Abstract
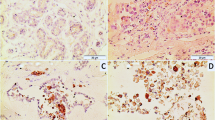
Metallothionein (MT) is a cysteine-rich, low molecular weight protein that binds zinc, copper, and cadmium. It is present in a number of normal cells including hepatocytes particularly during fetal and early postnatal life. It has been suggested that developmental profile of MT is similar to other oncofetal gene products and hence, it could be used as a marker for aggressive tumour behaviour. In order to test that hypothesis, we used a monoclonal antibody to MT and immunohistochemically evaluated formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues from 79 breast carcinomas. In non-neoplastic breast tissue, a strong nuclear and cytoplasmic staining was observed in myoepithelial cells. Positive staining for MT was present in 35 (44%) of breast carcinomas. In most positive cases, nuclear, or both nuclear and cytoplasmic staining was seen. All positive tumours were invasive ductal carcinomas, including a medullary and a metaplastic carcinoma. None of the mucinous, lobular, or intraductal papillary carcinomas reacted for MT. A statistically significant association was found between MT immunostaining and histological grade (P<0.01) as well as with nuclear grade (P<0.01). We also observed an inverse relationship between MT staining and oestrogen receptor content of tumours (P<0.01). Similarly, a statistically significant association was found between moderate and strong MT immunostainig and decreased overall survival and shorter disease-free survival (P<0.01). MT immunostaining was also predective of a worse prognosis in the subgroup of lymph node negative (P<0.001) and oestrogen receptor negative patients (P<0.01). No statistically significant association was found between MT staining and size of tumour or the presence of lymph node metastasis. We conclude that MT staining may be a useful marker of less differentiated and more aggressive carcinomas of the breast.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews PA, Murphy MP, Howell SB (1987) Metallothionein-mediated resistance in human ovarian carcinoma cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 19:149
Benerjee D, Onasaka S, Cherian MG (1982) Immunohistochemical localization of metallothionein in cell nucleus and cytoplasm on rat liver and kidney. Toxicology 24:95–105
Bloom HJG, Richardson WW (1957) Histological grading and prognosis in breast cancer. A study of 1049 cases of which 359 have been followed for 15 years. Br J Cancer 9:359–377
Bremner I, Willians RB, Young BW (1977) Distribution of copper and zinc in the liver of the developing fetus. Br J Nutr 38:87–92
Cherian MG, Goyer RA (1978) Metallothioneins and their role in the metabolism and toxicity of metals. Life Sci 23:1–8
Eastman A, Richon VM (1985) Biochemical mechanisms of platinum antitumor drugs. Mc Brien DC, Slater TF (eds) Oxford IRL Press, pp 91
Kagi JRR, Nordberg M (1979) Metallothionein. Birkhause, Basel, pp. 48–116
Kagi JHR, Himmelhoch SR, Whanger PDD, Betheune JL, Vallee BL (1974) Equine hepatic and renal metalothioneins: purification, molecular weight, amino acid composition, and metal content. Biol Chem 249:3537–3542
Kaplan EL, Meier P (1958) Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc 53:457–481
Kelleey SL, Basu A, Teicher BA, Halker MP, Hamer DH, Lazo JS (1988) Overexpression on MT confers resistance to anticancer drugs. Science 241:1813–1815
Kontozoglou TE, Banerjee D, Cherian G (1987) Immunohistochemical localization of metallothionein in human testicular embryonal carcinoma cells. Virchows Arch [A] 415:545–549
Murphy D, Mcgown AT, Crowther D, Mander A, Fox BW (1991) Metallothionein levels in ovarian tumours before and after chemotherapy. Br J Cancer 63:711–714
Nartey N, Cherian MJ Banerjee D (1987) Immunohistochemical localization of metallothionein in human thyroid tumours. Am J Pathol 129:177–182
Nishimura H, Nishimura N, Tohyama C (1990) Localization of metallothionein in genital organs of the male rat. J Histochem Cytochem 38:927–933
Panemangalore M, Banerjee D, Onosaka S, Cherian MG (1983) Changes in intracellular accumulation and distribution of metal-lothionein in rat liver and kidney during postnatal development. Dev Biol 97:95–102
Peto P, Pike MC, Armitage P et al. (1977) Design and analyses of randomized clinical trials requiring prolonged observation of each patient. II. Analyses and examples. Br J Cancer, 35:1–39
Ryden L, Deutsh HF (1978) Preparation and properties of the major copper-binding component in human fetal liver. J Biol Chem 253:519–524
Schmid KW, Ellis IO, Gee JMV et al. (1993) Presence and possible significance of immunohistochemically demonstrable metal-lothionein over-expression in primary invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. Virchows Arch [A] 422:153–159
Webb M, Cain K (1982) Functions of metallothionein. Biochem Pharmacol 31:137–142
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fresno, M., Wu, W., Rodriguez, J.M. et al. Localization of metallothionein in breast carcinomas. An immunohistochemical study. Vichows Archiv A Pathol Anat 423, 215–219 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01614773
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01614773