Summary
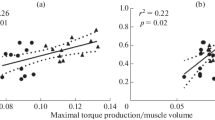
The present study was undertaken to assess the relationship between the mechanical power developed during new anaerobic power test and muscular fiber distribution. Ten track and field male athletes were used as subjects, whose muscle fiber composition (m. vastus lateralis) varied from 25 to 58 fast twitch (FT) fibers. The test consisted of measuring the flight time with a special timer during 60 s continuous jumping. A formula was derived to allow the calculation of mechanical power during a certain period of time (e.g., in the present study every 15 s during 60 s of jumping performance). The relationship between the mechanical power for the first 15 s period correlated best with fast twitch (FT) fiber distribution (r=0.86,p<0.005). However, the power output during the successive 15 s periods demonstrated lower correlation with FT, and this relationship became statistically non-significant after 30 s of work. The sensitivity to fatigue of the test was supported by the relationship observed between the decrease of power during 60 s jumping performance and the percentage of FT fibers (r=0.73,p<0.01). Thus, the present findings suggest that muscular performance, as determined by the new jumping test, is influenced by skeletal muscle fiber composition. The new test, which primarily evaluates maximal short term muscular power, also proved sensitive in assessing fatigue patterns during 60 s of strenuous work.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bar-Or O (1978) A new anaerobic capacity test — characteristics and applications. Med Esporte Porto Alegre 5: 73–82
Bergström J (1962) Muscle electrolytes in man. Scand J Clin Lab Invest [Suppl] 68
Bosco C (1980) Sei un grande atleta vediamo cosa dice l'Ergojump. Pallavolo no 5: 34–36
Bosco C (1981a) De nouveaux tests pour mesurer la capacité anaerobie et l'élasticité du muscle extenseur de la jambe dans le saut. Volleyball n 1, Revue officielle de la FIVB, pp 22–30
Bosco C (1981b) Mesurer la puissance musculaire des extenseurs des jambes pedant l'execution de sauts verticaux chez les adolescents. Volleyball n 3, Revue officielle de la FIVB, pp 41–47
Bosco C, Komi PV (1979) Mechanical characteristics and fiber composition of human leg extensor muscles. Eur J Appl Physiol 41: 275–284
Bosco C, Ito A, Komi PV, Luhtanen P, Rahkila P, Rusko H, Viitasalo JT (1982) Neuromuscular function and mechanical efficiency of human leg extensor muscles during jumping exercises. Acta Physiol Scand 114: 543–550
Bosco C, Luhtanen P, Komi PV (1983) A simple method for measurement of mechanical power in jumping. Eur J Appl Physiol 50: 273–282
Burke RE, Levine DN, Zajac FE III (1971) Mammalian motor units: physiological-histochemical correlation in three types in cat gastrocnemius. Science 174: 709–712
Gollnick PD, Armstrong RB, Saubert IV CW, Piehl K, Saltin B (1972) Enzyme activity and fiber composition in skeletal muscle of untrained and trained men. J Appl Physiol 33: 312–319
HÄkkinen K, Komi PV, Tesch P (1981) Effect of combined concentric and eccentric strength training and detraining on force-time, muscle fiber and metabolic characteristics of leg extensor muscles. Scand J Sports Sci 3: 50–58
Karlsson J (1980) Localized muscular fatigue: role of muscle metabolism and substrate depletion. In: Hutton RS, Miller DI (eds) Exercise and sport sciences reviews. Franklin Institute Press, Philadelphia, pp 1–42
Komi PV, Bosco C (1978) Utilization of stored elastic energy in leg extensor muscles by men and women. Med Sci Sports 10: 261–265
Komi PV, Karlsson J (1978) Skeletal muscle fibre types, enzyme activities and physical performance in young males and females. Acta Physiol Scand 103: 210–218
Komi PV, Tesch P (1979) EMG frequency spectrum, muscle structure, and fatigue during dynamic contractions in man. Eur J Appl Physiol 42: 41–50
Komi PV, Karlsson J, Tesch P, Suominen H, Heikkinen E (1982) Effects of heavy resistance and explosive type strength training methods on mechanical, functional and metabolic aspects of performance. In: Komi PV (ed) Exercise and sport biology. Human Kinetics Publishers, Champaign Ill, pp 90–102
Margaria R, Aghemo P, Rovelli E (1966) Measurement of muscular power (anaerobic) in man. J Appl Physiol 21: 1662–1664
Padykula HA, Herman E (1955) The specificity of the histochemical method of adenosine triphosphatase. J Histochem Cytochem 3: 170–195
Thorstensson A (1976) Muscle strength, fibre types and enzyme activities in man. Acta Physiol Scand [Suppl] 443
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by a grant from Italian Trak and Field Association and a grant (No. 9623/78/80) from the Ministry of Education (Finland)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bosco, C., Komi, P.V., Tihanyi, J. et al. Mechanical power test and fiber composition of human leg extensor muscles. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 51, 129–135 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00952545
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00952545