:365–378
Imamura K, Suzumura A, Hayashi F, Marunouchi T (1993) Cytokine production by peripheral blood monocytes/macrophages in multiple sclerosis patients. Acta Neurol Scand 87:281–285
Katz D, Taubenberger JK, Cannella B, McFarlin DE, Raine CS, McFarland HF (1993) Correlation between magnetic resonance imaging and lesion development in chronic active multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 34:661–669
Kermode AG, Thompson AJ, MacManus DG, Kendall BE, Kingsley DPE, Moseley IF, Rudge P, McDonald WI (1990) Breakdown of the bloodbrain barrier precedes symptoms and other MRI signs of new lesions in multiple sclerosis: pathogenetic and clinical implications. Brain 113:1477–1489
Kurtzke JF (1983) Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: an Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS). Neurology 33:1444–1452
Maimone D, Gregory S, Amason BG, Reder AT (1991) Cytokine levels in the cerebrospinal fluid and serum of patients with multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 32:67–74
Martino G, Clementi E, Brambilla E, Comi G, Meldolesi J, Grimaldi LME (1994) γ-IFN activated a previously undescribed Ca2+ influx in T-lymphocytes from multiple sclerosis patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:4825–4829
McCarron RM, Wang L, Racke MK, et al (1993) Cytokine-regulated adhesion between encephalitogenic T lymphocytes and cerebrovascular endothelial cells. J Neuroimmunol 43:23–30
Merrill JE (1992) Proinflammatory and antiinflammatory cytokines in multiple sclerosis and central nervous system acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Immunother 12:167–170
Miller DH, Rudge P, Johnson G, Kendall BE, MacManus DG, Moseley IF, Barnes D, McDonald WI (1988) Serial gadolinium enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in multiple sclerosis. Brain 111:927–939
Miller DH, Barkhof F, Berry I, Kappos L, Scotti G, Thompson AJ (1991) Magnetic resonance imaging in monitoring the treatment of multiple sclerosis: concerted action guidelines. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 54:683–688
Miller DH, Barkhof F, Nauta JJP (1993) Gadolinium enhancement increases the sensitivity of MRI in detecting disease activity in multiple sclerosis. Brain 116:1077–1094
Nesbit GM, Forbes GS, Scheithauer BW, Okazaki H, Rodriguez M (1991) Multiple sclerosis: histopathologic and MR and/or CT correlation in 37 cases at biopsy and three cases at autopsy. Radiology 180:467–474
Olsson T (1994) Role of cytokines in multiple sclerosis and experimental immune encephalomyelitis. Eur J Neurol 1:7–19
Ormerod IEC, Miller DH, McDonald WI, duBoulay EPGH, Rudge P, Kendall BE, Moseley IF, Johnson G, Tofts PS, Halliday AM, Bronstein AM, Scaravilli F, Harding AE, Barnes D, Zilkha KJ (1987) The role of NMR imaging in the assessment of multiple sclerosis and isolated neurological lesions. A quantitative study. Brain 110:1579–1616
Palo J, Ketonen L, Wikstrom M (1988) A follow-up study of very low field MRI findings and clinical course in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 84:177–187
Panitch HS, Hirsch RL, Schindler L, Johnson KP (1987) Treatment of multiple sclerosis with gamma interferon: exacerbations associated with activation of immune system. Neurology 37:1097–1103
Peter JB, Boctor FN, Tourtellotte WW (1991) Serum and CSF levels of IL-2, s-IL-2R, TNF-α, and IL-1 β in chronic progressive multiple sclerosis: expected lack of clinical utility. Neurology 41:121–123
Poser CM, Paty DW, Scheinberg L, McDonald WI, Davis FA, Ebers GC, Johnson KP, Sibley WA, Silberberg DH, Tourtellotte WW (1983) New diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: guidelines for research protocols. Ann Neurol 13:227–231
Raine CS (1994) McFarlin Memorial Lecture: the immunology of the multiple sclerosis lesion. Ann Neurol 36 [Suppl]: S61-S72
Raine CS (1995) Multiple sclerosis: TNF revisited, with promise. Nature Med 1:211–214
Revesz T, Kidd D, Thompson AJ, Barnard RO, McDonald WI (1994) A comparison of the pathology of primary and secondary progressive multiple sclerosis. Brain 117:759–765
Rieckmann P, Albrecht M, Kitze B, Weber T, Tumani H, Broocks A, Luer W, Poser S (1994) Cytokine mRNA levels in mononuclear blood cells from patients with multiple sclerosis. Neurology 44:1523–1526
39.Rieckmarm P, Albrecht M, Kitze B, Weber T, Tumani H, Broocks A, Luer W, Helwig A, Poser S (1995) Tumor necrosis factor-α messenger RNA expression in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis is associated with disease activity. Ann Neurol 37:82–88
Rodriguez M, Scheitauer BW, Forbes G, Kelly PJ (1993) Oligodendrocyte injury is an early event in lesions of multiple sclerosis. Mayo Clin Proc 68:627–636
Selmaj KW, Raine CS (1988) Tumor necrosis factor mediates myelin and oligodendrocyte damage in vitro. Ann Neurol 23:339–346
Sharief MK, Hentges R (1991) Association between tumor necrosis factor-α and disease progression in patients with multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med 325:467–472
Sharief MK, Thompson EJ (1992) In vivo relationship of tumor necrosis factor-α to blood-brain barrier damage in patients with active multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 38:27–33
Sharief MK, Hentges R, Ciardi M, Thompson EJ (1993) In vivo relationship of interleukin-2 and soluble IL-2 receptor to blood-brain barrier impairment in patients with active multiple sclerosis. J Neurol 240:46–50
Shaw CE, Dumbar PR, Macaulay HA, Neale TJ (1995) Measurement of immune markers in the serum and cerebrospinal fluid of multiple sclerosis patients during clinical remission. J Neurol 242:53–58
Sommer N, Loschmann PA, Northoff GH, Weller M, Steinbrecher A, Steinbach JP, Lichtenfels R, Meyermann R, Riethmuller A, Fontana A, Dichgans J, Martin R (1995) The antidepressant rolipram suppresses cytokine production and prevents autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Nature Med 1:244–248
The IFNB MS Study Group and the UBC MS/MRI Analysis Group (1995) Interferon beta-lb in the treatment of multiple sclerosis: final outcome of the randomized controlled trial. Neurology 45:1277–1285
Thompson AJ, Kermode AG, Wicks D, MacManus DG, Kendall BE, Kingsley DPE, McDonald WI (1991) Major differences in the dynamics of primary and secondary progressive multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 29:53–62
Thompson AJ, Miller DH, Youl B, MacManus DG, Moore S, Kingsley D, Kendall B, Feinstein A, McDonald WI (1992) Serial gadolinium-enhanced MRI in relapsing/remitting multiple sclerosis of varying disease duration. Neurology 42:60–63
Trotter JL, Collins KG, Veen RC van der (1991) Serum cytokine levels in chronic progressive multiple sclerosis: IL-2 levels parallel TNF-α levels. J Neuroimmunol 33:29–36
Truyen L, Gheuens J, Van de Vyver FL, Parizel PM, Peersman GV, Martin J-J (1990) Improved correlation of magnetic resonance imaging with clinical status in multiple sclerosis by use of an extensive standardized imaging-protocol. J Neurol Sci 96:173–182
Tsukada N, Miyagi K, Matsuda M, Yanagisawa N, Yone K (1991) Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 in the CSF and sera of patients with multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 102:230–234
Woodrofe MN, Cuzner ML (1993) Cytokine mRNA expression in inflammatory multiple sclerosis lesions: detection by non-radioactive in situ hybridization. Cytokine 5:583–588
Wucherpfennig KW, Newcombe J, Li H, Keddy C, Cuzner ML, Hafler DA (1992) T cell receptor Va-Vb repertoire and cytokine gene expression in active multiple sclerosis lesions. J Exp Med 175:993–1002
Zoukos Y, Kidd D, WoodrofeMN, Kendall BE, Thompson AJ, Cuzner ML (1994) Increased expression of high affinity IL-2 receptors and b-adrenoceptors on peripheral blood mononuclear cells is associated with clinical and MRI activity in multiple sclerosis. Brain 117:307–315
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rovaris, M., Barnes, D., Woodrofe, N. et al. Patterns of disease activity in multiple sclerosis patients: A study with quantitative gadolinium-enhanced brain MRI and cytokine measurement in different clinical subgroups. J Neurol 243, 536–542 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00886876
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00886876