Purpose
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the use of Plasmanate, a protein preparation containing human serum albumin and mixed globulins to autologous preovulatory maternal serum, as an in vitro fertilization (IVF) medium supplement. Plasmanate was used most often in cases involving unexplained infertility, sperm antibodies, and endometriosis or when serum was unavailable.
Results
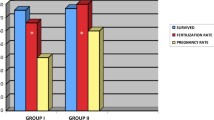
In a retrospective analysis of 1019 consecutive IVF cycles, Plasmanate was used as the protein supplement to the fertilization medium in 28.6% and maternal serum was used in 71.4% of the attempts. Attempting to eliminate the effects of different medium lots and laboratory conditions, 450 matched patient cycles were compared using the two protein supplements. Finally, the effects of Plasmanate versus maternal serum were compared in prospective randomized trial on patients diagnosed with tubal infertility who were attempting IVF for the first time. The clinical pregnancy rate was 34% for the Plasmanate group versus 24% for those using maternal serum in the retrospective investigation. However, this trend was reversed in the prospective trial.
Conclusion
Although further investigation is necessary, it appears that Plasmanate is an appropriate protein substitute in patient cases where serum is absent or unsuitable.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lopata A: Success and failure in human in vitro fertilization. Nature 1980;288:642
Edwards RG, Fishel SB, Cohen J, Fehilly CB, Purdy JM, Slater JM, Streptoe PC, Webster JM: Factors influencing the success of in vitro fertilization for alleviating human infertility. J Vitro Fert Embryo Transfer 1984;1:3–23
Kemeter P, Feichtinger W: Pregnancy following in vitro fertilization and embryo transfer using pure human serum as culture and transfer medium. Fertil Steril 1984;41:936–937
Holst N, Bertheussen K, Forsdahl F, Berger Hakonsen M, Hansen LJ, Nielsen HI: Optimization and simplification of culture conditions in in vitro fertilization (IVF) and preembryo replacement by serum-free media. J Vitro Fert Embryo Transfer 1990;7:47–53
Jinno M, Iida E, Iizuda R: A detrimental effect of platelets on mouse embryo development. J Vitro Fert Embryo Transfer 1987;4:324–330
Ross R, Raines EW, Bowen-Pope DF: The biology of platelet-derived growth factor. Cell 1986;46:155–169
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC: Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine. Oxford, Clarendon Press, 1986
Hensleigh HC: Optimal concentration of human serum albumin for in vitro murine embryonic development. SSR Meeting 1986;99
Quinn P, Warnes GM, Kerin JF, Kirby C: Culture factors in relation to the success of in vitro fertilization and embryo transfer. Fertil Steril 1984;41:202–209
Trounson A, Conti A: Research in human in vitro fertilisation and embryo transfer. Br Med J 1982;285:244–247
Ackerman SB, Swanson RJ, Stokes GK, Veeck L: Culture of mouse preimplantation embryos as a quality control assay for human in vitro fertilization. Gamete Res 1984;9:145–152
Case Gould M: Endotoxin in vertebrate cell culture: Its measurement and significance. Uses Standard Vertebr Cell Cultures 1984;5:125–136
Hink JH, Jr., Hildalgo J, Seeberg VP: Preparation and properties of a heat-treated human plasma protein fraction. Vox Sang 1957;2:174–186
Cohen J, Malter HE, Talansky BE, Grifo J: Micromanipulation of Human Gametes and Embryos. New York, Raven Press, 1992
Berkeley AS, Bedford JM, Rosenwaks Z: Clinical Aspects of Human in Vitro Fertilization, P Wassarman (ed). Boca Raton, FL, CRC Press, 1991
Rosenwaks Z, Davis OK: In vitro fertilization and related techniques.In Danforth's Obstetrics and Gynecology, 6th ed, JR Scott, PJ DiSaiz, CB Hammond, WN Spellacy (eds). Philadelphia, Lippincott, 1990, pp. 821–843
Sharma V, Riddle A, Mason BA, Pampiglione J, Campbell S: An analysis of factors influencing the establishment of a clinical pregnancy in an ultrasound-based ambulatory in vitro fertilization program. Fertil Steril 1988;48:468–478
Medical Research International, Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology and The American Fertility Society: In vitro fertilization-embryo transfer (IVF-ET) in the United States 1989 results from the IVF-ET Registry. Fertil Steril 1991;55:14–23
Menezo Y, Testart J, Perrone D: Serum is not necessary in human in vitro fertilization, early embryo culture, and transfer. Fertil Steril 1984;42:750–755
Caro CM, Trounson A: Successful fertilization, embryo development, and pregnancy in human in vitro fertilization (IVF) using chemically defined culture medium containing no protein. J Vitro Embryo Transfer 1984;3:215–217
Ashwood-Smith MJ, Hollands P, Edwards RG: The use of Albuminar (TM) as a medium supplement in clinical IVF. Hum Reprod 1989;4:702–705
Staissen C, Van den Abbeel E, Carle M, Khan I, Devroey P, Van den Steirteghem AC: Comparison between human serum and Albuminar-20 (TM) supplement for in-vitro fertilization. Hum Reprod 1990;5:336–341
de Ziegler D, Cedars MI, Hamilton F, Moreno T, Meldrum DR: Factors influencing maintenance of sperm motility during in vitro processing. Fertil Steril 1987;48:816–820
Caro CM, Trounson A: The effect of protein on preimplantation mouse embryo development in vitro. J Vitro Embryo Transfer 1984;1:183–187
Lippes J, Krasner J, Alfonso LA, Dacalos ED, Lacero R: Human oviductal fluid proteins. Fertil Steril 1981;36:623–629
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adler, A., McVicker Reing, A., Bedford, J.M. et al. Plasmanate as a medium supplement for in vitro fertilization. J Assist Reprod Genet 10, 67–71 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01204443
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01204443