Abstract
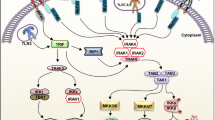
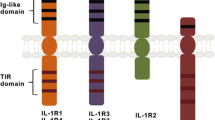
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) sense microbial products and play an important role in innate immunity. Currently, 11 members of TLRs have been identified in humans, with important function in host defense in early steps of the inflammatory response. TLRs are present in the plasma membrane (TLR1, TLR2, TLR4, TLR5, TLR6) and endosome (TLR3, TLR7, TLR8, TLR9) of leukocytes. TLRs and IL-1R are a family of receptors related to the innate immune response that contain an intracellular domain known as the Toll-IL-1R (TIR) domain that recruits the TIR-containing cytosolic adapters MyD88, TRIF, TIRAP and TRAM. The classical pathway results in the activation of both nuclear factor κB and MAPKs via the IRAK complex, with two active kinases (IRAK-1 and IRAK-4) and two non-catalytic subunits (IRAK-2 and IRAK-3/M). The classical pro-inflammatory TLR signaling pathway leads to the synthesis of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, such as IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, IL-12 and TNF-α. In humans, genetic defects have been identified that impair signaling of the TLR pathway and this may result in recurrent pyogenic infections, as well as virus and fungi infections. In this review, we discuss the main mechanisms of microbial recognition and the defects involving TLRs.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Autosomal dominant
- APCs:
-
Antigen-presenting cells
- BCG:
-
Bacillus Calmette-Guérin
- BTK:
-
Brutons’s tyrosine kinase
- CD62L:
-
CD62 ligand
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- CVID:
-
Common variable immunodeficiency
- DCs:
-
Dendritic cells
- dsRNA:
-
Double-stranded RNA
- EDA-ID:
-
Ectodermal dysplasia with immunodeficiency
- HClO:
-
Hypochlorous acid
- HO-1:
-
Heme oxygenase 1
- HSE:
-
Herpes simplex virus-encephalitis
- HSV-1:
-
Herpes simplex virus type 1
- IFN-γ:
-
Interferon-gamma
- IKK:
-
Inhibitor of NF-κB kinase complex
- IL-8:
-
Interleukin-8
- IRAK-4:
-
IL-1 receptor-associated kinase 4
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- LTA:
-
Lipoteichoic acid
- MALP-2:
-
Macrophage-activating lipopeptide-2
- MAPKs:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinases
- MBL:
-
Mannose-binding lectin
- MyD88:
-
Myeloid differentiation factor 88
- NADPH:
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide oxidase
- NEMO:
-
NF-κB essential modulator
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor kappaB
- NLRPs:
-
NOD leucine-rich repeat and pyrin domain containing proteins
- NLRs:
-
Leucine-rich repeat-containing receptors
- PAMPs:
-
Pathogen-associated molecular patterns
- PBMCs:
-
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells
- PDC:
-
Plasmacytoid DCs
- PIC:
-
Poly-riboinosinicribocytidylic acid
- PID:
-
Primary immunodeficiency diseases
- PMN:
-
Polymorphonuclear cells
- PRRs:
-
Pattern-recognition receptors
- RIG-I:
-
Retinoic acid-inducible gene I protein
- ssRNA:
-
Single-stranded RNA
- TIR:
-
Toll-IL-1R domain
- TIRAP:
-
TIR domain-containing adapter protein
- TLRs:
-
Toll-like receptors
- TRAM:
-
TRIF-related adapter molecule
- TRIF:
-
TIR domain-containing adapter-inducing IFN-β
- Xid:
-
X-linked immune deficiency
- XLA:
-
X-linked agammaglobulinemia
References
Abad C, Gonzalez-Escribano MF et al (2011) Association of Toll-like receptor 10 and susceptibility to Crohn’s disease independent of NOD2. Genes Immun 12:635–642
Adachi O, Kawai T et al (1998) Targeted disruption of the MyD88 gene results in loss of IL-1- and IL-18-mediated function. Immunity 9:143–150
Akira S, Hemmi H (2003) Recognition of pathogen-associated molecular patterns by TLR family. Immunol Lett 85:85–95
Akira S, Takeda K (2004) Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol 4:499–511
Akira S, Uematsu S et al (2006) Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 124:783–801
Baeuerle PA, Henkel T (1994) Function and activation of NF-kappa B in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol 12:141–179
Barchet W, Cella M et al (2005) Plasmacytoid dendritic cells–virus experts of innate immunity. Semin Immunol 17:253–261
Beutler B (2004) Inferences, questions and possibilities in Toll-like receptor signalling. Nature 430:257–263
Bochud PY, Magaret AS et al (2007) Polymorphisms in TLR2 are associated with increased viral shedding and lesional rate in patients with genital herpes simplex virus Type 2 infection. J Infect Dis 196:505–509
Botto M, Kirschfink M et al (2009) Complement in human diseases: lessons from complement deficiencies. Mol Immunol 46:2774–2783
Bousfiha A, Picard C et al (2010) Primary immunodeficiencies of protective immunity to primary infections. Clin Immunol 135:204–209
Bradley LA, Sweatman AK et al (1994) Mutation detection in the X-linked agammaglobulinemia gene, BTK, using single strand conformation polymorphism analysis. Hum Mol Genet 3:79–83
Bsibsi M, Ravid R et al (2002) Broad expression of Toll-like receptors in the human central nervous system. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 61:1013–1021
Bsibsi M, Persoon-Deen C et al (2006) Toll-like receptor 3 on adult human astrocytes triggers production of neuroprotective mediators. Glia 53:688–695
Bunk S, Sigel S et al (2010) Internalization and coreceptor expression are critical for TLR2-mediated recognition of lipoteichoic acid in human peripheral blood. J Immunol 185:3708–3717
Buwitt-Beckmann U, Heine H et al (2005) Lipopeptide structure determines TLR2 dependent cell activation level. FEBS J 272:6354–6364
Cai Z, Pang Y et al (2003) Differential roles of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1 beta in lipopolysaccharide-induced brain injury in the neonatal rat. Brain Res 975:37–47
Cardenes M, von Bernuth H et al (2006) Autosomal recessive interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 deficiency in fourth-degree relatives. J Pediatr 148:549–551
Carpentier PA, Begolka WS et al (2005) Differential activation of astrocytes by innate and adaptive immune stimuli. Glia 49:360–374
Carpentier PA, Duncan DS et al (2008) Glial Toll-like receptor signaling in central nervous system infection and autoimmunity. Brain Behav Immun 22:140–147
Casrouge A, Zhang SY et al (2006) Herpes simplex virus encephalitis in human UNC-93B deficiency. Science 314:308–312
Chao CC, Hu S et al (1992) Activated microglia mediate neuronal cell injury via a nitric oxide mechanism. J Immunol 149:2736–2741
Chapel H, Geha R et al (2003) Primary immunodeficiency diseases: an update. Clin Exp Immunol 132:9–15
Chapel H, Puel A et al (2005) Shigella sonnei meningitis due to interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-4 deficiency: first association with a primary immune deficiency. Clin Infect Dis 40:1227–1231
Chapgier A, Kong XF et al (2009) A partial form of recessive STAT1 deficiency in humans. J Clin Invest 119:1502–1514
Chin AC, Fournier B et al (2009) CD47 and TLR-2 cross-talk regulates neutrophil transmigration. J Immunol 183:5957–5963
Chuang TH, Ulevitch RJ (2000) Cloning and characterization of a sub-family of human Toll-like receptors: hTLR7, hTLR8 and hTLR9. Eur Cytokine Netw 11:372–378
Chuang T, Ulevitch RJ (2001) Identification of hTLR10: a novel human Toll-like receptor preferentially expressed in immune cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1518:157–161
Chung J, Gao AG et al (1997) Thrombospondin acts via integrin-associated protein to activate the platelet integrin alphaIIbbeta3. J Biol Chem 272:14740–14746
Clemente A, Pons J et al (2011) B cells from common variable immunodeficiency patients fail to differentiate to antibody secreting cells in response to TLR9 ligand (CpG-ODN) or anti-CD40+IL21. Cell Immunol 268:9–15
Comeau JL, Lin TJ et al (2008) Staphylococcal pericarditis, and liver and paratracheal abscesses as presentations in two new cases of interleukin-1 receptor associated kinase 4 deficiency. Pediatr Infect Dis J 27:170–174
Costa-Carvalho BT, Nudelman V et al (1998) Immune system and infections. J Pediatr 74(Suppl 1):S3–S11
Cunningham-Rundles C, Bodian C (1999) Common variable immunodeficiency: clinical and immunological features of 248 patients. Clin Immunol 92:34–48
Cunningham-Rundles C, Radigan L et al (2006) TLR9 activation is defective in common variable immune deficiency. J Immunol 176:1978–1987
Dasari P, Nicholson IC et al (2005) Expression of Toll-like receptors on B lymphocytes. Cell Immunol 236:140–145
Davidson DJ, Currie AJ et al (2006) IRAK-4 mutation (Q293X): rapid detection and characterization of defective post-transcriptional TLR/IL-1R responses in human myeloid and non-myeloid cells. J Immunol 177:8202–8211
De Tiege X, Rozenberg F et al (2008) The spectrum of herpes simplex encephalitis in children. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 12:72–81
Deering RP, Orange JS (2006) Development of a clinical assay to evaluate Toll-like receptor function. Clin Vaccine Immunol 13:68–76
Deininger S, Stadelmaier A et al (2003) Definition of structural prerequisites for lipoteichoic acid-inducible cytokine induction by synthetic derivatives. J Immunol 170:4134–4138
Demeure CE, Tanaka H et al (2000) CD47 engagement inhibits cytokine production and maturation of human dendritic cells. J Immunol 164:2193–2199
Dorahy DJ, Thorne RF et al (1997) Stimulation of platelet activation and aggregation by a carboxyl-terminal peptide from thrombospondin binding to the integrin-associated protein receptor. J Biol Chem 272:1323–1330
Doyle SL, O’Neill LA (2006) Toll-like receptors: from the discovery of NFkappaB to new insights into transcriptional regulations in innate immunity. Biochem Pharmacol 72:1102–1113
Doyle SL, Jefferies CA et al (2005) Bruton’s tyrosine kinase is involved in p65-mediated transactivation and phosphorylation of p65 on serine 536 during NFkappaB activation by lipopolysaccharide. J Biol Chem 280:23496–23501
Doyle SL, Jefferies CA et al (2007) Signaling by Toll-like receptors 8 and 9 requires Bruton’s tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem 282:36953–36960
Dupuis S, Jouanguy E et al (2003) Impaired response to interferon-alpha/beta and lethal viral disease in human STAT1 deficiency. Nat Genet 33:388–391
Dziarski R, Gupta D (2005) Staphylococcus aureus peptidoglycan is a Toll-like receptor 2 activator: a reevaluation. Infect Immun 73:5212–5216
Dziarski R, Gupta D (2006) The peptidoglycan recognition proteins (PGRPs). Genome Biol 7:232
Ear T, McDonald PP (2008) Cytokine generation, promoter activation, and oxidant-independent NF-kappaB activation in a transfectable human neutrophilic cellular model. BMC Immunol 9:14
Enoch T, Zinn K et al (1986) Activation of the human beta-interferon gene requires an interferon-inducible factor. Mol Cell Biol 6:801–810
Escobar D, Pons J et al (2010) Defective B cell response to TLR9 ligand (CpG-ODN), Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae extracts in common variable immunodeficiency patients. Cell Immunol 262:105–111
Ezekowitz RA, Sastry K et al (1990) Molecular characterization of the human macrophage mannose receptor: demonstration of multiple carbohydrate recognition-like domains and phagocytosis of yeasts in Cos-1 cells. J Exp Med 172:1785–1794
Farina C, Krumbholz M et al (2005) Preferential expression and function of Toll-like receptor 3 in human astrocytes. J Neuroimmunol 159:12–19
Fitzgerald KA, McWhirter SM et al (2003) IKKepsilon and TBK1 are essential components of the IRF3 signaling pathway. Nat Immunol 4:491–496
Galli SJ, Borregaard N et al (2011) Phenotypic and functional plasticity of cells of innate immunity: macrophages, mast cells and neutrophils. Nat Immunol 12:1035–1044
Gewirtz AT, Vijay-Kumar M et al (2006) Dominant-negative TLR5 polymorphism reduces adaptive immune response to flagellin and negatively associates with Crohn’s disease. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 290:G1157–G1163
Gordon S (2003) Alternative activation of macrophages. Nat Rev Immunol 3:23–35
Guirado M, Gil H et al (2012) Association between C13ORF31, NOD2, RIPK2 and TLR10 polymorphisms and urothelial bladder cancer. Hum Immunol 73:668–672
Guo Y, Audry M et al (2011) Herpes simplex virus encephalitis in a patient with complete TLR3 deficiency: TLR3 is otherwise redundant in protective immunity. J Exp Med 208:2083–2098
Hammarstrom L, Vorechovsky I et al (2000) Selective IgA deficiency (SIgAD) and common variable immunodeficiency (CVID). Clin Exp Immunol 120:225–231
Han X, Sterling H et al (2000) CD47, a ligand for the macrophage fusion receptor, participates in macrophage multinucleation. J Biol Chem 275:37984–37992
Hanisch UK, Kettenmann H (2007) Microglia: active sensor and versatile effector cells in the normal and pathologic brain. Nat Neurosci 10:1387–1394
Hansson GK, Edfeldt K (2005) Toll to be paid at the gateway to the vessel wall. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25:1085–1087
Harte M, Haga IR et al (2003) The poxvirus protein A52R targets Toll-like receptor signaling complexes to suppress host defense. J Exp Med 197:343–351
Hasan U, Chaffois C et al (2005) Human TLR10 is a functional receptor, expressed by B cells and plasmacytoid dendritic cells, which activates gene transcription through MyD88. J Immunol 174:2942–2950
Hashimoto S, Tsukada S et al (1996) Identification of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (Btk) gene mutations and characterization of the derived proteins in 35 X-linked agammaglobulinemia families: a nationwide study of Btk deficiency in Japan. Blood 88:561–573
Hashimoto M, Tawaratsumida K et al (2006a) Lipoprotein is a predominant Toll-like receptor 2 ligand in Staphylococcus aureus cell wall components. Int Immunol 18:355–362
Hashimoto M, Tawaratsumida K et al (2006b) Not lipoteichoic acid but lipoproteins appear to be the dominant immunobiologically active compounds in Staphylococcus aureus. J Immunol 177:3162–3169
Hashimoto M, Furuyashiki M et al (2007) Evidence of immunostimulating lipoprotein existing in the natural lipoteichoic acid fraction. Infect Immun 75:1926–1932
Hawn TR, Wu H et al (2005) A stop codon polymorphism of Toll-like receptor 5 is associated with resistance to systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:10593–10597
Hayashi F, Smith KD et al (2001) The innate immune response to bacterial flagellin is mediated by Toll-like receptor 5. Nature 410:1099–1103
Herman M, Ciancanelli M et al (2012) Heterozygous TBK1 mutations impair TLR3 immunity and underlie herpes simplex encephalitis of childhood. J Exp Med 209:1567–1582
Hermaszewski RA, Webster AD (1993) Primary hypogammaglobulinaemia: a survey of clinical manifestations and complications. Q J Med 86:31–42
Hickey MJ, Kubes P (2009) Intravascular immunity: the host-pathogen encounter in blood vessels. Nat Rev Immunol 9:364–375
Hochrein H, Schlatter B et al (2004) Herpes simplex virus type-1 induces IFN-alpha production via Toll-like receptor 9-dependent and -independent pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:11416–11421
Hoebe K, Georgel P et al (2005) CD36 is a sensor of diacylglycerides. Nature 433:523–527
Hornung V, Rothenfusser S et al (2002) Quantitative expression of Toll-like receptor 1-10 mRNA in cellular subsets of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells and sensitivity to CpG oligodeoxynucleotides. J Immunol 168:4531–4537
Ip WK, Takahashi K et al (2008) Mannose-binding lectin enhances Toll-like receptors 2 and 6 signaling from the phagosome. J Exp Med 205:169–181
Iwasaki A, Medzhitov R (2010) Regulation of adaptive immunity by the innate immune system. Science 327:291–295
Jack CS, Arbour N et al (2005) TLR signaling tailors innate immune responses in human microglia and astrocytes. J Immunol 175:4320–4330
Janeway CA Jr (1992) The immune system evolved to discriminate infectious nonself from noninfectious self. Immunol Today 13:11–16
Jefferies CA, Doyle S et al (2003) Bruton’s tyrosine kinase is a Toll/interleukin-1 receptor domain-binding protein that participates in nuclear factor kappaB activation by Toll-like receptor 4. J Biol Chem 278:26258–26264
Jimenez-Dalmaroni MJ, Xiao N et al (2009) Soluble CD36 ectodomain binds negatively charged diacylglycerol ligands and acts as a co-receptor for TLR2. PLoS ONE 4:e7411
Jin MS, Kim SE et al (2007) Crystal structure of the TLR1-TLR2 heterodimer induced by binding of a tri-acylated lipopeptide. Cell 130:1071–1082
Jouault T, Ibata-Ombetta S et al (2003) Candida albicans phospholipomannan is sensed through Toll-like receptors. J Infect Dis 188:165–172
Kang JY, Nan X et al (2009) Recognition of lipopeptide patterns by Toll-like receptor 2-Toll-like receptor 6 heterodimer. Immunity 31:873–884
Kawai T, Akira S (2007) Antiviral signaling through pattern recognition receptors. J Biochem 141:137–145
Khazen W, M’Bika JP et al (2005) Expression of macrophage-selective markers in human and rodent adipocytes. FEBS Lett 579:5631–5634
Kopp E, Medzhitov R (2003) Recognition of microbial infection by Toll-like receptors. Curr Opin Immunol 15:396–401
Kreutzberg GW (1996) Microglia: a sensor for pathological events in the CNS. Trends Neurosci 19:312–318
Krombach F, Munzing S et al (1997) Cell size of alveolar macrophages: an interspecies comparison. Environ Health Perspect 105(Suppl 5):1261–1263
Krutzik SR, Ochoa MT et al (2003) Activation and regulation of Toll-like receptors 2 and 1 in human leprosy. Nat Med 9:525–532
Ku CL, von Bernuth H et al (2007) Selective predisposition to bacterial infections in IRAK-4-deficient children: IRAK-4-dependent TLRs are otherwise redundant in protective immunity. J Exp Med 204:2407–2422
Ku JK, Kwon HJ et al (2008) Expression of Toll-like receptors in verruca and molluscum contagiosum. J Korean Med Sci 23:307–314
Kuhns DB, Long Priel DA et al (1997) Endotoxin and IL-1 hyporesponsiveness in a patient with recurrent bacterial infections. J Immunol 158:3959–3964
Lafaille FG, Pessach IM et al (2012) Impaired intrinsic immunity to HSV-1 in human iPSC-derived TLR3-deficient CNS cells. Nature 491:769–773
Laflamme N, Rivest S (2001) Toll-like receptor 4: the missing link of the cerebral innate immune response triggered by circulating Gram-negative bacterial cell wall components. FASEB J 15:155–163
Lai Y, Gallo RL (2008) Toll-like receptors in skin infections and inflammatory diseases. Infect Disord Drug Targets 8:144–155
Lehnardt S, Lachance C et al (2002) The toll-like receptor TLR4 is necessary for lipopolysaccharide-induced oligodendrocyte injury in the CNS. J Neurosci 22:2478–2486
Lemaitre B, Nicolas E et al (1996) The dorsoventral regulatory gene cassette spatzle/Toll/cactus controls the potent antifungal response in Drosophila adults. Cell 86:973–983
Lenardo MJ, Fan CM et al (1989) The involvement of NF-kappa B in beta-interferon gene regulation reveals its role as widely inducible mediator of signal transduction. Cell 57:287–294
Li Q, Cherayil BJ (2004) Toll-like receptor 4 mutation impairs the macrophage TNFalpha response to peptidoglycan. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 325:91–96
Lindberg FP, Bullard DC et al (1996) Decreased resistance to bacterial infection and granulocyte defects in IAP-deficient mice. Science 274:795–798
Liu Y, Merlin D et al (2001) The role of CD47 in neutrophil transmigration. Increased rate of migration correlates with increased cell surface expression of CD47. J Biol Chem 276:40156–40166
Lokensgard JR, Gekker G et al (1997) Proinflammatory cytokines inhibit HIV-1(SF162) expression in acutely infected human brain cell cultures. J Immunol 158:2449–2455
Maguire O, Collins C et al (2011) Quantifying nuclear p65 as a parameter for NF-kappaB activation: correlation between ImageStream cytometry, microscopy, and Western blot. Cytometry A 79:461–469
McKimmie CS, Fazakerley JK (2005) In response to pathogens, glial cells dynamically and differentially regulate Toll-like receptor gene expression. J Neuroimmunol 169:116–125
Medvedev AE, Lentschat A et al (2003) Distinct mutations in IRAK-4 confer hyporesponsiveness to lipopolysaccharide and interleukin-1 in a patient with recurrent bacterial infections. J Exp Med 198:521–531
Mempel M, Kalali BN et al (2007) Toll-like receptors in dermatology. Dermatol Clin 25:531–540, viii
Mizel SB, Honko AN et al (2003) Induction of macrophage nitric oxide production by Gram-negative flagellin involves signaling via heteromeric Toll-like receptor 5/Toll-like receptor 4 complexes. J Immunol 170:6217–6223
Moore ML, McKissic EL et al (2004) Fatal disseminated mouse adenovirus type 1 infection in mice lacking B cells or Bruton’s tyrosine kinase. J Virol 78:5584–5590
Morath S, Geyer A et al (2001) Structure-function relationship of cytokine induction by lipoteichoic acid from Staphylococcus aureus. J Exp Med 193:393–397
Morath S, Stadelmaier A et al (2002) Synthetic lipoteichoic acid from Staphylococcus aureus is a potent stimulus of cytokine release. J Exp Med 195:1635–1640
Moreira J, Aragao-Filho WC et al (2012) Human leucocytes response to viable, extended freeze-drying or heat-killed Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guerin. Scand J Immunol 75:96–101
Morgan AR, Lam WJ et al (2012) Genetic variation within TLR10 is associated with Crohn’s disease in a New Zealand population. Hum Immunol 73:416–420
Mulla MJ, Myrtolli K et al (2013) Cutting-edge report: TLR10 plays a role in mediating bacterial peptidoglycan-induced trophoblast apoptosis. Am J Reprod Immunol 69:449–453
Murray PJ, Wynn TA (2011) Protective and pathogenic functions of macrophage subsets. Nat Rev Immunol 11:723–737
Netea MG, van der Graaf C et al (2004) Toll-like receptors and the host defense against microbial pathogens: bringing specificity to the innate-immune system. J Leukoc Biol 75:749–755
Netea MG, Gow NA et al (2006) Immune sensing of Candida albicans requires cooperative recognition of mannans and glucans by lectin and Toll-like receptors. J Clin Invest 116:1642–1650
Oliveira RB, Ochoa MT et al (2003) Expression of Toll-like receptor 2 on human Schwann cells: a mechanism of nerve damage in leprosy. Infect Immun 71:1427–1433
O’Neill LA (2008) When signaling pathways collide: positive and negative regulation of Toll-like receptor signal transduction. Immunity 29:12–20
O’Neill LA, Bowie AG (2007) The family of five: TIR-domain-containing adaptors in Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol 7:353–364
O’Neill LA, Dinarello CA (2000) The IL-1 receptor/Toll-like receptor superfamily: crucial receptors for inflammation and host defense. Immunol Today 21:206–209
Oosting M, Ter Hofstede H et al (2011) TLR1/TLR2 heterodimers play an important role in the recognition of Borrelia spirochetes. PLoS ONE 6:e25998
Orange JS, Levy O et al (2004) Human nuclear factor kappa B essential modulator mutation can result in immunodeficiency without ectodermal dysplasia. J Allergy Clin Immunol 114:650–656
Orange JS, Levy O et al (2005) Human disease resulting from gene mutations that interfere with appropriate nuclear factor-kappaB activation. Immunol Rev 203:21–37
Park H, Wahl MI et al (1996) Regulation of Btk function by a major autophosphorylation site within the SH3 domain. Immunity 4:515–525
Park HJ, Hahn WH et al (2011) Association between Toll-like receptor 10 (TLR10) gene polymorphisms and childhood IgA nephropathy. Eur J Pediatr 170:503–509
Parkos CA, Colgan SP et al (1996) CD47 mediates post-adhesive events required for neutrophil migration across polarized intestinal epithelia. J Cell Biol 132:437–450
Perez de Diego R, Sancho-Shimizu V et al (2010) Human TRAF3 adaptor molecule deficiency leads to impaired Toll-like receptor 3 response and susceptibility to herpes simplex encephalitis. Immunity 33:400–411
Perry VH, Gordon S (1988) Macrophages and microglia in the nervous system. Trends Neurosci 11:273–277
Pettersen RD, Hestdal K et al (1999) CD47 signals T cell death. J Immunol 162:7031–7040
Picard C, Puel A et al (2003) Pyogenic bacterial infections in humans with IRAK-4 deficiency. Science 299:2076–2079
Picard C, von Bernuth H et al (2010) Clinical features and outcome of patients with IRAK-4 and MyD88 deficiency. Medicine 89:403–425
Picard C, Casanova JL et al (2011) Infectious diseases in patients with IRAK-4, MyD88, NEMO, or IkappaBalpha deficiency. Clin Microbiol Rev 24:490–497
Poltorak A, He X et al (1998) Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: mutations in Tlr4 gene. Science 282:2085–2088
Requena T, Gazquez I et al (2013) Allelic variants in TLR10 gene may influence bilateral affectation and clinical course of Meniere’s disease. Immunogenetics 65:345–355
Rivieccio MA, John GR et al (2005) The cytokine IL-1beta activates IFN response factor 3 in human fetal astrocytes in culture. J Immunol 174:3719–3726
Rivieccio MA, Suh HS et al (2006) TLR3 ligation activates an antiviral response in human fetal astrocytes: a role for viperin/cig5. J Immunol 177:4735–4741
Rock FL, Hardiman G et al (1998) A family of human receptors structurally related to Drosophila Toll. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:588–593
Ruckdeschel K, Mannel O et al (2001) Yersinia outer protein P of Yersinia enterocolitica simultaneously blocks the nuclear factor-kappa B pathway and exploits lipopolysaccharide signaling to trigger apoptosis in macrophages. J Immunol 166:1823–1831
Ryser O, Morell A et al (1988) Primary immunodeficiencies in Switzerland: first report of the national registry in adults and children. J Clin Immunol 8:479–485
Salio M, Cerundolo V (2005) Viral immunity: cross-priming with the help of TLR3. Curr Biol 15:R336–R339
Sancho-Shimizu V, Perez de Diego R et al (2011) Herpes simplex encephalitis in children with autosomal recessive and dominant TRIF deficiency. J Clin Invest 121:4889–4902
Sato A, Linehan MM et al (2006) Dual recognition of herpes simplex viruses by TLR2 and TLR9 in dendritic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:17343–17348
Schlaepfer E, Audige A et al (2006) TLR7/8 triggering exerts opposing effects in acute versus latent HIV infection. J Immunol 176:2888–2895
Schmitz ML, Bacher S et al (2001) I kappa B-independent control of NF-kappa B activity by modulatory phosphorylations. Trends Biochem Sci 26:186–190
Schroder NW, Morath S et al (2003) Lipoteichoic acid (LTA) of Streptococcus pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus activates immune cells via Toll-like receptor (TLR)-2, lipopolysaccharide-binding protein (LBP), and CD14, whereas TLR-4 and MD-2 are not involved. J Biol Chem 278:15587–15594
Schwartz M, Butovsky O et al (2006) Microglial phenotype: is the commitment reversible? Trends Neurosci 29:68–74
Segal AW (2005) How neutrophils kill microbes. Annu Rev Immunol 23:197–223
Seo HS, Michalek SM et al (2008) Lipoteichoic acid is important in innate immune responses to Gram-positive bacteria. Infect Immun 76:206–213
Seya T, Akazawa T et al (2003) Role of Toll-like receptors and their adaptors in adjuvant immunotherapy for cancer. Anticancer Res 23:4369–4376
Seya T, Akazawa T et al (2006) Role of Toll-like receptors in adjuvant-augmented immune therapies. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 3:31–38 discussion 133–137
Sharma S, ten Oever BR et al (2003) Triggering the interferon antiviral response through an IKK-related pathway. Science 300:1148–1151
Shearer WT, Paul ME et al (1994) Laboratory assessment of immunodeficiency disorders. Immunol Allergy Clin 14:265–297
Si Q, Zhao ML et al (2004) 15-deoxy-Delta12,14-prostaglandin J2 inhibits IFN-inducible protein 10/CXC chemokine ligand 10 expression in human microglia: mechanisms and implications. J Immunol 173:3504–3513
Sing A, Rost D et al (2002) Yersinia V-antigen exploits Toll-like receptor 2 and CD14 for interleukin 10-mediated immunosuppression. J Exp Med 196:1017–1024
Sivula J, Cordova ZM et al (2012) Toll-like receptor gene polymorphisms confer susceptibility to graft-versus-host disease in allogenic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Scand J Immunol 76:336–341
Stevens VL, Hsing AW et al (2008) Genetic variation in the Toll-like receptor gene cluster (TLR10-TLR1-TLR6) and prostate cancer risk. Int J Cancer 123:2644–2650
Streit WJ, Conde JR et al (2005) Role of microglia in the central nervous system’s immune response. Neurol Res 27:685–691
Stuart LM, Deng J et al (2005) Response to Staphylococcus aureus requires CD36-mediated phagocytosis triggered by the COOH-terminal cytoplasmic domain. J Cell Biol 170:477–485
Suh HS, Zhao ML et al (2007) Astrocyte indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase is induced by the TLR3 ligand poly(I:C): mechanism of induction and role in antiviral response. J Virol 81:9838–9850
Suzuki N, Suzuki S et al (2002) Severe impairment of interleukin-1 and Toll-like receptor signalling in mice lacking IRAK-4. Nature 416:750–756
Szabo J, Dobay O et al (2007) Recurrent infection with genetically identical pneumococcal isolates in a patient with interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-4 deficiency. J Med Microbiol 56(Pt 6):863–865
Tada H, Nemoto E et al (2002) Saccharomyces cerevisiae- and Candida albicans-derived mannan induced production of tumor necrosis factor alpha by human monocytes in a CD14- and Toll-like receptor 4-dependent manner. Microbiol Immunol 46:503–512
Takeuchi O, Hoshino K et al (2000) Cutting edge: TLR2-deficient and MyD88-deficient mice are highly susceptible to Staphylococcus aureus infection. J Immunol 165:5392–5396
Town T, Jeng D et al (2006) Microglia recognize double-stranded RNA via TLR3. J Immunol 176:3804–3812
Travassos LH, Girardin SE et al (2004) Toll-like receptor 2-dependent bacterial sensing does not occur via peptidoglycan recognition. EMBO Rep 5:1000–1006
Veltkamp M, van Moorsel CH et al (2012) Genetic variation in the Toll-like receptor gene cluster (TLR10-TLR1-TLR6) influences disease course in sarcoidosis. Tissue Antigens 79:25–32
Vijayan V, Baumgart-Vogt E et al (2011) Bruton’s tyrosine kinase is required for TLR-dependent heme oxygenase-1 gene activation via Nrf2 in macrophages. J Immunol 187:817–827
von Aulock S, Hartung T et al (2007) Comment on “Not lipoteichoic acid but lipoproteins appear to be the dominant immunobiologically active compounds in Staphylococcus aureus”. J Immunol 178:2610
von Bernuth H, Ku CL et al (2006) A fast procedure for the detection of defects in Toll-like receptor signaling. Pediatrics 118:2498–2503
von Bernuth H, Picard C et al (2008) Pyogenic bacterial infections in humans with MyD88 deficiency. Science 321:691–696
Wang J, Fei B et al (2010) Quantitative analysis of protein translocations by microfluidic total internal reflection fluorescence flow cytometry. Lab Chip 10:2673–2679
Weih F, Warr G et al (1997) Multifocal defects in immune responses in RelB-deficient mice. J Immunol 158:5211–5218
WHO (1997) Primary immunodeficiency diseases. Report of a WHO scientific group. Clin Exp Immunol 109(Suppl 1):1–28
Winkelstein JA, Marino MC et al (2006) X-linked agammaglobulinemia: report on a United States registry of 201 patients. Medicine 85:193–202
Wlasiuk G, Khan S et al (2009) A history of recurrent positive selection at the Toll-like receptor 5 in primates. Mol Biol Evol 26:937–949
Xu N, Yao HP et al (2012) Downregulation of TLR7/9 leads to deficient production of IFN-alpha from plasmacytoid dendritic cells in chronic hepatitis B. Inflamm Res 61:997–1004
Yang M, Gan H et al (2012) Effect of LPS on the level of TLR4 and on the expression of NF-kappaB and Notch1 in monocytes from patients with type 2 diabetic nephropathy. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 37:578–585
Zemskov AM, Zemskov VM et al (2005) Problem of specific and nonspecific factors in the induction and regulation of immunological reactions. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol 4:105–109
Zhang SY, Jouanguy E et al (2007) TLR3 deficiency in patients with herpes simplex encephalitis. Science 317:1522–1527
Zheng W, Zheng X et al (2012) TNFalpha and IL-1beta are mediated by both TLR4 and Nod1 pathways in the cultured HAPI cells stimulated by LPS. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 420:762–767
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Frazão, J.B., Errante, P.R. & Condino-Neto, A. Toll-Like Receptors’ Pathway Disturbances are Associated with Increased Susceptibility to Infections in Humans. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 61, 427–443 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00005-013-0243-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00005-013-0243-0