Abstract
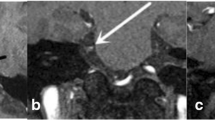
Three-dimensional MR tomography was used to examine the relationship between symptoms of trigeminal neuralgia and neurovascular compression of the nerve in 18 patients. The intensity of neurovascular interaction was classified according to neuroradiological criteria. We found that a radiologically defined compression or dislocation of the nerve by an artery was always associated with symptoms of trigeminal neuralgia. A simple contanct between vessel and nerve, however, was also observed on the asymptomatic sides of 10 out of 18 patients. In 6 of 18 patients, in contrast, trigeminal neuralgia was present in spite of the absence of neurovascular contact. In accordance with a cited study based on autopsy and intraoperative findings, our findings indicate that, in a certain proportion of cases, trigeminal neuralgia may be caused by neurovascular compression alone, whereas in other cases, other pathogenetic factors may be involved to a varying degree or be even exclusively responsible for the development of trigeminal neuralgia. The possible significance of the method for a preoperative estimation of the success of microvascular decompression of the trigeminal nerve is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldwin NG, Sahni KS, Jensen ME, Pieper DR, Anderson RL, Young HF (1991) Association of vascular compression in trigeminal neuralgia versus other “facial pain syndromes” by magenetic resonance imaging. Surg Neurol 36:447–452
Cidlinsky K, Stenglein C, Braun M (1992) Neurovaskuläre Kompression des VIII. Hirnnerven: direkte Darstellung durch MR-Angiographie. Klin Neuroradiol 2:6–10
Furuya Y, Ryu H, Uemura K, Sugiyama K, Isoda H, Hasegawa S, Takahashi M, Kaneko M (1992) MRI of intracranial neurovascular compression. J Comput Assist Tomogr 16:503–505
Hamlyn PJ, King TT (1992) Neurovascular compression in trigeminal neuralgia: a clinical and anatomical study. J Neurosurg 76:948–954
Jannetta PJ (1967) Arterial compression of the trigeminal nerve at the pons in patients with trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg 26:159–162
Jannetta PJ (1979) Treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurgery 4:93–94
Magnaldi S, Cecconi P, Skrap M, Ricci C, Cova MA, Pozzi-Mucelli RS (1992) Magnetic resonance in trigeminal neuralgia. Radiol Med Torino 83:700–705
Matsumoto S, Kishikawa T, Kudo S, Matsuo Y, Totoki T, Harano K (1991) Magnetic resonance imaging of idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia. Nippon Igaku Hoshasen Gakkai Zasshi 51:91–93
Møller AR (1991) The cranial nerve vascular compression syndrome. I. A review of treatment. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 113:18–23
Møller AR (1991) The cranial nerve vascular compression syndrome. II. A review of pathophysiology. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 113:24–30
Sens MA, Higer HP (1991) MRI of trigeminal neuralgia: initial clinical results in patients with vascular compression. Neurosurg Rev 14:69–73
Sindou M (1991) Does microsurgical vascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia work through a neo-compressive mechanism? Anatomical-surgical evidence for a decompressive effect. Acta Neurochir [Suppl] (Wien) 52:127–129
Yamaki T, Hashi K, Niwa J, Tanabe S, Nakagawa T, Nakamura T, Uede T, Tsuruno T (1992) Results of reoperation for failed microvascular decompression. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 115:1–7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Masur, H., Papke, K., Bongartz, G. et al. The significance of three-dimensional MR-defined neurovascular compression for the pathogenesis of trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurol 242, 93–98 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00887823
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00887823