Abstract
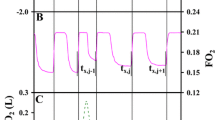
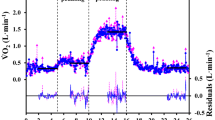
The O2-paramagnetic or polarographic and CO2-infra-red expired gas analyser have a response delay which results in an underestimation in breath-by-breath\(\dot vO_2 \) and\(\dot vCO_2 \) calculations. In this study, correction for this delay has been made. After measuring the step response of the O2-polarographic and CO2-infra-red analyser, the damping factor and the natural angular frequency were determined as well as the time constant, assuming the response was a first-order one.\(\dot vO_2 \) and\(\dot vCO_2 \) were calculated when the response of the analyser was corrected for the first- and second-order responses using the inverse Laplace transform. For the uncorrected\(\dot vO_2 \) and\(\dot vCO_2 \), values from the breath-by-breath method were 27·5 and 18·1 per cent systematically underestimated (p<0·001) compared with those of the Douglas bag method. When correction for the first-order response was made, values of the breath-by-breath method became equivalent to those of the Douglas bag method for\(\dot vCO_2 \) whereas there was still a 17·5 per cent systematic underestimation (p<0·001) for\(\dot vO_2 \). The correction for the second-order response gave equivalence and significant correlation (p<0·001) between the values of both methods for\(\dot vO_2 \) and\(\dot vCO_2 \). These results might indicate that breath-by-breath measurement of alveolar gas exchange with a slow-response gas analyser is valid when a second-order response delay correction is used.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beaver, W. L., Wasserman, K. andWhipp, B. J. (1973) On-line computer analysis and breath-by-breath graphical display of exercise function tests.J. Appl. Physiol.,34(1), 128–132.
Beaver, W. L., Lamarra, N. andWasserman, K. (1981) Breath-by-breath measurement of true alveolar gas exchange.J. Appl. Physiol.: Respirat. Environ. Exercise Physiol.,51, 1662–1675.
Noguchi, H., Ogushi, Y., Yoshiya, I., Itakura, N. andYamabayashi, H. (1982) Breath-by-breath VCO2 and VO2 require compensation for transport dealy and dynamic response.,52, 79–84.
Pearce, D. H., Milhorn, H. T. Jr.,Holloman, G. H. Jr., andReynolds, W. J. (1977) Computer-based system for analysis of respiratory responses to exercise.,42, 968–975.
Sue, D. Y., Hansen, J. E., Blais, M. andWasserman, K. (1980) Measurement and analysis of gas exchange during exercise using a programmable calculator.,49, 456–461.
Wessel, H. U., Stout, R. L., Basstanier, C. K. andPaul, M. H. (1979) Breath-by-breath variation of FRC: effect on VO2 and VCO2 measured at the mouth.,46, 1122–1126.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamamoto, Y., Takei, Y., Mokushi, K. et al. Breath-by-breath measurement of alveolar gas exchange with a slow-response gas analyser. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 25, 141–146 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02442842
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02442842