Abstract.
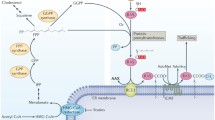
Isoprenoids are synthesized in all living organisms and are incorporated into diverse classes of end-products that participate in a multitude of cellular processes relating to cell growth, differentiation, cytoskeletal function and vesicle trafficking. In humans, the non-sterol isoprenoids, farnesyl pyrophosphate and geranylgeranyl-pyrophosphate, are synthesized via the mevalonate pathway and are covalently added to members of the small G protein superfamily. Isoprenylated proteins have key roles in membrane attachment and protein functionality, have been shown to have a central role in some cancers and are likely also to be involved in the pathogenesis and progression of atherosclerosis and Alzheimer disease. This review details current knowledge on the biosynthesis of isoprenoids, their incorporation into proteins by the process known as prenylation and the complex regulatory network that controls these proteins. An improved understanding of these processe is likely to lead to the development of novel therapies that will have important implications for human health and disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 5 July 2005; received after revision 17 October 2005; accepted 22 October 2005
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McTaggart, S.J. Isoprenylated proteins. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 63, 255–267 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-005-5298-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-005-5298-6