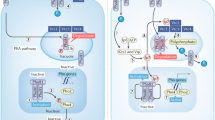
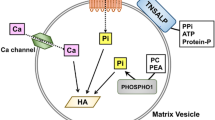
Abstract
Although considerable advances in our understanding of the mechanisms of phosphate homeostasis and skeleton mineralization have recently been made, little is known about the initial events involving the detection of changes in the phosphate serum concentrations and the subsequent downstream regulation cascade. Recent data has strengthened a long-established hypothesis that a phosphate-sensing mechanism may be present in various organs. Such a phosphate sensor would detect changes in serum or local phosphate concentration and would inform the body, the local environment, or the individual cell. This suggests that phosphate in itself could represent a signal regulating multiple factors necessary for diverse biological processes such as bone or vascular calcification. This review summarizes findings supporting the possibility that phosphate represents a signaling molecule, particularly in bone and cartilage, but also in other tissues. The involvement of various signaling pathways (ERK1/2), transcription factors (Fra-1, Runx2) and phosphate transporters (PiT1, PiT2) is discussed.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 1α,25(OH)2D3 :
-
1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D
- ALP:
-
Alkaline phosphatase
- Pi:
-
Inorganic phosphate
- IGF-1:
-
Insulin growth factor-1
- ESRD:
-
End-stage renal disease
- FGF-23:
-
Fibroblast growth factor 23
- HSMC:
-
Human aortic smooth muscle cell
- MGP:
-
Matrix gla protein
- PTH:
-
Parathyroid hormone
- PFA:
-
Phosphonoformic acid
- RANKL:
-
Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) (RANK) ligand
- VSMC:
-
Vascular smooth muscle cell
References
Hansen NM, Felix R, Bisaz S, Fleisch H (1976) Aggregation of hydroxyapatite crystals. Biochim Biophys Acta 451:549–559
Crook M, Swaminathan R (1996) Disorders of plasma phosphate and indications for its measurement. Ann Clin Biochem 33(Pt 5):376–396
Kornberg A (1979) The enzymatic replication of DNA. CRC Crit Rev Biochem 7:23–43
Rothfield L, Finkelstein A (1968) Membrane biochemistry. Annu Rev Biochem 37:463–496
Lehninger AL, Wadkins CL (1962) Oxidative phosphorylation. Annu Rev Biochem 31:47–78
Hubbard SR, Till JH (2000) Protein tyrosine kinase structure and function. Annu Rev Biochem 69:373–398
Krebs EG, Beavo JA (1979) Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation of enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem 48:923–959
Stock AM, Robinson VL, Goudreau PN (2000) Two-component signal transduction. Annu Rev Biochem 69:183–215
Fruman DA, Meyers RE, Cantley LC (1998) Phosphoinositide kinases. Annu Rev Biochem 67:481–507
Bessman SP, Carpenter CL (1985) The creatine–creatine phosphate energy shuttle. Annu Rev Biochem 54:831–862
Prié D, Beck L, Friedlander G, Silve C (2004) Sodium-phosphate cotransporters, nephrolithiasis and bone demineralization. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 13:675–681
Knochel JP, Barcenas C, Cotton JR, Fuller TJ, Haller R, Carter NW (1978) Hypophosphatemia and rhabdomyolysis. J Clin Invest 62:1240–1246
Knochel JP (1977) The pathophysiology and clinical characteristics of severe hypophosphatemia. Arch Intern Med 137:203–220
Berndt T, Kumar R (2009) Novel mechanisms in the regulation of phosphorus homeostasis. Physiology (Bethesda) 24:17–25
Hruska K, Slatopolsky E (1997) Disorders of phosphorus, calcium, and magnesium metabolism. In: Schrier R, Gottschalk C (eds) Diseases of the kidney. Little and Brown, Boston
Rutecki GW, Cugino A, Jarjoura D, Kilner JF, Whittier FC (1997) Nephrologists’ subjective attitudes towards end-of-life issues and the conduct of terminal care. Clin Nephrol 48:173–180
Weisinger JR, Bellorin-Font E (1998) Magnesium and phosphorus. Lancet 352:391–396
Shiber JR, Mattu A (2002) Serum phosphate abnormalities in the emergency department. J Emerg Med 23:395–400
Hruska KA, Mathew S, Lund RJ, Memon I, Saab G (2009) The pathogenesis of vascular calcification in the chronic kidney disease mineral bone disorder: the links between bone and the vasculature. Semin Nephrol 29:156–165
Kanbay M, Goldsmith D, Akcay A, Covic A (2009) Phosphate - the silent stealthy cardiorenal culprit in all stages of chronic kidney disease: a systematic review. Blood Purif 27:220–230
Hruska KA, Mathew S, Lund R, Qiu P, Pratt R (2008) Hyperphosphatemia of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 74:148–157
Pettifor JM (2008) What’s new in hypophosphataemic rickets? Eur J Pediatr 167:493–499
Murer H, Hernando N, Forster I, Biber J (2000) Proximal tubular phosphate reabsorption: molecular mechanisms. Physiol Rev 80:1373–1409
Tanaka Y, Deluca HF (1973) The control of 25-hydroxyvitamin D metabolism by inorganic phosphorus. Arch Biochem Biophys 154:566–574
DeLuca HF (2004) Overview of general physiologic features and functions of vitamin D. Am J Clin Nutr 80:1689S–1696S
Berndt TJ, Schiavi S, Kumar R (2005) “Phosphatonins” and the regulation of phosphorus homeostasis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 289:F1170–F1182
Berndt T, Knox F (1992) Renal regulation of phosphate excretion. In: Seldin D, Giebish G (eds) The kidney: physiology and pathophysiology. Raven Press, New York, pp 2511–2532
Chase LR, Aurbach GD (1967) Parathyroid function and the renal excretion of 3’5’-adenylic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 58:518–525
Muff R, Fischer JA, Biber J, Murer H (1992) Parathyroid hormone receptors in control of proximal tubule function. Annu Rev Physiol 54:67–79
Kiela PR, Ghishan FK (2009) Recent advances in the renal-skeletal-gut axis that controls phosphate homeostasis. Lab Invest 89:7–14
Strom TM, Jüppner H (2008) PHEX, FGF23, DMP1 and beyond. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 17:357–362
Johnston J, Ramos-Valdes Y, Stanton LA, Ladhani S, Beier F, Dimattia GE (2010) Human stanniocalcin-1 or -2 expressed in mice reduces bone size and severely inhibits cranial intramembranous bone growth. Transgenic Res. doi:10.1007/s11248-010-9376-7
Jüppner H (2007) Novel regulators of phosphate homeostasis and bone metabolism. Therapeutic apheresis and dialysis: official peer-reviewed journal of the International Society for Apheresis, the Japanese Society for Apheresis. Jpn Soc Dial Ther 11(Suppl 1):S3–S22
Shaikh A, Berndt T, Kumar R (2008) Regulation of phosphate homeostasis by the phosphatonins and other novel mediators. Pediatr Nephrol 23:1203–1210
Renkema K, Alexander RT, Bindels R, Hoenderop J (2008) Calcium and phosphate homeostasis: concerted interplay of new regulators. Ann Med 40:82–91
Prie D, Friedlander G (2010) Genetic disorders of renal phosphate transport. N Engl J Med 362:2399–2409
Werner A, Kinne RK (2001) Evolution of the Na-P(i) cotransport systems. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 280:R301–R312
Beck L, Silve C (2001) Molecular aspects of phosphate homeostasis in mammals. Nephrologie 22:149–159
Prie D, Urena Torres P, Friedlander G (2009) Latest findings in phosphate homeostasis. Kidney Int 75:882–889
Singer SJ (1990) The structure and insertion of integral proteins in membranes. Annu Rev Cell Biol 6:247–296
Chou KC, Elrod DW (1999) Prediction of membrane protein types and subcellular locations. Proteins 34:137–153
Chou KC, Cai YD (2005) Using GO-PseAA predictor to identify membrane proteins and their types. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 327:845–847
Werner A, Moore ML, Mantei N, Biber J, Semenza G, Murer H (1991) Cloning and expression of cDNA for a Na/Pi cotransport system of kidney cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:9608–9612
Busch AE, Schuster A, Waldegger S, Wagner CA, Zempel G, Broer S, Biber J, Murer H, Lang F (1996) Expression of a renal type I sodium/phosphate transporter (NaPi-1) induces a conductance in Xenopus oocytes permeable for organic and inorganic anions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:5347–5351
Yabuuchi H, Tamai I, Morita K, Kouda T, Miyamoto K, Takeda E, Tsuji A (1998) Hepatic sinusoidal membrane transport of anionic drugs mediated by anion transporter Npt1. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 286:1391–1396
Uchino H, Tamai I, Yamashita K, Minemoto Y, Sai Y, Yabuuchi H, Miyamoto K, Takeda E, Tsuji A (2000) p-aminohippuric acid transport at renal apical membrane mediated by human inorganic phosphate transporter NPT1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 270:254–259
Uchino H, Tamai I, Yabuuchi H, China K, Miyamoto K, Takeda E, Tsuji A (2000) Faropenem transport across the renal epithelial luminal membrane via inorganic phosphate transporter Npt1. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 44:574–577
Cheret C, Doyen A, Yaniv M, Pontoglio M (2002) Hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 alpha controls renal expression of the Npt1–Npt4 anionic transporter locus. J Mol Biol 322:929–941
Reimer RJ, Edwards RH (2004) Organic anion transport is the primary function of the SLC17/type I phosphate transporter family. Pflugers Arch 447:629–635
Urano W, Taniguchi A, Anzai N, Inoue E, Kanai Y, Yamanaka M, Endou H, Kamatani N, Yamanaka H (2010) Sodium-dependent phosphate cotransporter type 1 sequence polymorphisms in male patients with gout. Ann Rheum Dis 69:1232–1234
Murer H, Hernando N, Forster I, Biber J (2003) Regulation of Na/Pi transporter in the proximal tubule. Annu Rev Physiol 65:531–542
Beck L, Karaplis AC, Amizuka N, Hewson AS, Ozawa H, Tenenhouse HS (1998) Targeted inactivation of Npt2 in mice leads to severe renal phosphate wasting, hypercalciuria, and skeletal abnormalities. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:5372–5377
Hilfiker H, Hattenhauer O, Traebert M, Forster I, Murer H, Biber J (1998) Characterization of a murine type II sodium-phosphate cotransporter expressed in mammalian small intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:14564–14569
Sabbagh Y, O’Brien SP, Song W, Boulanger JH, Stockmann A, Arbeeny C, Schiavi SC (2009) Intestinal npt2b plays a major role in phosphate absorption and homeostasis. J Am Soc Nephrol 20:2348–2358
Segawa H, Onitsuka A, Furutani J, Kaneko I, Aranami F, Matsumoto N, Tomoe Y, Kuwahata M, Ito M, Matsumoto M, Li M, Amizuka N, Miyamoto K (2009) Npt2a and Npt2c in mice play distinct and synergistic roles in inorganic phosphate metabolism and skeletal development. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 297:F671–F678
Segawa H, Kaneko I, Takahashi A, Kuwahata M, Ito M, Ohkido I, Tatsumi S, Miyamoto K (2002) Growth-related renal type II Na/Pi cotransporter. J Biol Chem 277:19665–19672
Segawa H, Onitsuka A, Kuwahata M, Hanabusa E, Furutani J, Kaneko I, Tomoe Y, Aranami F, Matsumoto N, Ito M, Matsumoto M, Li M, Amizuka N, Miyamoto K (2009) Type IIc sodium-dependent phosphate transporter regulates calcium metabolism. J Am Soc Nephrol 20:104–113
Collins JF, Bai L, Ghishan FK (2004) The SLC20 family of proteins: dual functions as sodium-phosphate cotransporters and viral receptors. Pflugers Arch 447:647–652
Miller DG, Edwards RH, Miller AD (1994) Cloning of the cellular receptor for amphotropic murine retroviruses reveals homology to that for gibbon ape leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:78–82
Miller DG, Miller AD (1994) A family of retroviruses that utilize related phosphate transporters for cell entry. J Virol 68:8270–8276
Kavanaugh MP, Miller DG, Zhang W, Law W, Kozak SL, Kabat D, Miller AD (1994) Cell-surface receptors for gibbon ape leukemia virus and amphotropic murine retrovirus are inducible sodium-dependent phosphate symporters. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:7071–7075
Virkki LV, Biber J, Murer H, Forster IC (2007) Phosphate transporters: a tale of two solute carrier families. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 293:F643–F654
Giachelli CM (2009) The emerging role of phosphate in vascular calcification. Kidney Int 75:890–897
Li X, Giachelli CM (2007) Sodium-dependent phosphate cotransporters and vascular calcification. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 16:325–328
Yoshiko Y, Candeliere GA, Maeda N, Aubin JE (2007) Osteoblast autonomous Pi regulation via Pit1 plays a role in bone mineralization. Mol Cell Biol 27:4465–4474
Villa-Bellosta R, Ravera S, Sorribas V, Stange G, Levi M, Murer H, Biber J, Forster IC (2009) The Na+-Pi cotransporter PiT-2 (SLC20A2) is expressed in the apical membrane of rat renal proximal tubules and regulated by dietary Pi. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 296:F691–F699
Bellows CG, Heersche JN, Aubin JE (1992) Inorganic phosphate added exogenously or released from beta-glycerophosphate initiates mineralization of osteoid nodules in vitro. Bone Miner 17:15–29
Kumar R, Riggs B (1980) Pathologic bone physiology. In: Urist M (ed) Fundamental and clinical bone physiology. Lippincott, Philadelphia, pp 394–406
Conrads K, Yi M, Simpson K, Lucas D, Camalier C, Yu L, Veenstra T, Stephens R, Conrads T, Beck G (2005) A combined proteome and microarray investigation of inorganic phosphate-induced pre-osteoblast cells. Mol Cell Proteomics 4:1284–1296
Naviglio S, Spina A, Chiosi E, Fusco A, Illiano F, Pagano M, Romano M, Senatore G, Sorrentino A, Sorvillo L, Illiano G (2006) Inorganic phosphate inhibits growth of human osteosarcoma U2OS cells via adenylate cyclase/cAMP pathway. J Cell Biochem 98:1584–1596
Quarles LD, Yohay DA, Lever LW, Caton R, Wenstrup RJ (1992) Distinct proliferative and differentiated stages of murine MC3T3-E1 cells in culture: an in vitro model of osteoblast development. J Bone Miner Res 7:683–692
Conrads K, Yu L, Lucas D, Zhou M, Chan K, Simpson K, Schaefer C, Issaq H, Veenstra T, Beck G, Conrads T (2004) Quantitative proteomic analysis of inorganic phosphate-induced murine MC3T3-E1 osteoblast cells. Electrophoresis 25:1342–1352
Beck G, Moran E, Knecht N (2003) Inorganic phosphate regulates multiple genes during osteoblast differentiation, including Nrf2. Exp Cell Res 288:288–300
Kanatani M, Sugimoto T, Kano J, Chihara K (2002) IGF-I mediates the stimulatory effect of high phosphate concentration on osteoblastic cell proliferation. J Cell Physiol 190:306–312
Baylink DJ, Finkelman RD, Mohan S (1993) Growth factors to stimulate bone formation. J Bone Miner Res 8(Suppl 2):S565–S572
Sugimoto T, Kanatani M, Kano J, Kobayashi T, Yamaguchi T, Fukase M, Chihara K (1994) IGF-I mediates the stimulatory effect of high calcium concentration on osteoblastic cell proliferation. Am J Physiol 266:E709–E716
Schmid C, Keller C, Schlapfer I, Veldman C, Zapf J (1998) Calcium and insulin-like growth factor I stimulation of sodium-dependent phosphate transport and proliferation of cultured rat osteoblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 245:220–225
Beck GR Jr, Sullivan EC, Moran E, Zerler B (1998) Relationship between alkaline phosphatase levels, osteopontin expression, and mineralization in differentiating MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts. J Cell Biochem 68:269–280
Beck G, Zerler B, Moran E (2000) Phosphate is a specific signal for induction of osteopontin gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:8352–8357
Adams CS, Mansfield K, Perlot RL, Shapiro IM (2001) Matrix regulation of skeletal cell apoptosis. Role of calcium and phosphate ions. J Biol Chem 276:20316–20322
Meleti Z, Shapiro IM, Adams CS (2000) Inorganic phosphate induces apoptosis of osteoblast-like cells in culture. Bone 27:359–366
Wittrant Y, Bourgine A, Khoshniat S, Alliot-Licht B, Masson M, Gatius M, Rouillon T, Weiss P, Beck L, Guicheux J (2009) Inorganic phosphate regulates Glvr-1 and -2 expression: role of calcium and ERK1/2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 381:259–263
Julien M, Khoshniat S, Lacreusette A, Gatius M, Bozec A, Wagner EF, Wittrant Y, Masson M, Weiss P, Beck L, Magne D, Guicheux J (2009) Phosphate-dependent regulation of MGP in osteoblasts: role of ERK1/2 and Fra-1. J Bone Miner Res 24:1856–1868
Teitelbaum SL (2000) Bone resorption by osteoclasts. Science 289:1504–1508
Anderson DM, Maraskovsky E, Billingsley WL, Dougall WC, Tometsko ME, Roux ER, Teepe MC, DuBose RF, Cosman D, Galibert L (1997) A homologue of the TNF receptor and its ligand enhance T-cell growth and dendritic-cell function. Nature 390:175–179
Lacey DL, Timms E, Tan HL, Kelley MJ, Dunstan CR, Burgess T, Elliott R, Colombero A, Elliott G, Scully S, Hsu H, Sullivan J, Hawkins N, Davy E, Capparelli C, Eli A, Qian YX, Kaufman S, Sarosi I, Shalhoub V, Senaldi G, Guo J, Delaney J, Boyle WJ (1998) Osteoprotegerin ligand is a cytokine that regulates osteoclast differentiation and activation. Cell 93:165–176
Wong BR, Rho J, Arron J, Robinson E, Orlinick J, Chao M, Kalachikov S, Cayani E, Bartlett FS 3rd, Frankel WN, Lee SY, Choi Y (1997) TRANCE is a novel ligand of the tumor necrosis factor receptor family that activates c-Jun N-terminal kinase in T cells. J Biol Chem 272:25190–25194
Yasuda H, Shima N, Nakagawa N, Yamaguchi K, Kinosaki M, Mochizuki S, Tomoyasu A, Yano K, Goto M, Murakami A, Tsuda E, Morinaga T, Higashio K, Udagawa N, Takahashi N, Suda T (1998) Osteoclast differentiation factor is a ligand for osteoprotegerin/osteoclastogenesis-inhibitory factor and is identical to TRANCE/RANKL. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:3597–3602
Simonet WS, Lacey DL, Dunstan CR, Kelley M, Chang MS, Luthy R, Nguyen HQ, Wooden S, Bennett L, Boone T, Shimamoto G, DeRose M, Elliott R, Colombero A, Tan HL, Trail G, Sullivan J, Davy E, Bucay N, Renshaw-Gegg L, Hughes TM, Hill D, Pattison W, Campbell P, Sander S, Van G, Tarpley J, Derby P, Lee R, Boyle WJ (1997) Osteoprotegerin: a novel secreted protein involved in the regulation of bone density. Cell 89:309–319
Baylink D, Wergedal J, Stauffer M (1971) Formation, mineralization, and resorption of bone in hypophosphatemic rats. J Clin Invest 50:2519–2530
Bruin WJ, Baylink DJ, Wergedal JE (1975) Acute inhibition of mineralization and stimulation of bone resorption mediated by hypophosphatemia. Endocrinology 96:394–399
Thompson ER, Baylink DJ, Wergedal JE (1975) Increases in number and size of osteoclasts in response to calcium or phosphorus deficiency in the rat. Endocrinology 97:283–289
Yates AJ, Oreffo RO, Mayor K, Mundy GR (1991) Inhibition of bone resorption by inorganic phosphate is mediated by both reduced osteoclast formation and decreased activity of mature osteoclasts. J Bone Miner Res 6:473–478
Kanatani M, Sugimoto T, Kano J, Kanzawa M, Chihara K (2003) Effect of high phosphate concentration on osteoclast differentiation as well as bone-resorbing activity. J Cell Physiol 196:180–189
Mozar A, Haren N, Chasseraud M, Louvet L, Maziere C, Wattel A, Mentaverri R, Morliere P, Kamel S, Brazier M, Maziere JC, Massy ZA (2008) High extracellular inorganic phosphate concentration inhibits RANK–RANKL signaling in osteoclast-like cells. J Cell Physiol 215:47–54
Bingham PJ, Raisz LG (1974) Bone growth in organ culture: effects of phosphate and other nutrients on bone and cartilage. Calcif Tissue Res 14:31–48
Kakuta S, Golub EE, Shapiro IM (1985) Morphochemical analysis of phosphorus pools in calcifying cartilage. Calcif Tissue Int 37:293–299
Wang D, Canaff L, Davidson D, Corluka A, Liu H, Hendy GN, Henderson JE (2001) Alterations in the sensing and transport of phosphate and calcium by differentiating chondrocytes. J Biol Chem 276:33995–34005
Fujita T, Meguro T, Izumo N, Yasutomi C, Fukuyama R, Nakamuta H, Koida M (2001) Phosphate stimulates differentiation and mineralization of the chondroprogenitor clone ATDC5. Jpn J Pharmacol 85:278–281
Magne D, Bluteau G, Faucheux C, Palmer G, Vignes-Colombeix C, Pilet P, Rouillon T, Caverzasio J, Weiss P, Daculsi G, Guicheux J (2003) Phosphate is a specific signal for ATDC5 chondrocyte maturation and apoptosis-associated mineralization: possible implication of apoptosis in the regulation of endochondral ossification. J Bone Miner Res 18:1430–1442
Cecil DL, Rose DM, Terkeltaub R, Liu-Bryan R (2005) Role of interleukin-8 in PiT-1 expression and CXCR1-mediated inorganic phosphate uptake in chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum 52:144–154
Magne D, Julien M, Vinatier C, Merhi-Soussi F, Weiss P, Guicheux J (2005) Cartilage formation in growth plate and arteries: from physiology to pathology. Bioessays 27:708–716
Anderson HC (2003) Matrix vesicles and calcification. Curr Rheumatol Rep 5:222–226
Alini M, Carey D, Hirata S, Grynpas MD, Pidoux I, Poole AR (1994) Cellular and matrix changes before and at the time of calcification in the growth plate studied in vitro: arrest of type X collagen synthesis and net loss of collagen when calcification is initiated. J Bone Miner Res 9:1077–1087
Mansfield K, Rajpurohit R, Shapiro IM (1999) Extracellular phosphate ions cause apoptosis of terminally differentiated epiphyseal chondrocytes. J Cell Physiol 179:276–286
Mansfield K, Teixeira CC, Adams CS, Shapiro IM (2001) Phosphate ions mediate chondrocyte apoptosis through a plasma membrane transporter mechanism. Bone 28:1–8
Teixeira CC, Mansfield K, Hertkorn C, Ischiropoulos H, Shapiro IM (2001) Phosphate-induced chondrocyte apoptosis is linked to nitric oxide generation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 281:C833–C839
Sabbagh Y, Carpenter TO, Demay MB (2005) Hypophosphatemia leads to rickets by impairing caspase-mediated apoptosis of hypertrophic chondrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:9637–9642
Mansfield K, Pucci B, Adams CS, Shapiro IM (2003) Induction of apoptosis in skeletal tissues: phosphate-mediated chick chondrocyte apoptosis is calcium dependent. Calcif Tissue Int 73:161–172
Jono S, McKee MD, Murry CE, Shioi A, Nishizawa Y, Mori K, Morii H, Giachelli CM (2000) Phosphate regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell calcification. Circ Res 87:E10–E17
Giachelli CM, Jono S, Shioi A, Nishizawa Y, Mori K, Morii H (2001) Vascular calcification and inorganic phosphate. Am J Kidney Dis 38:S34–S37
Li X, Yang HY, Giachelli CM (2006) Role of the sodium-dependent phosphate cotransporter, Pit-1, in vascular smooth muscle cell calcification. Circ Res 98:905–912
Kido S, Miyamoto K, Mizobuchi H, Taketani Y, Ohkido I, Ogawa N, Kaneko Y, Harashima S, Takeda E (1999) Identification of regulatory sequences and binding proteins in the type II sodium/phosphate cotransporter NPT2 gene responsive to dietary phosphate. J Biol Chem 274:28256–28263
Biber J, Forgo J, Murer H (1988) Modulation of Na + -Pi cotransport in opossum kidney cells by extracellular phosphate. Am J Physiol 255:C155–C161
Jin H, Hwang SK, Yu K, Anderson HK, Lee YS, Lee KH, Prats AC, Morello D, Beck GR Jr, Cho MH (2006) A high inorganic phosphate diet perturbs brain growth, alters Akt-ERK signaling, and results in changes in cap-dependent translation. Toxicol Sci 90:221–229
Jin H, Hwang SK, Kwon JT, Lee YS, An GH, Lee KH, Prats AC, Morello D, Beck GR Jr, Cho MH (2008) Low dietary inorganic phosphate affects the brain by controlling apoptosis, cell cycle and protein translation. J Nutr Biochem 19:16–25
Xu CX, Jin H, Lim HT, Kim JE, Shin JY, Lee ES, Chung YS, Lee YS, Beck G Jr, Lee KH, Cho MH (2008) High dietary inorganic phosphate enhances cap-dependent protein translation, cell-cycle progression, and angiogenesis in the livers of young mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 295:G654–G663
Chang SH, Yu KN, Lee YS, An GH, Beck GR Jr, Colburn NH, Lee KH, Cho MH (2006) Elevated inorganic phosphate stimulates Akt-ERK1/2-Mnk1 signaling in human lung cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 35:528–539
Jin H, Chang SH, Xu CX, Shin JY, Chung YS, Park SJ, Lee YS, An GH, Lee KH, Cho MH (2007) High dietary inorganic phosphate affects lung through altering protein translation, cell cycle, and angiogenesis in developing mice. Toxicol Sci 100:215–223
Jin H, Xu CX, Lim HT, Park SJ, Shin JY, Chung YS, Park SC, Chang SH, Youn HJ, Lee KH, Lee YS, Ha YC, Chae CH, Beck GR Jr, Cho MH (2009) High dietary inorganic phosphate increases lung tumorigenesis and alters Akt signaling. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 179:59–68
Xu CX, Jin H, Chung YS, Shin JY, Hwang SK, Kwon JT, Park SJ, Lee ES, Minai-Tehrani A, Chang SH, Woo MA, Noh MS, An GH, Lee KH, Cho MH (2009) Low dietary inorganic phosphate affects the lung growth of developing mice. J Vet Sci 10:105–113
Glinn M, Ni B, Irwin RP, Kelley SW, Lin SZ, Paul SM (1998) Inorganic Pi increases neuronal survival in the acute early phase following excitotoxic/oxidative insults. J Neurochem 70:1850–1858
Slatopolsky E, Finch J, Denda M, Ritter C, Zhong M, Dusso A, MacDonald PN, Brown AJ (1996) Phosphorus restriction prevents parathyroid gland growth. High phosphorus directly stimulates PTH secretion in vitro. J Clin Invest 97:2534–2540
Almaden Y, Canalejo A, Hernandez A, Ballesteros E, Garcia-Navarro S, Torres A, Rodriguez M (1996) Direct effect of phosphorus on PTH secretion from whole rat parathyroid glands in vitro. J Bone Miner Res 11:970–976
Silver J, Kilav R, Naveh-Many T (2002) Mechanisms of secondary hyperparathyroidism. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 283:F367–F376
Beck G, Knecht N (2003) Osteopontin regulation by inorganic phosphate is ERK1/2-, protein kinase C-, and proteasome-dependent. J Biol Chem 278:41921–41929
Fujita T, Izumo N, Fukuyama R, Meguro T, Yasutomi C, Nakamuta H, Koida M (2001) Incadronate and etidronate accelerate phosphate-primed mineralization of MC4 cells via ERK1/2-Cbfa1 signaling pathway in a Ras-independent manner: further involvement of mevalonate-pathway blockade for incadronate. Jpn J Pharmacol 86:86–96
Julien M, Magne D, Masson M, Rolli-Derkinderen M, Chassande O, Cario-Toumaniantz C, Cherel Y, Weiss P, Guicheux J (2007) Phosphate stimulates matrix Gla protein expression in chondrocytes through the extracellular signal regulated kinase signaling pathway. Endocrinology 148:530–537
Fujita T, Izumo N, Fukuyama R, Meguro T, Nakamuta H, Kohno T, Koida M (2001) Phosphate provides an extracellular signal that drives nuclear export of Runx2/Cbfa1 in bone cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 280:348–352
Vial E, Marshall CJ (2003) Elevated ERK-MAP kinase activity protects the FOS family member FRA-1 against proteasomal degradation in colon carcinoma cells. J Cell Sci 116:4957–4963
Casalino L, De Cesare D, Verde P (2003) Accumulation of Fra-1 in ras-transformed cells depends on both transcriptional autoregulation and MEK-dependent posttranslational stabilization. Mol Cell Biol 23:4401–4415
Busch AE, Wagner CA, Schuster A, Waldegger S, Biber J, Murer H, Lang F (1995) Properties of electrogenic Pi transport by a human renal brush border Na+/Pi transporter. J Am Soc Nephrol 6:1547–1551
Szczepanska-Konkel M, Yusufi AN, VanScoy M, Webster SK, Dousa TP (1986) Phosphonocarboxylic acids as specific inhibitors of Na+-dependent transport of phosphate across renal brush border membrane. J Biol Chem 261:6375–6383
Bai L, Collins JF, Ghishan FK (2000) Cloning and characterization of a type III Na-dependent phosphate cotransporter from mouse intestine. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 279:C1135–C1143
Ravera S, Virkki LV, Murer H, Forster IC (2007) Deciphering PiT transport kinetics and substrate specificity using electrophysiology and flux measurements. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 293:C606–C620
Villa-Bellosta R, Bogaert YE, Levi M, Sorribas V (2007) Characterization of phosphate transport in rat vascular smooth muscle cells: implications for vascular calcification. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27:1030–1036
Villa-Bellosta R, Sorribas V (2009) Phosphonoformic acid prevents vascular smooth muscle cell calcification by inhibiting calcium-phosphate deposition. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 29:761–766
Suzuki A, Ghayor C, Guicheux J, Magne D, Quillard S, Kakita A, Ono Y, Miura Y, Oiso Y, Itoh M, Caverzasio J (2006) Enhanced expression of the inorganic phosphate transporter Pit-1 is involved in BMP-2-induced matrix mineralization in osteoblast-like cells. J Bone Miner Res 21:674–683
Fleisch HA, Russell RG, Bisaz S, Muhlbauer RC, Williams DA (1970) The inhibitory effect of phosphonates on the formation of calcium phosphate crystals in vitro and on aortic and kidney calcification in vivo. Eur J Clin Invest 1:12–18
Beck L, Leroy C, Beck-cormier S, Forand A, Salaun C, Paris N, Bernier A, Urena-Torres P, Prié D, Ollero M, Coulombel L, Friedlander G (2010) The phosphate transporter PiT1 (Slc20a1) revealed as a new essential gene for mouse liver development. PLoS One 5:e9148
Festing MH, Speer MY, Yang HY, Giachelli CM (2009) Generation of mouse conditional and null alleles of the type III sodium-dependent phosphate cotransporter PiT-1. Genesis 47:858–863
Kumar R (2009) Phosphate sensing. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 18:281–284
Markovich D, Verri T, Sorribas V, Forgo J, Biber J, Murer H (1995) Regulation of opossum kidney (OK) cell Na/Pi cotransport by Pi deprivation involves mRNA stability. Pflugers Arch 430:459–463
Segawa H, Kaneko I, Yamanaka S, Ito M, Kuwahata M, Inoue Y, Kato S, Miyamoto K (2004) Intestinal Na-P(i) cotransporter adaptation to dietary P(i) content in vitamin D receptor null mice. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 287:F39–F47
Rizzoli R, Fleisch H, Bonjour JP (1977) Role of 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 on intestinal phosphate absorption in rats with a normal vitamin D supply. J Clin Invest 60:639–647
Goseki-Sone M, Yamada A, Hamatani R, Mizoi L, Iimura T, Ezawa I (2002) Phosphate depletion enhances bone morphogenetic protein-4 gene expression in a cultured mouse marrow stromal cell line ST2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 299:395–399
Goseki-Sone M, Yamada A, Asahi K, Hirota A, Ezawa I, Iimura T (1999) Phosphate depletion enhances tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase gene expression in a cultured mouse marrow stromal cell line ST2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 265:24–28
Delmez JA, Slatopolsky E (1992) Hyperphosphatemia: its consequences and treatment in patients with chronic renal disease. Am J Kidney Dis 19:303–317
Topaz O, Shurman DL, Bergman R, Indelman M, Ratajczak P, Mizrachi M, Khamaysi Z, Behar D, Petronius D, Friedman V, Zelikovic I, Raimer S, Metzker A, Richard G, Sprecher E (2004) Mutations in GALNT3, encoding a protein involved in O-linked glycosylation, cause familial tumoral calcinosis. Nat Genet 36:579–581
Benet-Pages A, Orlik P, Strom TM, Lorenz-Depiereux B (2005) An FGF23 missense mutation causes familial tumoral calcinosis with hyperphosphatemia. Hum Mol Genet 14:385–390
Ichikawa S, Imel EA, Kreiter ML, Yu X, Mackenzie DS, Sorenson AH, Goetz R, Mohammadi M, White KE, Econs MJ (2007) A homozygous missense mutation in human KLOTHO causes severe tumoral calcinosis. J Clin Invest 117:2684–2691
Chefetz I, Kohno K, Izumi H, Uitto J, Richard G, Sprecher E (2009) GALNT3, a gene associated with hyperphosphatemic familial tumoral calcinosis, is transcriptionally regulated by extracellular phosphate and modulates matrix metalloproteinase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta 1792:61–67
Shimada T, Kakitani M, Yamazaki Y, Hasegawa H, Takeuchi Y, Fujita T, Fukumoto S, Tomizuka K, Yamashita T (2004) Targeted ablation of Fgf23 demonstrates an essential physiological role of FGF23 in phosphate and vitamin D metabolism. J Clin Invest 113:561–568
Stubbs JR, Liu S, Tang W, Zhou J, Wang Y, Yao X, Quarles LD (2007) Role of hyperphosphatemia and 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D in vascular calcification and mortality in fibroblastic growth factor 23 null mice. J Am Soc Nephrol 18:2116–2124
Kuro-o M, Matsumura Y, Aizawa H, Kawaguchi H, Suga T, Utsugi T, Ohyama Y, Kurabayashi M, Kaname T, Kume E, Iwasaki H, Iida A, Shiraki-Iida T, Nishikawa S, Nagai R, Nabeshima YI (1997) Mutation of the mouse klotho gene leads to a syndrome resembling ageing. Nature 390:45–51
Block GA (2000) Prevalence and clinical consequences of elevated Ca x P product in hemodialysis patients. Clin Nephrol 54:318–324
Tonelli M, Sacks F, Pfeffer M, Gao Z, Curhan G (2005) Relation between serum phosphate level and cardiovascular event rate in people with coronary disease. Circulation 112:2627–2633
Foley RN (2009) Phosphate levels and cardiovascular disease in the general population. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 4:1136–1139
Loghman-Adham M (1999) Phosphate binders for control of phosphate retention in chronic renal failure. Pediatr Nephrol 13:701–708
Russo D, Miranda I, Ruocco C, Battaglia Y, Buonanno E, Manzi S, Russo L, Scafarto A, Andreucci VE (2007) The progression of coronary artery calcification in predialysis patients on calcium carbonate or sevelamer. Kidney Int 72:1255–1261
Slatopolsky E, Bricker NS (1973) The role of phosphorus restriction in the prevention of secondary hyperparathyroidism in chronic renal disease. Kidney Int 4:141–145
Lopez-Hilker S, Dusso AS, Rapp NS, Martin KJ, Slatopolsky E (1990) Phosphorus restriction reverses hyperparathyroidism in uremia independent of changes in calcium and calcitriol. Am J Physiol 259:F432–F437
Nielsen PK, Feldt-Rasmussen U, Olgaard K (1996) A direct effect in vitro of phosphate on PTH release from bovine parathyroid tissue slices but not from dispersed parathyroid cells. Nephrol Dial Transplant 11:1762–1768
Silver J, Naveh-Many T (2009) Phosphate and the parathyroid. Kidney Int 75:898–905
Martin DR, Ritter CS, Slatopolsky E, Brown AJ (2005) Acute regulation of parathyroid hormone by dietary phosphate. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 289:E729–E734
Berndt T, Thomas LF, Craig TA, Sommer S, Li X, Bergstralh EJ, Kumar R (2007) Evidence for a signaling axis by which intestinal phosphate rapidly modulates renal phosphate reabsorption. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:11085–11090
Lennane RJ, Carey RM, Goodwin TJ, Peart WS (1975) A comparison of natriuresis after oral and intravenous sodium loading in sodium-depleted man: evidence for a gastrointestinal or portal monitor of sodium intake. Clin Sci Mol Med 49:437–440
Lennane RJ, Peart WS, Carey RM, Shaw J (1975) A comparison on natriuresis after oral and intravenous sodium loading in sodium-depleted rabbits: evidence for a gastrointestinal or portal monitor of sodium intake. Clin Sci Mol Med 49:433–436
Lee FN, Oh G, McDonough AA, Youn JH (2007) Evidence for gut factor in K+ homeostasis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 293:F541–F547
Conigrave AD, Brown EM (2006) Taste receptors in the gastrointestinal tract. II. L-amino acid sensing by calcium-sensing receptors: implications for GI physiology. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 291:G753–G761
Hsieh YJ, Wanner BL (2010) Global regulation by the seven-component Pi signaling system. Curr Opin Microbiol 13:198–203
Lamarche MG, Wanner BL, Crepin S, Harel J (2008) The phosphate regulon and bacterial virulence: a regulatory network connecting phosphate homeostasis and pathogenesis. FEMS Microbiol Rev 32:461–473
Mouillon JM, Persson BL (2006) New aspects on phosphate sensing and signalling in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Yeast Res 6:171–176
Giots F, Donaton MC, Thevelein JM (2003) Inorganic phosphate is sensed by specific phosphate carriers and acts in concert with glucose as a nutrient signal for activation of the protein kinase A pathway in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Microbiol 47:1163–1181
Popova Y, Thayumanavan P, Lonati E, Agrochao M, Thevelein JM (2010) Transport and signaling through the phosphate-binding site of the yeast Pho84 phosphate transceptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:2890–2895
Carroll AS, O’Shea EK (2002) Pho85 and signaling environmental conditions. Trends Biochem Sci 27:87–93
Wilson WA, Roach PJ (2002) Nutrient-regulated protein kinases in budding yeast. Cell 111:155–158
Silver J (2001) Cycling with the parathyroid. J Clin Invest 107:1079–1080
Miyamoto K, Tatsumi S, Morita K, Takeda E (1998) Does the parathyroid ‘see’ phosphate? Nephrol Dial Transplant 13:2727–2729
Miyamoto K, Tatsumi S, Segawa H, Morita K, Nii T, Fujioka A, Kitano M, Inoue Y, Takeda E (1999) Regulation of PiT-1, a sodium-dependent phosphate co-transporter in rat parathyroid glands. Nephrol Dial Transplant 14(Suppl 1):73–75
Tatsumi S, Segawa H, Morita K, Haga H, Kouda T, Yamamoto H, Inoue Y, Nii T, Katai K, Taketani Y, Miyamoto KI, Takeda E (1998) Molecular cloning and hormonal regulation of PiT-1, a sodium-dependent phosphate cotransporter from rat parathyroid glands. Endocrinology 139:1692–1699
Salaun C, Marechal V, Heard JM (2004) Transport-deficient Pit2 phosphate transporters still modify cell surface oligomers structure in response to inorganic phosphate. J Mol Biol 340:39–47
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge Joanna Ashton-Chess for critical reading of the manuscript. This work was partially supported by grants from INSERM, ANR (PHYSIOPATH ANR-07-PHYSIO-017-01), La Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale (AAP “Vieillissement ostéoarticulaire”), BIOREGOS and Région des Pays de la Loire. Marion Julien received a fellowship from INSERM/Région des Pays de la Loire and La Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale, Solmaz Khoshniat from the French Ministry of Research and la Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale and Annabelle Bourgine from INSERM/Région des Pays de la Loire.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
J. Guicheux and L. Beck contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khoshniat, S., Bourgine, A., Julien, M. et al. The emergence of phosphate as a specific signaling molecule in bone and other cell types in mammals. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 68, 205–218 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-010-0527-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-010-0527-z