Abstract
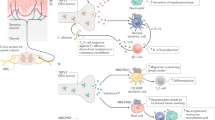
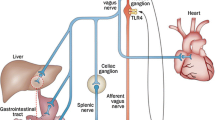
The nervous system regulates immune function and inflammation. Experimental evidence shows an important role of the autonomic nervous system in the bidirectional communication between the brain and the immune system, underlying the ability of the brain to monitor immune status and control inflammation. Here we review the involvement of the autonomic nervous system in regulating inflammation, with a focus on the vagus nerve. The clinical implications of the recently discovered anti-inflammatory role of the efferent vagus nerve are also discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 8 March 2004; received after revision 26 April 2004; accepted 29 April 2004
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pavlov, V.A., Tracey, K.J. Neural regulators of innate immune responses and inflammation. CMLS, Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 61, 2322–2331 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-004-4102-3
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-004-4102-3