Abstract
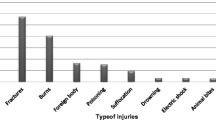
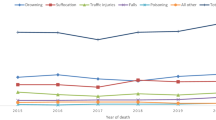
Most of the studies dealing with morbidity and mortality in childhood in less developed countries do not include injuries as an important cause. However, a few hospital based studies indicate that injuries make a significant contribution to childhood morbidity in India. The present paper summarises the information regarding burns, falls, poisoning, drowning and traffc injuries. The data indicate that the patterns of injuries in India are different from those in highly industrialised countries. Principles and strategies for control of injuries are described.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vaidyanathan KE.Studies on mortality in India. The Ghandhigram Institute of Rural Rural Health and Planning, Madurai Distt., Tamilnadu, 1972.
Agarwal V, Gupta A. Accidental poisonings in children.Indian Pediatr 1974;11: 617
Ghosh BN, Dhikhpathy K. Morbidity pattern of the South Indian adolescent.Indian J Pediatr 1966;33: 171
International Childrens Centre:Accidents Bibliography 1982;3: 2
W.H.O.The prevention of accidents in childhood. Copenhagen, 1960
Baker SP. Childhood injuries. The community approach to prevention.J Health Policy 1981;2: 235
Baker SP, Fisher RS. Childhood asphyxiation by choking.J A Med Ass 1980;244: 1343
McLoughlin E, Clarke M, Stehl K, Crawford JD. One pediatric burn unit’s experience with sleepwear related injuries.Pediatrics 1977;60: 405
Melvin JW, Stalnaker RL, Mohan D. Protection of child occupants in automobile crashes.22nd Car Crash Conference SAE Paper 780904. Warrendale: Society of Automotive Engineers, 1978
Williams AF, Wells JAK. The Tennesee Child restraint law in its third year.Am J Public Health 1981;71: 163–165
Government of India (undated).National policy for children. Ministry of Social Welfare, New Delhi
Agarwal DK, Katiyar GP, Yadav KNS, Agarwal KN. Morbidity pattern in under-five children.J Trop Pediatr 1982;28: 139
Chaudhuri A, Chaudhuri KC. Studies on the morbidity pattern of children in an urban community.Indian J Pediatr 1962;29: 145
Fernando MA. Morbidity and medical care in Ceylon.Ceylon Med J 1964;9: 26
Grounds JG. Mortality of children under six years old in Kenya with reference to contributory causes, especially malnutrition.J Tropic Med Hyg 1964;67: 257
Gandhi VK. Morbidity and mortality in children.Indian J Child Hlth 1963;12: 790
Mukhopadhyay S. A study of accidental injury cases among children (1–12 years) in an industrial township of West Bengal.J Indian Med Assoc 1981;76: 210.
Chatterjee B, Banerjee DP. Accidental poisoning in children.Indian Pediatr 1981;18: 157
Haddon W, Baker SP. Injury control, inPreventive Medicine eds. D Clark, B MacMohan, Little Brown & Co., 109, 1981
Sinha RN. Burns in tropical countries.Clin Plastic Surg 1974;1: 121
Learmonth AM. Domestic child burn and scald accidents.J Indian Med Assoc 1980;74: 139
Mukherjee GD. Problem of burn and scald accidents in children.J Indian Med Ass 1979;73: 41
Mohan Det al. Firework injuries during diwali: A study of patients brought to two hospitals in Delhi.J Indian Med Ass. (in print)
Learmonth AM. Domestic child burn and scald accidents.J Indian Med Assoc 1979;73: 43
Kimati VP. Childhood accidents in Daressalaam.Trop Geogr Med 1971;29: 91.
Ebong WW. Falls from trees.Trop Geogr Med 1978;30: 63
Pendse AK, Saran HS, Dandia SD, Narula IMS. Closed pediatric head injury.Indian Pediatr 1971;38: 385
Chandra RK. Accidents and poisoning in children with reference to data from India and Canada.Indian J Pediatr 1976;43: 260
Ghooi AM, Khanna T, Gupta MM. An analysis of 500 cases of head injury in children.Indian Pediatr 1976;43: 191.
Blaszczyk E, Kulczyk E, Klincewics. Les introxications accidentelles de L’enfant traitees entre 1973 et 1978 a 1’Hospital Pediat rique regional Ponzan.Pediatr Pol 1980;10: 1127
Done AK. Aspirin Overdosage: Incidence, diagnosis and management.Pediatrics 1978;59: 890 (Suppl)
Sanathanakrishnan BR, Balagopalaraju U. Poisoning in childhood.Indian J Pediatr 1972;39: 158
Sanathanakrishnan BR, Chithra S. Accidental kerosene poisoning in infants and children.Indian J Pediatr 1978;45: 265.
Bara D, Sarkar AK. A study of accidental poisoning in children in West Bengal.Indian J Pediatr 1977;44: 278
Banerjee P, Bhattacharrya S. Changing pattern of poisoning in childrn in developing countries.Trop Pediatr and Environ Chld Hlth 1978; 136
Bull D.A growing problem: pesticides and the third world poor. London: Oxfam, 1982
Mohan D. Food vs limbs. Pesticides and physical disability in India.Econ Pol Weekly 1986; (in print)
Statistical Abstracts India 1978. Central Statistical Organisation, Ministry of Planning, New Delhi, 1978
Mohan D, Bawa PS. An analysis of road traffic fatalities in India.Accident Analysis and Prevention 1985;17: 33–45
Singh KP, Singh JI. Accidents in agriculture.Journal Indian Med Assoc 1980;75: 4
Gordon JE, Gulati PV, Wyon JB. Traumatic accidents in rural tropical regions: An epidemiological field study in Punjab, India.The Amn J Field Sciences 1962;243: 158
Mohan D. Accidental death and disability in India: A case of criminal neglect.Industrial Safety Cronicle 1982;13: 34
Robertson LS.Injuries: causes, control strategies and public policy. Lexington Books, Lexing MA USA, 1983
Owings CL, Chaffin DB, Snyder RG, Norcutt RH. Strength characteristics of US children for product safety design. FDA 73–32, Consumer Product Safety Commission, Washington D.C. 1975
Snyder RGet al. Anthropometry of infants, children and youths to age 18 for product safety design. UM-HSRI-77-17, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, 1977
Snyder RG, Foust DR, Bowman BM. Study of impact tolerance through free-fall investigation. UM-HSRI-77-B, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan
Mohan D, Bowman BM, Snyder RG, Foust DR. A biomechanical analysis of head impact injuries to children.J Biomechanical Engineering 1979;101: 250
Mohan D, Schneider LW. An evaluation of adult clasping strength for restraining lapheld infants.Human Factors 1979;21: 635–645
Dershequitz RA, Williamson JW. Prevention of childhood household injuries: A controlled clinical trial.Am J Public Hlth 1977;67: 1148
Reisinger KS, Williams AF. Evaluation of programs designed to increase protection of infants in cars.Pediatrics 1978;62: 280
Spiegal CN, Lindaman C. Children Can’t Fly: A program to prevent childhood morbidity and mortality from window falls.Am J Public Hlth 1977;67: 1143
Miller REet al. Pediatri counselling and subsequent use of smoke detectors.Am J Public Hlth 1982;79: 392.
Kravitz H. Prevention of falls in infancy by counselling mothers.Illinois Med J 1973144: 570
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohan, D. Childhood injuries in India: extent of the problem and strategies for control. Indian J Pediatr 53, 607–615 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02748664
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02748664