Summary
The abdominal intraperitoneal cerebrospinal fluid pseudocyst is an infrequent but important complication in patients with ventriculoperitoneal shunts. Since 1954, 115 cases of paediatric pseudocysts have been reported in the literature. One additional report deals with an adult patient.
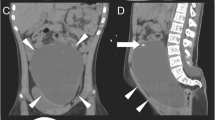
We report on 14 cases of sonographically diagnosed abdominal pseudocysts. Their aetiology, diagnosis, clinical signs and symptoms and surgical management are investigated. In our hydrocephalus series we have an incidence of pseudocyst formation of 4,5%. The most common presentation of the paediatric patients is with symptoms of elevated intracranial pressure and abdominal pain, whereas the adults have predominantly local abdominal signs. Diagnosis is readily made with ultrasonography. Predisposing factors for pseudocyst formation are multiple shunt revisions and infection. Microscopically, the pseudocysts consist of fibrous tissue without epithelial lining. The treatment involves surgical removal of the catheter with or without excision of the pseudocyst wall and placement of a new catheter intraperitoneally in a different quadrant or an intra-atrial shunt. Recurrences are rare, especially under appropriate medical treatment of infection. In our series, microbiologically proven infection was present in 30% of the cases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agha FP, Amendola MA, Shirazi KK, Amendola BE, Chandler WF (1983) Abdominal complications of ventriculoperitoneal shunts with emphasis of the role of imaging methods. Surg Gynecol Obstet 156: 473–478
Baumgartner FJ, Moore TC, Mitchner JR (1990) Recurrent ventriculoperitoneal shunt pseudocyst in a nine-year-old girl. Klin Wochenschr 68: 485–487
Brenbridge ANAG, Bushi AJ, Lees RF, Sims T (1979) Sonography of CSF pseudocyst. Am J Dis Child 133: 646–647
Briggs JR, Hendry GMA, Minns RA (1984) Abdominal ultrasound in the diagnosis of cerebrospinal fluid pseudocysts complicating ventriculoperitoneal shunts. Arch Dis Child 59: 661–664
Bryant MS, Bremer AM, Tepas JJ 3rd, Mollitt DL, Nquyen TQ, Talbert JL (1988) Abdominal complications of ventriculoperitoneal shunts. Case reports and review of the literature. Am Surg 54: 50–55
Burchianti M, Cantini R (1988) Peritoneal cerebrospinal fluid pseudocysts: a complication of ventriculoperitoneal shunts. Childs Nerv Syst 4: 286–290
Chuang VP, Fried AM, Oliff M, Ellis GT, Sachatello CR (1978) Abdominal CSF pseudocyst secondary to ventriculoperitoneal shunt: diagnosis by computed tomography in two cases. J Comp Assist Tomogr 2: 88–91
Davidson DI, Lingley JF (1975) Intraperitoneal pseudocyst: treatment by aspiration. Surg Neurol 4: 33–36
Deindl C, Kellnar S (1986) Zur Diagnostik und Therapie der intraperitonealen Liquorpseudozyste bei ventrikuloperitonealer Liquorableitung von Hydrozephaluspatienten. Z Kinderchir 41: 295–298
Egelhoff J, Babcock DS, McLaurin R (1985–86) Cerebrospinal fluid pseudocysts: sonographic appearance and clinical management. Pediatr Neurosci 12: 80–86
Engelhard HH, Miller FB (1992) Abdominal pain resulting from cerebrospinal fluid pseudocyst and cholelithiasis. South Med J 85: 851–852
Fisher EG, Shillito J Jr (1969) Large abdominal cysts: a complication of peritoneal shunts. Report of three cases. J Neurosurg 31: 441–444
Gaskill SJ, Marlin AE (1989) Pseudocysts of the abdomen associated with ventriculoperitoneal shunts: a report of twelve cases and a review of the literature. Pediatr Neurosci 15: 23–26
Gebarski KS, Gebarski SS, McGillicuddy JE (1984) Cerebrospinal fluid abdominal cyst: computed tomographic resolution of a sonographic dilemma. Surg Neurol 21: 414–416
Goldfine SL, Turetz F, Beck RA, Eider M (1978) Cerebrospinal fluid intraperitoneal cyst: an unusual abdominal mass. Am J Roentgenol 130: 568–569
Grosfeld JL, Cooney DR, Smith J, Campbell RL (1974) Intraabdominal complications following ventriculoperitoneal shunt procedures. Pediatrics 54: 791–796
Grunebaum M, Ziv N, Kornreich L, Horev G, Lombrozo R (1988) The sonographic signs of the peritoneal pseudocyst obstructing the ventriculo-peritoneal shunt in children. Neuroradiology 30: 433–438
Guice KS, Kosloske AM (1978) Recurrent pseudocyst from a ventriculoperitoneal shunt: an unusual abdominal mass. Am J Dis Child 132: 285–286
Gutierrez FA, Raimondi AJ (1976) Peritoneal cysts: a complication of ventriculo-peritoneal shunts. Surgery 79: 188–192
Hahn YS, Engelhard H, McLone DG (1985–86) Abdominal CSF pseudocyst. Clinical features and surgical management. Pediatr Neurosci 12: 75–79
Harsh GR (1954) Peritoneal shunt for hydrocephalus: utilizing the fimbria of the fallopian tube for entrance to the peritoneal cavity. J Neurosurgery 11: 284–294
Kausch W (1905) Die Behandlung des Hydrocephalus der kleinen Kinder. Arch Clin Chir 87: 709–796
Lee TG, Parsons PM (1978) Ultrasound diagnosis of cerebrospinal fluid abdominal cyst. Radiology 127: 220
Murtagh FR, Quencer RM, Poole CA (1980) Extracranial complications of cerebrospinal fluid shunt function in childhood hydrocephalus. Am J Roentgenol 135: 763–766
Narashimharao KL, Purohit A, Yadav K, Pathak IC (1984) Recurrent abdominal pseudocyst after ventriculoperitoneal shunt. Aust Pediatr J 20: 73–74
Norfray JF, Harvey HM, Givens JD, Sparberg MS (1979) Abdominal complications from peritoneal shunt. Gastroenterology 77: 337–340
Parry SW, Schuhmacher JF, Llewellyn RC (1975) Abdominal pseudocysts and ascites formation after ventriculoperitoneal shunt procedures: report of four cases. J Neurosurg 43: 476–480
Price HI, Rosenthal SJ, Batnitzky S, Lee KR, Wilson ME (1981) Abdominal pseudocysts as a complication of ventriculoperitoneal shunt: a report of two cases. Neuroradiology 21: 273–276
Raghavendra BN, Epstein FJ, Subramanyam BR, Becker MH (1981) Ultrasonographic evaluation of intraperitoneal CSF pseudocyst: report of three cases. Childs Brain 8: 39–43
Rekate HL, Yonas H, White RJ, Nulsen FE (1979) The acute abdomen in patients with ventriculoperitoneal shunts. Surg Neurol 11: 442–445
Rush DS, Walsh JW (1982) Abdominal complications of CSF-peritoneal shunts. Monogr Neural Sci 8: 52–54
Rush DS, Walsh JW, Belin RP, Pulito AR (1985) Ventricular sepsis and abdominally related complications in children with cerebrospinal fluid shunts. Surgery 97: 420–427
Sivalingam S, Corkill G, Getzen L, Matolo N (1976) Recurrent abdominal cysts: a complication of ventriculoperitoneal shunt and its management. J Pediatr Surg 11: 1029–1030
White B, Kropp K, Rayport M (1991) Abdominal cerebrospinal fluid pseudocyst: occurrence after intraperitoneal urological surgery in children with ventriculo-peritoneal shunts. J Urol 146: 583–587
Wirth S, Baumann W, Alzen G (1983) Sonographische Diagnostik von abdominellen Komplikationen bei ventrikulo-peritonealem Shunt. In: Voth Det al (eds) Hydrozephalus im frühen Kindesalter. Enke, Stuttgart, pp 297–302
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rainov, N., Schobeß, A., Heidecke, V. et al. Abdominal CSF pseudocysts in patients with ventriculo-peritoneal shunts. Report of fourteen cases and review of the literature. Acta neurochir 127, 73–78 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01808551
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01808551