Summary
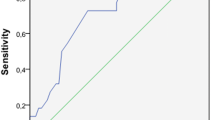
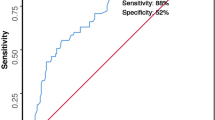
From June 1982 to May 1984 257 patients underwent surgery for bacterial peritonitis in two surgical departments. The documentation of cases was prospective and uniform. Cases with especially favourable or unfavourable prognoses were excluded from the study and the results from only 185 patients with peritonitis sensu strictu were statistically analysed by the logistic discrimination model of Anderson. Only eight pre- and intra-operative parameters were prognostically significant and were charged (x) as follows: age > 50 years (5), female sex (5), coexistent organ failure (7), presence of malignancy (4), preoperative duration of peritonitis > 24 h (4), diffuse peritonitis (6) and nature of exudate [clear (0), turbid-purulent (6) or faecal (12)]. The sum of the scores for each positive parameter gives the Mannheim Peritonitis-Index (MPI), yielding values ranging from 0 to 47. At a score of 26, for instance, with a mean mortality of 24%, the MPI has a sensitivity of 84% and an accuracy of 81 %. The MPI warrants validation in other surgical departments.
Zusammenfassung
257 Patienten mit bakterieller Peritonitis wurden von VI/82 bis V/1984 an 2 Chirurgischen Kliniken operiert und einheitlich dokumentiert. Unter Ausschluß bestimmter Peritonitiden mit besonders günstiger oder ungünstiger Prognose wurden die Daten von 185 Kranken mit „Peritonitis im engeren Sinne” einem multivariaten mathematischen Entscheidungsmodell (Anderson) unterzogen. Lediglich 8 prä- und intraoperative Risikofaktoren erwiesen sich als prognostisch relevant und wurden geladen (x): Alter > 50 Jahre (5), Geschlecht ♀ (5), Organversagen (7), Malignom (4), präop. Peritonitisdauer > 24 h (4), Peritonitisausbreitung diffus (6), Exsudat: Klar (0), trübeitrig (6), kotig jauchig (12). Die Summe der geladenen Ja-Antworten ergibt den MPI, der von 0–47 reicht. Bei der Indexzahl 26, durchschnittliche Letalität von 24%, erreicht der Index eine Sensitivität von 84%, eine Richtigkeit von 81%. Er sollte noch an anderen Kliniken validiert werden.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Linder, M.M., Wacha, H., Wesch, G. et al. 265. Welche klinischen Faktoren beeinflussen die Letalität bei bakterieller Peritonitis: Mannheimer Peritonitis-Index (MPI). Langenbecks Arch Chiv 369, 788 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01274584
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01274584