Summary
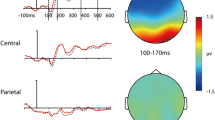
Visual event-related potential (ERP) studies show effects due to target detection in the P3 and in earlier negativities over posterior recording sites. The topography of these earlier components suggests contributions from both anterior and posterior neural generators, however these studies were performed with sparse recording arrays and may not have provided a full description of the scalp topography of the visual ERP. The current study employed a high-density recording array (64 channels) and spherical spline interpolated topographic voltage and current density maps to describe the scalp distribution of the major deflections in the visual ERP from a visual oddball paradigm: the P1, N1, N2/P2a (a temporally coincident posterior negativity and anterior positivity) and P3. A modified difference wave analysis was also performed to track the time-course of target detection effects in the ERP. Target detection effects were found in the N2/P2a and P3 components. The scalp distribution of the N2/P2a was consistent with separate frontal and posterior neural generators and this is discussed in reference to human hemodynamic and nonhuman primate studies of neural activity in the inferior temporal visual object recognition system and in frontal systems of selective attention and working memory in visual target detection tasks.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aine, C.J. and Harter, M.R. Visual event-related potentials to colored patterns and color names: Attention to features and dimensions. Electroencephalography and clinical Neurophysiology, 1986, 64: 228–245.
Corbetta, M., Miezin, F.M., Dobmeyer, S., Shulman, G.L. and Petersen, S.E. Attentional modulation of neural processing of shape, color and velocity in humans. Science, 1990, 22: 1556–1559.
Corbetta, M., Miezin, F.M., Shulman, G.L. and Petersen, S.E. A PET study of visuospatial attention. The Journal of Neuroscience, 1993, 13(3): 1202–1226.
Courchesne, E., Hillyard, S.A. and Galambos, R.. Stimulus novelty, task relevance and the visual evoked potential in man. Electroencephalography and clinical Neurophysiology, 1975, 39: 131–143.
Curran, T., Tucker, D.M., Kutas, M. and Posner, M.I. Topography of the N400: Brain electrical activity reflecting semantic expectancy. Electroencephalography and clinical Neurophysiology, 1993, 88, 188–209.
Desimone, R., Miller, E.K. and Chelazzi, L. The interaction of neural systems for attention and memory. In C. Kock and J.L. Davis (Eds.), Large-scale neuronal theories of the brain. Computational Neuroscience (pp. 75–91). Cambridge: MIT Press, 1994.
Donchin, E. Event-related potentials: A tool in the study of human information processing. In H. Begleiter (Eds.), Evoked Brain Potentials and Behavior New York: Plenum, 1979.
Donchin, E. and Coles, M.G.H. Is the P300 component a manifestation of context updating? Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 1988, 11, 357–374.
Egly, R., Rafal, R.D. and Driver, J. Shifting visual attention between objects and locations: Evidence from normal and parietal-lesion patients. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 1994, 123(2), 161–177.
Eskandar, E.N., Richmond, B.J. and Optican, L.M. Role of inferior temporal neurons in visual memory I. Temporal encoding of information about visual images, recalled images and behavioral context. Journal of Neurophysiology, 1992, 68(4), 1277–1295.
Fuster, J.M. The Prefrontal Cortex. New York: Raven, 1989.
Fuster, J.M., Bauer, R.H. and Jervey, J.P. Functional interactions between inferotemporal and prefrontal cortex in a cognitive task. Brain Research, 1985, 330, 299–307.
Fuster, J.M. and Jervey, J.P. Neuronal firing in the inferotemporal cortex of the monkey in a visual memory task. Journal of Neuroscience, 1982, 2(3), 361–375.
Goldman-Rakic, P.S. Topography of cognition: Parallel distributed networks in primate association cortex. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 1988, 11, 137–156.
Harter, M.R. and Aine, C.J. Brain mechanisms of visual selective attention. In R. Parasuraman and D. R. Davies (Eds.), Varieties of attention (pp. 293–321). London: Academic Press, 1984.
Harter, M.R., Aine, C. and Schroeder, C. Hemispheric differences in neural processing of stimulus location and type: Effects of selective attention on visual evoked potentials. Neuropsychologia, 1982, 20(1), 421–438.
Harter, M.R. and Guido, W. Attention to pattern orientation: Negative cortical potentials, reaction time and the selection process. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, 1980, 49, 461–475.
Harter, M.R. and Previc, F.H. Size-specific information channels and selective attention: Visual evoked potentials and behavioral measures. Electroencephalography and clinical Neurophysiology, 1978, 45, 531–546.
Hillyard, S.A. and Münte, T.F. Selective attention to color and location: An analysis with event-related brain potentials. Perception and Psychophysics, 1984, 36, 185–198.
Hjorth, B. An adaptive EEG derivation technique. Electroencephalography and clinical Neurophysiology, 1982, 54, 654–661.
Johnson, R., Jr. The amplitude of the P300 component of the event-related potential: Review and synthesis. Advances in Psychophysiology, 1988, 3, 69–137.
Luck, S.J., Heinze, H.J., Mangun, G.R. and Hillyard, S.A. Visual event-related potentials index focused attention within bilateral stimulus arrays. II. Functional dissociation of P1 and N1 components. Electroencephalography and clinical Neurophysiology, 1990, 75, 528–542.
Luria, A.R. The frontal lobes and the regulation of behavior. In K. H. Pribram and A. R. Luria (Eds.), Psychophysiology of the frontal lobes (pp. 3–26). New York: Academic Press, 1973.
Mangun, G.R. Neural mechanisms of visual selective attention. Psychophysiology, 1995, 32, 4–18.
Mangun, G.R. and Hillyard, S.A. The spatial allocation of visual attention as indexed by event-related potentials. Human Factors, 1987, 29(2): 195–211.
Mangun, G.R. and Hillyard, S.A. Electrophysiological studies of visual selective attention in humans. In A. B. Scheibel and A. F. Wechsler (Eds.), Neurobiology of Higher Cognitive Function (pp. 271–295). New York: Guilford, 1990.
Mangun, G.R. and Hillyard, S.A. Modulations of sensory-evoked brain potentials indicate changes in perceptual processing during visual-spatial priming. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 1991, 17(4): 1057–1074.
Miller, E.K., Li, L. and Desimone, R. A neural mechanism for working and recognition memory in inferior temporal cortex. Science, 1991, 254: 1377–1379.
Miller, E.K. and Desimone, R. Parallel neuronal mechanisms for short-term memory. Science, 1994, 263: 520–522.
Näätänen, R. Attention and Brain Function. Hillsdale, New Jersey: Erlbaum, 1992.
Nunez, P.L. Electric Fields of the Brain: The Neurophysics of EEG. New York: Oxford University Press, 1981.
Nunez, P.L., Silberstein, R.B., Cadusch, P.J., Westdorp, A.F. and Srinivasan, R. A theoretical and experimental study of high resolution EEG based on surface Laplacians and cortical imaging. Electroencephalography and clinical Neurophysiology, 1994, 90: 40–57.
Osgood, G. The electrophysiological graphical imaging systems: Part I. Technical Report No. 90-9. Eugene: Institute of Cognitive and Decision Sciences, University of Oregon, 1990.
Perrin, F., Pernier, J., Bertrand, O. and Echallier, J.F. Spherical splines for scalp potential and current density mapping. Electroencephalography and clinical Neurophysiology, 1989, 72: 184–187.
Posner, M.I. and Petersen, S.E. The attention systems of the human brain. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 1990, 13: 25–42.
Pribram, K.H. The primate frontal cortex — executive of the brain. In K. H. Pribram and A. R. Luria (Eds.), Psychophysiology of the Frontal Lobes (pp. 293–314). New York: Academic Press, 1973.
Ritter, W., Vaughan Jr., H.G. and Costa, L.D. Orienting and habituation to auditory stimuli: A study of short term changes in averaged evoked responses. Electroencephalography and clinical Neurophysiology, 1968, 25: 550–556.
Roland, P.E. Cortical organization of voluntary behavior in man. Human Neurobiology, 1985, 4: 155–167.
Sokolov, E.N. Perception and the conditioned reflex. New York: Macmillan, 1963.
Sokolov, E.N. Orienting reflex as information regulator. In A. Leontyev, A. Luria and A. Smirnov (Eds.), Psychological research in the U.S.S.R. (pp. 334–360). Moscow, Russia: Progress, 1966.
Tucker, D.M. Spatial sampling of head electrical fields: The geodesic sensor net. Electroencephalography and clinical Neurophysiology, 1993, 87: 154–163.
Tucker, D.M. and Derryberry, D. Anxiety and the frontal executive functions. Neuropsychiatry, Neuropsychology and Behavioral Neurology, 1992, 5(4): 233–252.
Tucker, D.M., Liotti, M., Potts, G.F., Russell, G.S. and Posner, M.I. Spatiotemporal analysis of brain electrical fields. Human Brain Mapping, 1994, 1: 134–152.
Ungerleider, L.G. and Haxby, J.W. ‘What’ and ‘where’ in the human brain. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 1994, 4(2): 157–165.
Ungerleider, L.G. and Mishkin, M. Two cortical visual systems. In D.J. Ingle, M.A. Goodale and R.J.W. Mansfield (Eds.), Analysis of Visual Behavior Cambridge, Mass: MIT Press, 1982.
Verleger, R. Event-related potentials and cognition: A critique of the context updating hypothesis and an alternative interpretation of P3. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 1988, 11: 343–427.
Walsh, V. and Perrett, D.I. Visual attention in the occipitotemporal processing stream of the macaque. Cognitive Neuropsychology, 1994, 11(2): 243–263.
Wijers, A.A., Lamain, W., Slopsema, S., Mulder, G. and Mulder, L.J.M. An electrophysiological investigation of the spatial distribution of attention to colored stimuli in focused and divided attention conditions. Biological Psychology, 1989(a), 29: 213–245.
Wijers, A.A., Mulder, G., Okita, T. and Mulder, L.J.M. An ERP study on memory search and selective attention to letter size and conjunctions of letter size and color. Psychophysiology, 1989(b), 26: 529–547.
Wijers, A. A., Mulder, G., Okita, T., Mulder, L.J.M. and Scheffers, M.K. Attention to color: An ERP analysis of selective attention, controlled search and motor activation. Psychophysiology, 1989(c), 26: 89–109.
Wikswo, J.P.J., Gevins, A. and Williamson, S.J. The future of the EEG and MEG. Electroencephalography and clinical Neurophysiology, 1993, 87: 1–9.
Wilson, F.A.W., Scalaidhe, S.P.O. and Goldman-Rakic, P.S. Dissociation of object and spatial processing domains in primate prefrontal cortex. Science, 1993, 260: 1955–1958.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research was supported by NIMH grants MH 42669, MH 42129, MH 18935 and the James S. McDonnell Foundation and Pew Charitable Trust grant to support the Oregon Center for the Cognitive Neuroscience of Attention.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Potts, G.F., Liotti, M., Tucker, D.M. et al. Frontal and inferior temporal cortical activity in visual target detection: Evidence from high spatially sampled event-related potentials. Brain Topogr 9, 3–14 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01191637
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01191637