Abstract
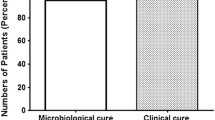
In a coordinated, double-blind multi-centre trial, adults with symptoms of acute pyelonephritis were randomly assigned to receive a two-week course of oral treatment with either 400 mg norfloxacin twice daily or 1 g cefadroxil twice daily. Of 197 patients enrolled in the study, 140 could be evaluated for drug efficacy and 193 for drug safety. Norfloxacin gave a significantly higher bacteriological cure rate than cefadroxil, both at 3 to 10 days (98 % versus 65 %; p<0.0001; 95 % confidence interval (CI) for difference in proportions 21–46 %) and up to eight weeks (87 % versus 48 %; p<0.0001; 95 % CI 25–54 %) after cessation of treatment. The differences between the two regimens were most pronounced in men and in patients with complicating factors such as diabetes mellitus and urinary tract abnormalities. The clinical response during treatment did not differ between the two groups, but symptomatic recurrences at follow-up were more common in the cefadroxil group (28 % versus 3 %; p<0.0001; 95 % CI 14–36 %). Adverse events were more often reported by patients receiving cefadroxil (39 % versus 22 %; p=0.011; 95 % CI 4–30 %) and consisted mainly of gastrointestinal disturbances and vulvo-vaginitis. In terms of bacteriological and clinical efficacy and safety, a two-week course of norfloxacin was superior to a two-week course of cefadroxil for oral treatment of community-acquired acute pyelonephritis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eriksson S, Zbornik J, Dahnsjö H, Erlanson P, Kahlmeter O, Fritz H, Bauer C-A The combination of pivampicillin and pivmecillinam versus pivampicillin alone in the treatment of acute pyelonephritis. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases 1986, 18: 431–438.
Stamm WE, McKevitt M, Counts GW Acute renal infection in women: treatment with trimethoprimsulfamethoxazole or ampicillin for two or six weeks. A randomized trial. Annals of Internal Medicine 1987, 106: 341–345.
Jernelius H, Zbornik J, Bauer C-A One or three weeks' treatment of acute pyelonephritis? A double-blind comparison, using a fixed combination of pivampicillin plus pivmecillinam. Acta Medica Scandinavica 1988, 223: 469–477.
Khan MY, Grunninger RP, Nelson SM, Klicker RE Comparative in vitro activity of norfloxacin (MK-0366) and ten other oral antimicrobial agents against urinary bacterial isolates. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1982, 21: 848–851.
The Urinary Tract Infection Study Group Coordinated multicenter study of norfloxacin versus trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole treatment of symptomatic urinary tract infections. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1987, 155: 170–177.
The Inter-Nordic Urinary Tract Infection Study Group Double-blind comparison of 3-day versus 7-day treatment with norfloxacin in symptomatic urinary tract infections. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases 1988, 20: 619–624.
Hamilton-Miller JMT Microbiological investigation of cephalosporins. Drugs 1987, 34, Supplement 2: 23–43.
Gower PE, Tasker PRW Comparative double-blind study of cephalexin and co-trimoxazole in urinary tract infections. British Medical Journal 1976, i: 684–686.
Preiksaitis JK, Thompson L, Harding GKM, Marrie TJ, Hoban S, Ronald AR A comparison of the efficacy of nalidixic acid and cephalexin in bacteriuric women and their effect on fecal and periurethral carriage ofEnterobacteriaceae. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1981, 143: 603–608.
Sandberg T, Henning C, Iwarson S, Paulsen O Cefadroxil once daily for three or seven days versus amoxicillin for seven days in uncomplicated urinary tract infections in women. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases 1985, 17: 83–87.
Lidin-Janson G, Falsen E, Jodal U, Kaijser B, Lincoln K Characteristics of antibiotic-resistantEscherichia coli in the rectum of healthy school-children. Journal of Medical Microbiology 1977, 10: 299–308.
Ericsson HM, Sherris JC Antibiotic sensitivity testing. Report of an international collaborative study. Acta Pathologica Microbiologica Scandinavica (B) 1971, Supplement 217: 1–90.
Blackwelder WC “Proving the null hypothesis” in clinical trials. Controlled Clinical Trials 1982, 3: 345–353.
Sandberg T, Stokland E, Brolin I, Lidin-Janson G, Svanborg-Edén C Selective use of excretory urography in women with acute pyelonephritis. Journal of Urology 1989, 141: 1290–1294.
Bergan T Pharmakokinetic properties of the cephalosporins. Drugs 1987, 34, Supplement 2: 89–104.
Bergeron MG Therapeutic potential of high renal levels of aminoglycosides in pyelonephritis. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1985, 15: 4–8.
Domingue GJ, Schlegel JU The possible role of microbial L-forms in pyelonephritis. Journal of Urology 1970, 104: 790–798.
Grüneberg RN Relationship of infecting urinary organism to the faecal flora in patients with symptomatic urinary infection. Lancet 1969, ii: 766–768.
Stamey TA A clinical classification of urinary tract infections based upon origin. Southern Medical Journal 1975, 68: 934–939.
Haase DA, Harding GKM, Thomson MJ, Kennedy JK, Urias BA, Ronald AR Comparative trial of norfloxacin and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in the treatment of women with localized, acute, symptomatic urinary tract infections and antimicrobial effect on periurethral and fecal microflora. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1984, 26: 481–484.
Edlund C, Nord CE A review of the impact of 4-quinolones on the normal oropharyngeal and intestinal human microflora. Infection 1988, 16: 8–12.
Smith JT, Lewin CS Chemistry and mechanisms of action of the quinolone antibacterials. In: Andriole VT (ed): The quinolones. Academic Press, London, 1988, p. 23–82.
Bergeron MG, Thabet M, Roy R, Lessard C, Foucault P Norfloxacin penetration into human renal and prostatic tissues. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1985, 28: 349–350.
Bergan T Pharmacokinetics of fluorinated quinolones. In: Andriole VT (ed): The quinolones. Academic Press, London, 1988, p. 119–154.
Lipsky BA Urinary tract infections in men. Epidemiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Annals of Internal Medicine 1989, 110: 138–150.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Investigators: Dr G. Lekås, Department of Infectious Diseases, Central Hospital, Gävle; Dr V. Friman and Dr T. Sandberg, Department of Infectious Diseases, Östra Hospital, Göteborg; Dr H. Montelius and Dr R. Neringer, Department of Infectious Diseases, Central Hospital, Karlskrona; Dr S.-E. Lundin and Dr O. Wik, Department of Infectious Diseases, Central Hospital, Karlstadt, Dr C. Franzén, Department of Infectious Diseases, Central Hospital, Sundsvall; Dr M. Hebelka, Department of Infectious Diseases, Central Hospital, Uddevalla, Sweden.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sandberg, T., Englund, G., Lincoln, K. et al. Randomised double-blind study of norfloxacin and cefadroxil in the treatment of acute pyelonephritis. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 9, 317–323 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01973737
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01973737