Abstract
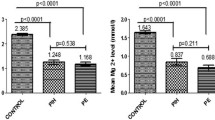
Four groups of subjects: normal healthy normotensive nonpregnant women (Group A), normal normotensive pregnant women (Group B), women with preeclamptic toxaemia (Group C) and eclamptic women (Group D): with fifty subjects in each group, were investigated for serum lipid profile in the third trimester of pregnancy. There was significant increase in serum triglyceride and VLDL cholesterol leve as well as decrease in LDL cholesterol in normal pregnancy, while total cholesterol and HDL cholesterol levels did not show any statistically significant alteration. The preeclampsia (Group C) was associated with a significant rise in triglyceride and VLDL cholesterol and fall in HDL cholesterol concentration, while eclamptic women showed significant fall in HDL cholesterol and rise in LDL cholesterol as compared to normal pregnant women. However, interestingly, elevation of the ratios of total cholesterol: HDL cholesterol and triglyceride: HDL cholesterol as well as diminuition of the ratio of HDL cholesterol: VLDL cholesterol showed statistical significance in pregnancy induced hypertension in both Groups C and D, while eclamptic women showed significant elevation of LDL cholesterol: HDL cholesterol ratio in addition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dutta, D.C. (2001) Hypertensive disorders in pregnancy, In: Textbook of Obstetrics, Ed. Konar, H.L., 5th edition, New Central Book Agency, Kolkata, p 234–55.
Robson, S.C. (1999) Hypertension and renal disease in pregnancy, In: Dewhurst's Textbook of Obstetrics and Gynaecology for postgraduates, Ed. Edmonds, D.K., 6th edition, Blackwell Science Ltd., New York, p 167–9.
Chiang, A.N., Yang, M.L., Hung, J.H., Chon, P., Shyn, S.K. and Ng, H.T. (1995) Alterations of serum lipid levels and their biological relevances during and after pregnancy. Life Sci. 56(26), 2367–75.
Glueck, C.J., Fallet, R.W. and Scheel, D. (1975) Effects of oestrogenic compounds on triglyceride kinetics. Metabolism 24, 537–45.
Adegoke, O.A., Lyare, E.E. and Gbenebitse, S.O. (2003) Fasting plasma glucose and cholesterollevels in pregnant Nigerian women. Niger. Postgrad. Med. J. 10(1), 32–6.
Enquobahrie, D.A., Williams, M.A., Butler, C.L., Frederick, I.O., Miller, R.S. and Luthy, D.A. (2004) Maternal plasma lipid concentrations in early pregnancy and risk of preeclampsia, Am. J. Hypertens. 17(7), 574–81.
Cekmen, M.B., Erbagci, A.B., Balat, A., Duman, C., Maral, H., Ergen, K., Osden, M., Balat, O. and Kuskay, S. (2003) Plasma lipid and lipoprotein concentrations in pregnancy induced hypertension, Clin. Biochem. 36(7), 575–8.
Mikhail, M.S., Basu, J., Palan, P.R., Furgiusle, J., Romney, S.L. and Anyaegbunam, A. (1995) Lipid profile in women with preeclampsia: relationship between plasma triglyceride levels and severity of preeclampsia. J. Assoc. Acad. Minor Phys. 6(1), 43–5.
Sattar, N., Bendomir, A., Berry, C., Shepherd, J., Greer, I.A. and Packard, C.J. (1997) Lipoprotein subfraction concentrations in preeclampsia: pathogenic parallels to atherosclerosis. Obstet. Gynecol. 89(3), 403–8.
Kokia, E., Barkai, G., Reichman, B., Segal, P., Goldman, B. and Mashiach, S. (1990) Maternal serum lipid profile in pregnancies complicated by hypertensive disorders. J. Perinat. Med. (Germany) 18(6), 473–8.
Yamaguchi, K. (1988) Triglycerides and apoproteins in toxaemia of pregnancy, Nippon Sanka Fujika Gakkai Zasshi (Japan) 40(2), 1875–82.
Hubel, C.A., Lyall F., Weissfeld, L., Gandley, R.E. and Roberts, J.M. (1998) Small low-density lipoproteins and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 are increased in association with hyperlipidemia in preeclampsia, Metabolism 47(10), 1281–8.
Bradley, R. and Crook, D. (1995) Pregnancy, oral contraception and hormone replacement therapy, In: Textbook of Clinical Biochemistry: Metabolic and Clinical aspects, Eds. Marshall, W.J. and Bangert, S.K., 1st edition, Churchill Livingstone, London, p 413–22
Kaaja, R., Tirkkanen, M.J., Viinnkka, L. and Ylikorkala, O. (1995) Serum lipoproteins, insulin and urinary prostanoid metabolites in normal and hypertensive pregnant women, Obstet. Gynecol. 85(3), 353–6.
Teichmann, A.T., Wieland, H., Cremer, P., Knlow, G. and Mehle, U. (1988) Serum lipid and lipoprotein concentrations in pregnancy and at onset of labour in normal and complicated pregnancies caused by hypertensive gestosis and fetal growth retardation. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd (Germany, West) 48(3), 134–9.
Knopp, R.H., Warth, M.R., Charles, D., Childs, M., Li, J.R., Mabuchi, H. and Von, M.I.A. (1986) Lipoprotein metabolism in pregnancy, fat transport to the fetus and the effects of diabetes. Biol. Neonate (Switzerland) 50(6), 297–317.
Potter, J.M. and Netel, P.J. (1979) The hyperlipidaemia of pregnancy in normal and complicated pregnancies. Am. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. (United States) 133(2), 165–70.
Arbogast, B.W., Leeper, S.C., Merrick, R.D., Olive, K.E. and Taylor, R.N. (1994) Which plasma factors bring about disturbance of endothelial function in preeclampsia? Lancet 343(8893), 340–1.
Gratacos, E., Casals, E., Gomez, O., Llurba, E., Mercader, I., Cararach, V. and Cabero, L. (2003) Increased susceptibility to low density lipoprotein oxidation in women with a history of preeclampsia. British Journal of Obst. & Gynae. 110(4), 400–4.
Wakatsuki, A., Ikenoue, N., Okatani, Y., Shinohara, K. and Fukaya, T. (2000) Lipoprotein particles in preeclampsia: susceptibility to oxidative modification, Obstet. Gynecol 96(1), 55–9.
Barden, A., Ritchie, J., Walters, B., Michael, C., Rivera, J., Mori, T., Croft, K. and Beilin, L. (2001) Study of plasma factors associated with neutrophil activation and lipid peroxidation in preeclampsia. Hypertension, 38(4), 803–8.
Lorentsen, B. and Henriksen, T. (1998) Plasma lipids and vascular dysfunction in pre-eclampsia. Semin Reprod. Endocrinol 16(1), 33–39.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De, J., Mukhopadhyay, A. & Saha, P.K. Study of serum lipid profile in pregnancy induced hypertension. Indian J Clin Biochem 21, 165–168 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02912935
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02912935