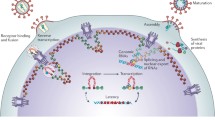
Abstract
Integration is central to HIV-1 replication and helps mold the reservoir of cells that persists in AIDS patients. HIV-1 interacts with specific cellular factors to target integration to interior regions of transcriptionally active genes within gene-dense regions of chromatin. The viral capsid interacts with several proteins that are additionally implicated in virus nuclear import, including cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor 6, to suppress integration into heterochromatin. The viral integrase protein interacts with transcriptional co-activator lens epithelium-derived growth factor p75 to principally position integration within gene bodies. The integrase additionally senses target DNA distortion and nucleotide sequence to help fine-tune the specific phosphodiester bonds that are cleaved at integration sites. Research into virus–host interactions that underlie HIV-1 integration targeting has aided the development of a novel class of integrase inhibitors and may help to improve the safety of viral-based gene therapy vectors.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PIC:
-
Preintegration complex
- MoMLV:
-
Moloney murine leukemia virus
- LEDGF:
-
Lens epithelium-derived growth factor
- CPSF6:
-
Cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor 6
- RNAi:
-
RNA interference
- MLL:
-
Mixed-lineage leukemia
- HDGF:
-
Hepatoma-derived growth factor
- HRP:
-
HDGF-related protein
- HDGFL:
-
HDGF like
- CR:
-
Charged regions
- IBD:
-
Integrase-binding domain
- PHAT:
-
Pseudo HEAT repeat analogous topology
- NTD:
-
N-terminal domain
- CCD:
-
Catalytic core domain
- CTD:
-
C-terminal domain
- PHD:
-
Plant homeodomain
- SMARCB1:
-
SWI/SNF-related, matrix-associated, actin-dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily B, member 1
- INI1:
-
Integrase interactor 1
- NPC:
-
Nuclear pore complex
- NUP:
-
Nucleoporin
- CYPA:
-
Cyclophilin A
- RNP:
-
Ribonucleoprotein
- RRM:
-
RNA recognition motif
- PRD:
-
Pro-rich domain
- RSLD:
-
RS-like domain
- IN:
-
Integrase
- GFP:
-
Green fluorescent protein
- NLS:
-
Nuclear localization signal
- CFIm:
-
Cleavage factor I mammalian
- ChIP-Seq:
-
Chromatin-immunoprecipitation sequencing
- Y:
-
Pyrimidine
- R:
-
Purine
- LEDGIN:
-
LEDGF/p75-integrase interaction site
- ALLINI:
-
Allosteric integrase inhibitor
- NCINI:
-
Non-catalytic site integrase inhibitor
- INLAI:
-
Integrase-LEDGF allosteric inhibitor
- MDM:
-
Monocyte-derived macrophages
- LRA:
-
Latency-reversing agent
- PDB:
-
Protein database
- TNPO1:
-
Transportin 1
- TNPO3:
-
Transportin 3
- CA:
-
Capsid
References
Fassati A, Goff SP (1999) Characterization of intracellular reverse transcription complexes of Moloney murine leukemia virus. J Virol 73:8919–8925
Bowerman B, Brown PO, Bishop JM, Varmus HE (1989) A nucleoprotein complex mediates the integration of retroviral DNA. Genes Dev 3:469–478
Miller MD, Farnet CM, Bushman FD (1997) Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 preintegration complexes: studies of organization and composition. J Virol 71:5382–5390
Wei SQ, Mizuuchi K, Craigie R (1997) A large nucleoprotein assembly at the ends of the viral DNA mediates retroviral DNA integration. EMBO J 16:7511–7520
Chen H, Wei S-Q, Engelman A (1999) Multiple integrase functions are required to form the native structure of the human immunodeficiency virus type I intasome. J Biol Chem 274:17358–17364
Hare S, Gupta SS, Valkov E, Engelman A, Cherepanov P (2010) Retroviral intasome assembly and inhibition of DNA strand transfer. Nature 464:232–236
Ballandras-Colas A, Maskell DP, Serrao E, Locke J, Swuec P, Jonsson SR, Kotecha A, Cook NJ, Pye VE, Taylor IA, Andresdottir V, Engelman AN, Costa A, Cherepanov P (2017) A supramolecular assembly mediates lentiviral DNA integration. Science 355:93–95
Passos DO, Li M, Yang R, Regensburg S, Ghirlando R, Jeon Y, Kvaratskhelia M, Craigie R, Lyumkis D (2017) CryoEM structures and atomic model of the HIV-1 strand transfer complex intasome. Science 355:89–92
Engelman AN, Cherepanov P (2017) Retroviral intasomes arising. Curr Opin Struct Biol 47:23–29
Katzman M, Katz RA, Skalka AM, Leis J (1989) The avian retroviral integration protein cleaves the terminal sequences of linear viral DNA at the in vivo sites of integration. J Virol 63:5319–5327
Roth MJ, Schwartzberg PL, Goff SP (1989) Structure of the termini of DNA intermediates in the integration of retroviral DNA: dependence on IN function and terminal DNA sequence. Cell 58:47–54
Craigie R, Fujiwara T, Bushman F (1990) The IN protein of Moloney murine leukemia virus processes the viral DNA ends and accomplishes their integration in vitro. Cell 62:829–837
Sherman PA, Fyfe JA (1990) Human immunodeficiency virus integration protein expressed in Escherichia coli possesses selective DNA cleaving activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:5119–5123
Engelman A, Mizuuchi K, Craigie R (1991) HIV-1 DNA integration: mechanism of viral DNA cleavage and DNA strand transfer. Cell 67:1211–1221
Hare S, Vos AM, Clayton RF, Thuring JW, Cummings MD, Cherepanov P (2010) Molecular mechanisms of retroviral integrase inhibition and the evolution of viral resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:20057–20062
Lesbats P, Engelman AN, Cherepanov P (2016) Retroviral DNA integration. Chem Rev 116:12730–12757
Kvaratskhelia M, Sharma A, Larue RC, Serrao E, Engelman A (2014) Molecular mechanisms of retroviral integration site selection. Nucleic Acids Res 42:10209–10225
Craigie R, Bushman FD (2014) Host factors in retroviral integration and the selection of integration target sites. Microbiol Spectr 2:6
Demeulemeester J, Rijck JD, Gijsbers R, Debyser Z (2015) Retroviral integration: site matters: mechanisms and consequences of retroviral integration site selection. BioEssays 37:1202–1214
Schroder ARW, Shinn P, Chen H, Berry C, Ecker JR, Bushman F (2002) HIV-1 integration in the human genome favors active genes and local hotspots. Cell 110:521–529
Wu X, Li Y, Crise B, Burgess SM (2003) Transcription start regions in the human genome are favored targets for MLV integration. Science 300:1749–1751
LaFave MC, Varshney GK, Gildea DE, Wolfsberg TG, Baxevanis AD, Burgess SM (2014) MLV integration site selection is driven by strong enhancers and active promoters. Nucleic Acids Res 42:4257–4269
De Ravin SS, Su L, Theobald N, Choi U, Macpherson JL, Poidinger M, Symonds G, Pond SM, Ferris AL, Hughes SH, Malech HL, Wu X (2014) Enhancers are major targets for murine leukemia virus vector integration. J Virol 88:4504–4513
Mitchell RS, Beitzel BF, Schroder AR, Shinn P, Chen H, Berry CC, Ecker JR, Bushman FD (2004) Retroviral DNA integration: ASLV, HIV, and MLV show distinct target site preferences. PLoS Biol 2:E234
Sowd GA, Serrao E, Wang H, Wang W, Fadel HJ, Poeschla EM, Engelman AN (2016) A critical role for alternative polyadenylation factor CPSF6 in targeting HIV-1 integration to transcriptionally active chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:E1054–E1063
Cherepanov P, Maertens G, Proost P, Devreese B, Van Beeumen J, Engelborghs Y, De Clercq E, Debyser Z (2003) HIV-1 integrase forms stable tetramers and associates with LEDGF/p75 protein in human cells. J Biol Chem 278:372–381
Lee K, Ambrose Z, Martin TD, Oztop I, Mulky A, Julias JG, Vandegraaff N, Baumann JG, Wang R, Yuen W, Takemura T, Shelton K, Taniuchi I, Li Y, Sodroski J, Littman DR, Coffin JM, Hughes SH, Unutmaz D, Engelman A, KewalRamani VN (2010) Flexible use of nuclear import pathways by HIV-1. Cell Host Microbe 7:221–233
Pryciak PM, Varmus HE (1992) Nucleosomes, DNA-binding proteins, and DNA sequence modulate retroviral integration target site selection. Cell 69:769–780
Pruss D, Bushman FD, Wolffe AP (1994) Human immunodeficiency virus integrase directs integration to sites of severe DNA distortion within the nucleosome core. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:5913–5917
Pruss D, Reeves R, Bushman FD, Wolffe AP (1994) The influence of DNA and nucleosome structure on integration events directed by HIV integrase. J Biol Chem 269:25031–25041
Wang GP, Ciuffi A, Leipzig J, Berry CC, Bushman FD (2007) HIV integration site selection: analysis by massively parallel pyrosequencing reveals association with epigenetic modifications. Genome Res 17:1186–1194
Benleulmi MS, Matysiak J, Henriquez DR, Vaillant C, Lesbats P, Calmels C, Naughtin M, Leon O, Skalka AM, Ruff M, Lavigne M, Andreola ML, Parissi V (2015) Intasome architecture and chromatin density modulate retroviral integration into nucleosome. Retrovirology 12:13
Naughtin M, Haftek-Terreau Z, Xavier J, Meyer S, Silvain M, Jaszczyszyn Y, Levy N, Miele V, Benleulmi MS, Ruff M, Parissi V, Vaillant C, Lavigne M (2015) DNA physical properties and nucleosome positions are major determinants of HIV-1 integrase selectivity. PLoS One 10:e0129427
Holman AG, Coffin JM (2005) Symmetrical base preferences surrounding HIV-1, avian sarcoma/leukosis virus, and murine leukemia virus integration sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:6103–6107
Wu X, Li Y, Crise B, Burgess SM, Munroe DJ (2005) Weak palindromic consensus sequences are a common feature found at the integration target sites of many retroviruses. J Virol 79:5211–5214
Serrao E, Krishnan L, Shun MC, Li X, Cherepanov P, Engelman A, Maertens GN (2014) Integrase residues that determine nucleotide preferences at sites of HIV-1 integration: implications for the mechanism of target DNA binding. Nucleic Acids Res 42:5164–5176
Serrao E, Ballandras-Colas A, Cherepanov P, Maertens GN, Engelman AN (2015) Key determinants of target DNA recognition by retroviral intasomes. Retrovirology 12:39
Kirk PDW, Huvet M, Melamed A, Maertens GN, Bangham CRM (2016) Retroviruses integrate into a shared, non-palindromic DNA motif. Nat Microbiol 2:16212
Albanese A, Arosio D, Terreni M, Cereseto A (2008) HIV-1 pre-integration complexes selectively target decondensed chromatin in the nuclear periphery. PLoS One 3:e2413
Burdick RC, Hu W-S, Pathak VK (2013) Nuclear import of APOBEC3F-labeled HIV-1 preintegration complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:E4780–E4789
Di Primio C, Quercioli V, Allouch A, Gijsbers R, Christ F, Debyser Z, Arosio D, Cereseto A (2013) Single-cell imaging of HIV-1 provirus (SCIP). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:5636–5641
Lelek M, Casartelli N, Pellin D, Rizzi E, Souque P, Severgnini M, Di Serio C, Fricke T, Diaz-Griffero F, Zimmer C, Charneau P, Di Nunzio F (2015) Chromatin organization at the nuclear pore favours HIV replication. Nat Commun 6:6483
Marini B, Kertesz-Farkas A, Ali H, Lucic B, Lisek K, Manganaro L, Pongor S, Luzzati R, Recchia A, Mavilio F, Giacca M, Lusic M (2015) Nuclear architecture dictates HIV-1 integration site selection. Nature 521:227–231
Bushman FD, Craigie R (1991) Activities of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) integration protein in vitro: specific cleavage and integration of HIV DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:1339–1343
Bushman F, Lewinski M, Ciuffi A, Barr S, Leipzig J, Hannenhalli S, Hoffmann C (2005) Genome-wide analysis of retroviral DNA integration. Nat Rev Microbiol 3:848–858
Engelman A (2005) The ups and downs of gene expression and retroviral DNA integration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:1275–1276
Engelman A (2007) Host cell factors and HIV-1 integration. Future HIV Ther 1:415–426
Christ F, Thys W, De Rijck J, Gijsbers R, Albanese A, Arosio D, Emiliani S, Rain JC, Benarous R, Cereseto A, Debyser Z (2008) Transportin-SR2 imports HIV into the nucleus. Curr Biol 18:1192–1202
Huang L, G-l Xu, J-q Zhang, Tian L, J-l Xue, J-z Chen, Jia W (2008) Daxx interacts with HIV-1 integrase and inhibits lentiviral gene expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 373:241–245
Studamire B, Goff SP (2008) Host proteins interacting with the Moloney murine leukemia virus integrase: multiple transcriptional regulators and chromatin binding factors. Retrovirology 5:48
Woodward CL, Prakobwanakit S, Mosessian S, Chow SA (2009) Integrase interacts with nucleoporin NUP153 to mediate the nuclear import of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol 83:6522–6533
J-q Zhang, J-j Wang, W-j Li, Huang L, Tian L, J-l Xue, J-z Chen, Jia W (2009) Cellular protein TTRAP interacts with HIV-1 integrase to facilitate viral integration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 387:256–260
Ao Z, Danappa Jayappa K, Wang B, Zheng Y, Kung S, Rassart E, Depping R, Kohler M, Cohen EA, Yao X (2010) Importin α3 interacts with HIV-1 integrase and contributes to HIV-1 nuclear import and replication. J Virol 84:8650–8663
Manganaro L, Lusic M, Gutierrez MI, Cereseto A, Del Sal G, Giacca M (2010) Concerted action of cellular JNK and Pin1 restricts HIV-1 genome integration to activated CD4+ T lymphocytes. Nat Med 16:329–333
Terreni M, Valentini P, Liverani V, Gutierrez MI, Di Primio C, Di Fenza A, Tozzini V, Allouch A, Albanese A, Giacca M, Cereseto A (2010) GCN5-dependent acetylation of HIV-1 integrase enhances viral integration. Retrovirology 7:18
Allouch A, Cereseto A (2011) Identification of cellular factors binding to acetylated HIV-1 integrase. Amino Acids 41:1137–1145
Allouch A, Di Primio C, Alpi E, Lusic M, Arosio D, Giacca M, Cereseto A (2011) The TRIM family protein KAP1 inhibits HIV-1 integration. Cell Host Microbe 9:484–495
Kobbi L, Octobre G, Dias J, Comisso M, Mirande M (2011) Association of mitochondrial lysyl-tRNA synthetase with HIV-1 GagPol involves catalytic domain of the synthetase and transframe and integrase domains of Pol. J Mol Biol 410:875–886
Sorin M, Cano J, Das S, Mathew S, Wu X, Davies KP, Shi X, Cheng SW, Ott D, Kalpana GV (2011) Recruitment of a SAP18-HDAC1 complex into HIV-1 virions and its requirement for viral replication. PLoS Pathog 5:e1000463
Yamamoto SP, Okawa K, Nakano T, Sano K, Ogawa K, Masuda T, Morikawa Y, Koyanagi Y, Suzuki Y (2011) Huwe1, a novel cellular interactor of Gag-Pol through integrase binding, negatively influences HIV-1 infectivity. Microbes Infect 13:339–349
Zheng Y, Ao Z, Wang B, Jayappa KD, Yao X (2011) Host protein Ku70 binds and protects HIV-1 integrase from proteasomal degradation and is required for HIV replication. J Biol Chem 286:17722–17735
Ao Z, Jayappa KD, Wang B, Zheng Y, Wang X, Peng J, Yao X (2012) Contribution of host nucleoporin 62 in HIV-1 integrase chromatin association and viral DNA integration. J Biol Chem 287:10544–10555
Jager S, Cimermancic P, Gulbahce N, Johnson JR, McGovern KE, Clarke SC, Shales M, Mercenne G, Pache L, Li K, Hernandez H, Jang GM, Roth SL, Akiva E, Marlett J, Stephens M, D’Orso I, Fernandes J, Fahey M, Mahon C, O’Donoghue AJ, Todorovic A, Morris JH, Maltby DA, Alber T, Cagney G, Bushman FD, Young JA, Chanda SK, Sundquist WI, Kortemme T, Hernandez RD, Craik CS, Burlingame A, Sali A, Frankel AD, Krogan NJ (2012) Global landscape of HIV-human protein complexes. Nature 481:365–370
Matysiak J, Lesbats P, Mauro E, Lapaillerie D, Dupuy J-W, Lopez AP, Benleulmi MS, Calmels C, Andreola M-L, Ruff M, Llano M, Delelis O, Lavigne M, Parissi V (2017) Modulation of chromatin structure by the FACT histone chaperone complex regulates HIV-1 integration. Retrovirology 14:39
Ako-Adjei D, Fu W, Wallin C, Katz KS, Song G, Darji D, Brister JR, Ptak RG, Pruitt KD (2015) HIV-1, human interaction database: current status and new features. Nucleic Acids Res 43:D566–D570
Vandekerckhove L, Christ F, Van Maele B, De Rijck J, Gijsbers R, Van den Haute C, Witvrouw M, Debyser Z (2006) Transient and stable knockdown of the integrase cofactor LEDGF/p75 reveals its role in the replication cycle of human immunodeficiency virus. J Virol 80:1886–1896
Zielske SP, Stevenson M (2006) Modest but reproducible inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection in macrophages following LEDGFp75 silencing. J Virol 80:7275–7280
Llano M, Vanegas M, Fregoso O, Saenz D, Chung S, Peretz M (2004) LEDGF/p75 determines cellular trafficking of diverse lentiviral but not murine oncoretroviral integrase proteins and is a component of functional lentiviral preintegration complexes. J Virol 78:9524–9537
Vandegraaff N, Devroe E, Turlure F, Silver PA, Engelman A (2006) Biochemical and genetic analyses of integrase-interacting proteins lens epithelium-derived growth factor (LEDGF)/p75 and hepatoma-derived growth factor related protein 2 (HRP2) in preintegration complex function and HIV-1 replication. Virology 346:415–426
Llano M, Saenz DT, Meehan A, Wongthida P, Peretz M, Walker WH, Teo W, Poeschla EM (2006) An essential role for LEDGF/p75 in HIV integration. Science 314:461–464
Marshall HM, Ronen K, Berry C, Llano M, Sutherland H, Saenz D, Bickmore W, Poeschla E, Bushman FD (2007) Role of PSIP1/LEDGF/p75 in lentiviral infectivity and integration targeting. PLoS One 2:e1340
Shun MC, Raghavendra NK, Vandegraaff N, Daigle JE, Hughes S, Kellam P, Cherepanov P, Engelman A (2007) LEDGF/p75 functions downstream from preintegration complex formation to effect gene-specific HIV-1 integration. Genes Dev 21:1767–1778
Schrijvers R, De Rijck J, Demeulemeester J, Adachi N, Vets S, Ronen K, Christ F, Bushman FD, Debyser Z, Gijsbers R (2012) LEDGF/p75-independent HIV-1 replication demonstrates a role for HRP-2 and remains sensitive to inhibition by LEDGINs. PLoS Pathog 8:e1002558
Wang H, Jurado KA, Wu X, Shun MC, Li X, Ferris AL, Smith SJ, Patel PA, Fuchs JR, Cherepanov P, Kvaratskhelia M, Hughes SH, Engelman A (2012) HRP2 determines the efficiency and specificity of HIV-1 integration in LEDGF/p75 knockout cells but does not contribute to the antiviral activity of a potent LEDGF/p75-binding site integrase inhibitor. Nucleic Acids Res 40:11518–11530
Fadel HJ, Morrison JH, Saenz DT, Fuchs JR, Kvaratskhelia M, Ekker SC, Poeschla EM (2014) TALEN knockout of the PSIP1 gene in human cells: analyses of HIV-1 replication and allosteric integrase inhibitor mechanism. J Virol 88:9704–9717
Hultquist JF, Schumann K, Woo JM, Manganaro L, McGregor MJ, Doudna J, Simon V, Krogan NJ, Marson A (2016) A Cas9 ribonucleoprotein platform for functional genetic studies of HIV-host interactions in primary human T cells. Cell Rep 17:1438–1452
Ciuffi A, Llano M, Poeschla E, Hoffmann C, Leipzig J, Shinn P, Ecker JR, Bushman F (2005) A role for LEDGF/p75 in targeting HIV DNA integration. Nat Med 11:1287–1289
Schrijvers R, Vets S, De Rijck J, Malani N, Bushman FD, Debyser Z, Gijsbers R (2012) HRP-2 determines HIV-1 integration site selection in LEDGF/p75 depleted cells. Retrovirology 9:84
Singh PK, Plumb MR, Ferris AL, Iben JR, Wu X, Fadel HJ, Luke BT, Esnault C, Poeschla EM, Hughes SH, Kvaratskhelia M, Levin HL (2015) LEDGF/p75 interacts with mRNA splicing factors and targets HIV-1 integration to highly spliced genes. Genes Dev 29:2287–2297
Ge H, Si Y, Roeder RG (1998) Isolation of cDNAs encoding novel transcription coactivators p52 and p75 reveals an alternate regulatory mechanism of transcriptional activation. EMBO J 17:6723–6729
Ge H, Si Y, Wolffe AP (1998) A novel transcriptional coactivator, p52, functionally interacts with the essential splicing factor ASF/SF2. Mol Cell 2:751–759
Morchikh M, Naughtin M, Di Nunzio F, Xavier J, Charneau P, Jacob Y, Lavigne M (2013) TOX4 and NOVA1 proteins are partners of the LEDGF PWWP domain and affect HIV-1 replication. PLoS One 7:e1001280
Daugaard M, Baude A, Fugger K, Povlsen LK, Beck H, Sorensen CS, Petersen NH, Sorensen PH, Lukas C, Bartek J, Lukas J, Rohde M, Jaattela M (2012) LEDGF (p75) promotes DNA-end resection and homologous recombination. Nat Struct Mol Biol 19:803–810
Yokoyama A, Cleary ML (2008) Menin critically links MLL proteins with LEDGF on cancer-associated target genes. Cancer Cell 14:36–46
Čermáková K, Tesina P, Demeulemeester J, El Ashkar S, Méreau H, Schwaller J, Řezáčová P, Veverka V, De Rijck J (2014) Validation and structural characterization of the LEDGF/p75–MLL interface as a new target for the treatment of MLL-dependent leukemia. Cancer Res 74:5139–5151
Murai MJ, Pollock J, He S, Miao H, Purohit T, Yokom A, Hess JL, Muntean AG, Grembecka J, Cierpicki T (2014) The same site on the integrase-binding domain of lens epithelium–derived growth factor is a therapeutic target for MLL leukemia and HIV. Blood 124:3730–3737
El Ashkar S, Schwaller J, Pieters T, Goossens S, Demeulemeester J, Christ F, Van Belle S, Juge S, Boeckx N, Engelman A, Van Vlierberghe P, Debyser Z, De Rijck J (2018) LEDGF/p75 is dispensable for hematopoiesis but essential for MLL-rearranged leukemogenesis. Blood 131:95–107
Izumoto Y, Kuroda T, Harada H, Kishimoto T, Nakamura H (1997) Hepatoma-derived growth factor belongs to a gene family in mice showing significant homology in the amino terminus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 238:26–32
Qin S, Min J (2014) Structure and function of the nucleosome-binding PWWP domain. Trends Biochem Sci 39:536–547
Pradeepa MM, Sutherland HG, Ule J, Grimes GR, Bickmore WA (2012) Psip1/Ledgf p52 binds methylated histone H3K36 and splicing factors and contributes to the regulation of alternative splicing. PLoS Genet 8:e1002717
Eidahl JO, Crowe BL, North JA, McKee CJ, Shkriabai N, Feng L, Plumb M, Graham RL, Gorelick RJ, Hess S, Poirier MG, Foster MP, Kvaratskhelia M (2013) Structural basis for high-affinity binding of LEDGF PWWP to mononucleosomes. Nucleic Acids Res 41:3924–3936
van Nuland R, van Schaik FM, Simonis M, van Heesch S, Cuppen E, Boelens R, Timmers HM, van Ingen H (2013) Nucleosomal DNA binding drives the recognition of H3K36-methylated nucleosomes by the PSIP1-PWWP domain. Epigenetics Chromatin 6:12
Nishizawa Y, Usukura J, Singh DP, Chylack LTJ, Shinohara T (2001) Spatial and temporal dynamics of two alternatively spliced regulatory factors, lens epithelium-derived growth factor (ledgf/p75) and p52, in the nucleus. Cell Tissue Res 305:107–114
Maertens G, Cherepanov P, Pluymers W, Busschots K, De Clercq E, Debyser Z, Engelborghs Y (2003) LEDGF/p75 is essential for nuclear and chromosomal targeting of HIV-1 integrase in human cells. J Biol Chem 278:33528–33539
Llano M, Vanegas M, Hutchins N, Thompson D, Delgado S, Poeschla EM (2006) Identification and characterization of the chromatin-binding domains of the HIV-1 integrase interactor LEDGF/p75. J Mol Biol 360:760–773
Turlure F, Maertens G, Rahman S, Cherepanov P, Engelman A (2006) A tripartite DNA-binding element, comprised of the nuclear localization signal and two AT-hook motifs, mediates the association of LEDGF/p75 with chromatin in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res 34:1653–1665
Tsutsui KM, Sano K, Hosoya O, Miyamoto T, Tsutsui K (2011) Nuclear protein LEDGF/p75 recognizes supercoiled DNA by a novel DNA-binding domain. Nucleic Acids Res 39:5067–5081
Busschots K, Vercammen J, Emiliani S, Benarous R, Engelborghs Y, Christ F, Debyser Z (2005) The interaction of LEDGF/p75 with integrase Is lentivirus-specific and promotes DNA binding. J Biol Chem 280:17841–17847
Cherepanov P (2007) LEDGF/p75 interacts with divergent lentiviral integrases and modulates their enzymatic activity in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res 35:113–124
Cherepanov P, Devroe E, Silver PA, Engelman A (2004) Identification of an evolutionarily conserved domain in human lens epithelium-derived growth factor/transcriptional co-activator p75 (LEDGF/p75) that binds HIV-1 integrase. J Biol Chem 279:48883–48892
Cherepanov P, Sun Z-YJ, Rahman S, Maertens G, Wagner G, Engelman A (2005) Solution structure of the HIV-1 integrase-binding domain in LEDGF/p75. Nat Struct Mol Biol 12:526–532
Cherepanov P, Ambrosio AL, Rahman S, Ellenberger T, Engelman A (2005) Structural basis for the recognition between HIV-1 integrase and transcriptional coactivator p75. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:17308–17313
Hare S, Shun MC, Gupta SS, Valkov E, Engelman A, Cherepanov P (2009) A novel co-crystal structure affords the design of gain-of-function lentiviral integrase mutants in the presence of modified PSIP1/LEDGF/p75. PLoS Pathog 5:e1000259
Wang H, Shun MC, Li X, Di Nunzio F, Hare S, Cherepanov P, Engelman A (2014) Efficient transduction of LEDGF/p75 mutant cells by gain-of-function HIV-1 integrase mutant viruses. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev 1:2
Shun M-C, Botbol Y, Li X, Di Nunzio F, Daigle JE, Yan N, Lieberman J, Lavigne M, Engelman A (2008) Identification and characterization of PWWP domain residues critical for LEDGF/p75 chromatin binding and human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infectivity. J Virol 82:11555–11567
Tesina P, Čermáková K, Hořejší M, Procházková K, Fábry M, Sharma S, Christ F, Demeulemeester J, Debyser Z, Rijck JD, Veverka V, Řezáčová P (2015) Multiple cellular proteins interact with LEDGF/p75 through a conserved unstructured consensus motif. Nat Commun 6:7968
Meehan AM, Saenz DT, Morrison JH, Garcia-Rivera JA, Peretz M, Llano M, Poeschla EM (2009) LEDGF/p75 proteins with alternative chromatin tethers are functional HIV-1 cofactors. PLoS Pathog 5:e1000522
Ferris AL, Wu X, Hughes CM, Stewart C, Smith SJ, Milne TA, Wang GG, Shun MC, Allis CD, Engelman A, Hughes SH (2010) Lens epithelium-derived growth factor fusion proteins redirect HIV-1 DNA integration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:3135–3140
Gijsbers R, Ronen K, Vets S, Malani N, De Rijck J, McNeely M, Bushman FD, Debyser Z (2010) LEDGF hybrids efficiently retarget lentiviral integration into heterochromatin. Mol Ther 18:552–560
Silvers RM, Smith JA, Schowalter M, Litwin S, Liang Z, Geary K, Daniel R (2010) Modification of integration site preferences of an HIV-1-based vector by expression of a novel synthetic protein. Hum Gene Ther 21:337–349
Vranckx LS, Demeulemeester J, Debyser Z, Gijsbers R (2016) Towards a safer, more randomized lentiviral vector integration profile exploring artificial LEDGF chimeras. PLoS One 11:e0164167
Hacein-Bey-Abina S, Garrigue A, Wang GP, Soulier J, Lim A, Morillon E, Clappier E, Caccavelli L, Delabesse E, Beldjord K, Asnafi V, MacIntyre E, Dal Cortivo L, Radford I, Brousse N, Sigaux F, Moshous D, Hauer J, Borkhardt A, Belohradsky BH, Wintergerst U, Velez MC, Leiva L, Sorensen R, Wulffraat N, Blanche S, Bushman FD, Fischer A, Cavazzana-Calvo M (2008) Insertional oncogenesis in 4 patients after retrovirus-mediated gene therapy of SCID-X1. J Clin Invest 118:3132–3142
Desimmie BA, Weydert C, Schrijvers R, Vets S, Demeulemeester J, Proost P, Paron I, De Rijck J, Mast J, Bannert N, Gijsbers R, Christ F, Debyser Z (2015) HIV-1 IN/Pol recruits LEDGF/p75 into viral particles. Retrovirology 12:16
Vets S, De Rijck J, Brendel C, Grez M, Bushman F, Debyser Z, Gijsbers R (2013) Transient expression of an LEDGF/p75 chimera retargets lentivector integration and functionally rescues in a model for X-CGD. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 2:e77
Kalpana G, Marmon S, Wang W, Crabtree G, Goff S (1994) Binding and stimulation of HIV-1 integrase by a human homolog of yeast transcription factor SNF5. Science 266:2002–2006
Roberts CWM, Orkin SH (2004) The SWI/SNF complex—chromatin and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 4:133–142
Lesbats P, Botbol Y, Chevereau G, Vaillant C, Calmels C, Arneodo A, Andreola ML, Lavigne M, Parissi V (2011) Functional coupling between HIV-1 integrase and the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex for efficient in vitro integration into stable nucleosomes. PLoS Pathog 7:e1001280
Weinberg JB, Matthews TJ, Cullen BR, Malim MH (1991) Productive human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection of nonproliferating human monocytes. J Exp Med 174:1477–1482
Lewis P, Hensel M, Emerman M (1992) Human immunodeficiency virus infection of cells arrested in the cell cycle. EMBO J 11:3053–3058
Roe T, Reynolds TC, Yu G, Brown PO (1993) Integration of murine leukemia virus DNA depends on mitosis. EMBO J 12:2099–2108
Lewis PF, Emerman M (1994) Passage through mitosis is required for oncoretroviruses but not for the human immunodeficiency virus. J Virol 68:510–516
Matreyek KA, Engelman A (2013) Viral and cellular requirements for the nuclear entry of retroviral preintegration nucleoprotein complexes. Viruses 5:2483–2511
Bukrinsky MI, Sharova N, Dempsey MP, Stanwick TL, Bukrinskaya AG, Haggerty S, Stevenson M (1992) Active nuclear import of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 preintegration complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:6580–6584
Elis E, Ehrlich M, Prizan-Ravid A, Laham-Karam N, Bacharach E (2012) p12 tethers the murine leukemia virus pre-integration complex to mitotic chromosomes. PLoS Pathog 8:e1003103
Schneider WM, Brzezinski JD, Aiyer S, Malani N, Gyuricza M, Bushman FD, Roth MJ (2013) Viral DNA tethering domains complement replication-defective mutations in the p12 protein of MuLV Gag. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:9487–9492
Yamashita M, Emerman M (2004) Capsid is a dominant determinant of retrovirus infectivity in nondividing cells. J Virol 78:5670–5678
Lewinski MK, Yamashita M, Emerman M, Ciuffi A, Marshall H, Crawford G, Collins F, Shinn P, Leipzig J, Hannenhalli S, Berry CC, Ecker JR, Bushman FD (2006) Retroviral DNA integration: viral and cellular determinants of target-site selection. PLoS Pathog 2:e60
Matreyek KA, Yucel SS, Li X, Engelman A (2013) Nucleoporin NUP153 phenylalanine-glycine motifs engage a common binding pocket within the HIV-1 capsid protein to mediate lentiviral infectivity. PLoS Pathog 9:e1003693
Schaller T, Ocwieja KE, Rasaiyaah J, Price AJ, Brady TL, Roth SL, Hue S, Fletcher AJ, Lee K, KewalRamani VN, Noursadeghi M, Jenner RG, James LC, Bushman FD, Towers GJ (2011) HIV-1 capsid-cyclophilin interactions determine nuclear import pathway, integration targeting and replication efficiency. PLoS Pathog 7:e1002439
Price AJ, Fletcher AJ, Schaller T, Elliott T, Lee K, KewalRamani VN, Chin JW, Towers GJ, James LC (2012) CPSF6 defines a conserved capsid interface that modulates HIV-1 replication. PLoS Pathog 8:e1002896
Luban J, Bossolt KL, Franke EK, Kalpana GV, Goff SP (1993) Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Gag protein binds to cyclophilins A and B. Cell 73:1067–1078
Gamble TR, Vajdos FF, Yoo S, Worthylake DK, Houseweart M, Sundquist WI, Hill CP (1996) Crystal structure of human cyclophilin A bound to the amino-terminal domain of HIV-1 capsid. Cell 87:1285–1294
De Iaco A, Luban J (2014) Cyclophilin A promotes HIV-1 reverse transcription but its effect on transduction correlates best with its effect on nuclear entry of viral cDNA. Retrovirology 11:11
Ocwieja KE, Brady TL, Ronen K, Huegel A, Roth SL, Schaller T, James LC, Towers GJ, Young JA, Chanda SK, Konig R, Malani N, Berry CC, Bushman FD (2011) HIV integration targeting: a pathway involving Transportin-3 and the nuclear pore protein RanBP2. PLoS Pathog 7:e1001313
Di Nunzio F, Fricke T, Miccio A, Valle-Casuso JC, Perez P, Souque P, Rizzi E, Severgnini M, Mavilio F, Charneau P, Diaz-Griffero F (2013) Nup153 and Nup98 bind the HIV-1 core and contribute to the early steps of HIV-1 replication. Virology 440:8–18
Koh Y, Wu X, Ferris AL, Matreyek KA, Smith SJ, Lee K, KewalRamani VN, Hughes SH, Engelman A (2013) Differential effects of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 capsid and cellular factors nucleoporin 153 and LEDGF/p75 on the efficiency and specificity of viral DNA integration. J Virol 87:648–658
Konig R, Zhou Y, Elleder D, Diamond TL, Bonamy GM, Irelan JT, Chiang CY, Tu BP, De Jesus PD, Lilley CE (2008) Global analysis of host-pathogen interactions that regulate early-stage HIV-1 replication. Cell 135:49–60
Di Nunzio F (2013) New insights in the role of nucleoporins: a bridge leading to concerted steps from HIV-1 nuclear entry until integration. Virus Res 178:187–196
Pornillos O, Ganser-Pornillos BK, Kelly BN, Hua Y, Whitby FG, Stout CD, Sundquist WI, Hill CP, Yeager M (2009) X-ray structures of the hexameric building block of the HIV capsid. Cell 137:1282–1292
Pornillos O, Ganser-Pornillos BK, Yeager M (2011) Atomic-level modelling of the HIV capsid. Nature 469:424–427
Sundquist WI, Kräusslich H-G (2012) HIV-1 assembly, budding, and maturation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2:a006924
Saito A, Henning MS, Serrao E, Dubose BN, Teng S, Huang J, Li X, Saito N, Roy SP, Siddiqui MA, Ahn J, Tsuji M, Hatziioannou T, Engelman AN, Yamashita M (2016) Capsid-CPSF6 interaction is dispensable for HIV-1 replication in primary cells but is selected during virus passage in vivo. J Virol 90:6918–6935
Bichel K, Price AJ, Schaller T, Towers GJ, Freund SM, James LC (2013) HIV-1 capsid undergoes coupled binding and isomerization by the nuclear pore protein NUP358. Retrovirology 10:81
Lin DH, Zimmermann S, Stuwe T, Stuwe E, Hoelz A (2013) Structural and functional analysis of the C-terminal domain of Nup358/RanBP2. J Mol Biol 425:1318–1329
Yamashita M, Engelman AN (2017) Capsid-dependent host factors in HIV-1 infection. Trends Microbiol 25:741–755
Yokoyama N, Hayashi N, Seki T, Pante N, Ohba T, Nishii K, Kuma K, Hayashida T, Miyata T, Aebi U (1995) A giant nucleopore protein that binds Ran/TC4. Nature 376:184–188
Wu J, Matunis MJ, Kraemer D, Blobel G, Coutavas E (1995) Nup358, a cytoplasmically exposed nucleoporin with peptide repeats, Ran-GTP binding sites, zinc fingers, a cyclophilin A homologous domain, and a leucine-rich region. J Biol Chem 270:14209–14213
Dharan A, Talley S, Tripathi A, Mamede JI, Majetschak M, Hope TJ, Campbell EM (2016) KIF5B and Nup358 cooperatively mediate the nuclear import of HIV-1 during infection. PLoS Pathog 12:e1005700
Roth SL, Malani N, Bushman FD (2011) Gammaretroviral integration into nucleosomal target DNA in vivo. J Virol 85:7393–7401
Maertens GN, Cook NJ, Wang W, Hare S, Gupta SS, Öztop I, Lee K, Pye VE, Cosnefroy O, Snijders AP, KewalRamani VN, Fassati A, Engelman A, Cherepanov P (2014) Structural basis for nuclear import of splicing factors by human Transportin 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:2728–2733
Peng K, Muranyi W, Glass B, Laketa V, Yant SR, Tsai L, Cihlar T, Müller B, Kräusslich H-G (2014) Quantitative microscopy of functional HIV post-entry complexes reveals association of replication with the viral capsid. eLife 3:e04114
Chin CR, Perreira JM, Savidis G, Portmann JM, Aker AM, Feeley EM, Smith MC, Brass AL (2015) Direct visualization of HIV-1 replication intermediates shows that capsid and CPSF6 modulate HIV-1 intra-nuclear invasion and integration. Cell Rep 13:1717–1731
De Iaco A, Santoni F, Vannier A, Guipponi M, Antonarakis S, Luban J (2013) TNPO3 protects HIV-1 replication from CPSF6-mediated capsid stabilization in the host cell cytoplasm. Retrovirology 10:20
Fricke T, Valle-Casuso JC, White TE, Brandariz-Nuñez A, Bosche WJ, Reszka N, Gorelick R, Diaz-Griffero F (2013) The ability of TNPO3-depleted cells to inhibit HIV-1 infection requires CPSF6. Retrovirology 10:46
Hori T, Takeuchi H, Saito H, Sakuma R, Inagaki Y, Yamaoka S (2013) A carboxy-terminally truncated human CPSF6 lacking residues encoded by exon 6 inhibits HIV-1 cDNA synthesis and promotes capsid disassembly. J Virol 87:7726–7736
Meehan AM, Saenz DT, Morrison J, Hu C, Peretz M, Poeschla EM (2011) LEDGF dominant interference proteins demonstrate prenuclear exposure of HIV-1 integrase and synergize with LEDGF depletion to destroy viral infectivity. J Virol 85:3570–3583
Yan N, Cherepanov P, Daigle JE, Engelman A, Lieberman J (2009) The SET complex acts as a barrier to autointegration of HIV-1. PLoS Pathog 5:e1000327
Gérard A, Soler N, Ségéral E, Belshan M, Emiliani S (2013) Identification of low molecular weight nuclear complexes containing integrase during the early stages of HIV-1 infection. Retrovirology 10:13
Botbol Y, Raghavendra NK, Rahman S, Engelman A, Lavigne M (2008) Chromatinized templates reveal the requirement for the LEDGF/p75 PWWP domain during HIV-1 integration in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res 36:1237–1246
McKee CJ, Kessl JJ, Shkriabai N, Dar MJ, Engelman A, Kvaratskhelia M (2008) Dynamic modulation of HIV-1 integrase structure and function by cellular lens epithelium-derived growth factor (LEDGF) protein. J Biol Chem 283:31802–31812
Zhyvoloup A, Melamed A, Anderson I, Planas D, Lee CH, Kriston-Vizi J, Ketteler R, Merritt A, Routy JP, Ancuta P, Bangham CRM, Fassati A (2017) Digoxin reveals a functional connection between HIV-1 integration preference and T-cell activation. PLoS Pathog 13:e1006460
Dettwiler S, Aringhieri C, Cardinale S, Keller W, Barabino SML (2004) Distinct sequence motifs within the 68-kDa subunit of cleavage factor Im mediate RNA binding, protein-protein interactions, and subcellular localization. J Biol Chem 279:35788–35797
Lee K, Mulky A, Yuen W, Martin TD, Meyerson NR, Choi L, Yu H, Sawyer SL, Kewalramani VN (2012) HIV-1 capsid-targeting domain of cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor 6. J Virol 86:3851–3860
Bhattacharya A, Alam SL, Fricke T, Zadrozny K, Sedzicki J, Taylor AB, Demeler B, Pornillos O, Ganser-Pornillos BK, Diaz-Griffero F, Ivanov DN, Yeager M (2014) Structural basis of HIV-1 capsid recognition by PF74 and CPSF6. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:18625–18630
Price AJ, Jacques DA, McEwan WA, Fletcher AJ, Essig S, Chin JW, Halambage UD, Aiken C, James LC (2014) Host cofactors and pharmacologic ligands share an essential interface in HIV-1 capsid that is lost upon disassembly. PLoS Pathog 10:e1004459
Lee BJ, Cansizoglu AE, Süel KE, Louis TH, Zhang Z, Chook YM (2006) Rules for nuclear localization sequence recognition by karyopherin beta2. Cell 126:543–558
Rüegsegger U, Beyer K, Keller W (1996) Purification and characterization of human cleavage factor I involved in the 3′ end processing of messenger RNA precursors. J Biol Chem 271:6107–6113
Gruber AR, Martin G, Keller W, Zavolan M (2012) Cleavage factor Im is a key regulator of 3′ UTR length. RNA Biol 9:1405–1412
Martin G, Gruber AR, Keller W, Zavolan M (2012) Genome-wide analysis of pre-mRNA 3′ end processing reveals a decisive role of human cleavage factor I in the regulation of 3′ UTR length. Cell Rep 1:753–763
Yang Q, Coseno M, Gilmartin GM, Doublié S (2011) Crystal structure of a human cleavage factor CFIm25/CFIm68/RNA complex provides an insight into poly(A) site recognition and RNA looping. Structure 19:368–377
Rasheedi S, Shun M-C, Serrao E, Sowd GA, Qian J, Hao C, Dasgupta T, Engelman AN, Skowronski J (2016) The cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor 6 (CPSF6) subunit of the capsid-recruited pre-messenger RNA cleavage factor I (CFIm) complex mediates HIV-1 integration into genes. J Biol Chem 291:11809–11819
Cardinale S, Cisterna B, Bonetti P, Aringhieri C, Biggiogera M, Barabino SML (2007) Subnuclear localization and dynamics of the pre-mRNA 3′ end processing factor mammalian cleavage factor I 68-kDa subunit. Mol Biol Cell 18:1282–1292
Katahira J, Okuzaki D, Inoue H, Yoneda Y, Maehara K, Ohkawa Y (2013) Human TREX component Thoc5 affects alternative polyadenylation site choice by recruiting mammalian cleavage factor I. Nucleic Acids Res 41:7060–7072
Lusic M, Siliciano RF (2016) Nuclear landscape of HIV-1 infection and integration. Nat Rev Microbiol 15:69–82
Vranckx LS, Demeulemeester J, Saleh S, Boll A, Vansant G, Schrijvers R, Weydert C, Battivelli E, Verdin E, Cereseto A, Christ F, Gijsbers R, Debyser Z (2016) LEDGIN-mediated inhibition of integrase–LEDGF/p75 interaction reduces reactivation of residual latent HIV. EBioMedicine 8:248–264
Quercioli V, Di Primio C, Casini A, Mulder LCF, Vranckx LS, Borrenberghs D, Gijsbers R, Debyser Z, Cereseto A (2016) Comparative analysis of HIV-1 and murine leukemia virus three-dimensional nuclear distributions. J Virol 90:5205–5209
Burdick RC, Delviks-Frankenberry KA, Chen J, Janaka SK, Sastri J, Hu WS, Pathak VK (2017) Dynamics and regulation of nuclear import and nuclear movements of HIV-1 complexes. PLoS Pathog 13:e1006570
Maertens GN, Hare S, Cherepanov P (2010) The mechanism of retroviral integration from X-ray structures of its key intermediates. Nature 468:326–329
Johnson RC, Stella S, Heiss JK (2008) Bending and compaction of DNA by proteins. In: Rice PA, Correll CC (eds) Protein-nucleic acid interactions. RCS Publishing, London, pp 176–220
Demeulemeester J, Vets S, Schrijvers R, Madlala P, De Maeyer M, De Rijck J, Ndung’u T, Debyser Z, Gijsbers R (2014) HIV-1 integrase variants retarget viral integration and are associated with disease progression in a chronic infection cohort. Cell Host Microbe 16:651–662
Maskell DP, Renault L, Serrao E, Lesbats P, Matadeen R, Hare S, Lindemann D, Engelman AN, Costa A, Cherepanov P (2015) Structural basis for retroviral integration into nucleosomes. Nature 523:366–369
De Rijck J, Vandekerckhove L, Gijsbers R, Hombrouck A, Hendrix J, Vercammen J, Engelborghs Y, Christ F, Debyser Z (2006) Overexpression of the lens epithelium-derived growth factor/p75 integrase binding domain inhibits human immunodeficiency virus replication. J Virol 80:11498–11509
Fader LD, Malenfant E, Parisien M, Carson R, Bilodeau F, Landry S, Pesant M, Brochu C, Morin S, Chabot C, Halmos T, Bousquet Y, Bailey MD, Kawai SH, Coulombe R, LaPlante S, Jakalian A, Bhardwaj PK, Wernic D, Schroeder P, Amad M, Edwards P, Garneau M, Duan J, Cordingley M, Bethell R, Mason SW, Bös M, Bonneau P, Poupart MA, Faucher AM, Simoneau B, Fenwick C, Yoakim C, Tsantrizos Y (2014) Discovery of BI 224436, a noncatalytic site integrase inhibitor (NCINI) of HIV-1. ACS Med Chem Lett 5:422–427
Christ F, Voet A, Marchand A, Nicolet S, Desimmie BA, Marchand D, Bardiot D, Van der Veken NJ, Van Remoortel B, Strelkov SV, De Maeyer M, Chaltin P, Debyser Z (2010) Rational design of small-molecule inhibitors of the LEDGF/p75-integrase interaction and HIV replication. Nat Chem Biol 6:442–448
Fenwick C, Amad M, Bailey MD, Bethell R, Bös M, Bonneau P, Cordingley M, Coulombe R, Duan J, Edwards P, Fader LD, Faucher AM, Garneau M, Jakalian A, Kawai S, Lamorte L, LaPlante S, Luo L, Mason S, Poupart MA, Rioux N, Schroeder P, Simoneau B, Tremblay S, Tsantrizos Y, Witvrouw M, Yoakim C (2014) Preclinical profile of BI 224436, a novel HIV-1 non-catalytic-site integrase inhibitor. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 58:3233–3244
Kessl JJ, Jena N, Koh Y, Taskent-Sezgin H, Slaughter A, Feng L, de Silva S, Wu L, Le Grice SF, Engelman A, Fuchs JR, Kvaratskhelia M (2012) Multimode, cooperative mechanism of action of allosteric HIV-1 integrase inhibitors. J Biol Chem 287:16801–16811
Balakrishnan M, Yant SR, Tsai L, O’Sullivan C, Bam RA, Tsai A, Niedziela-Majka A, Stray KM, Sakowicz R, Cihlar T (2013) Non-catalytic site HIV-1 integrase inhibitors disrupt core maturation and induce a reverse transcription block in target cells. PLoS One 8:e74163
Le Rouzic E, Bonnard D, Chasset S, Bruneau JM, Chevreuil F, Le Strat F, Nguyen J, Beauvoir R, Amadori C, Brias J, Vomscheid S, Eiler S, Levy N, Delelis O, Deprez E, Saib A, Zamborlini A, Emiliani S, Ruff M, Ledoussal B, Moreau F, Benarous R (2013) Dual inhibition of HIV-1 replication by integrase-LEDGF allosteric inhibitors is predominant at the post-integration stage. Retrovirology 10:144
Desimmie BA, Schrijvers R, Demeulemeester J, Borrenberghs D, Weydert C, Thys W, Vets S, Van Remoortel B, Hofkens J, De Rijck J, Hendrix J, Bannert N, Gijsbers R, Christ F, Debyser Z (2013) LEDGINs inhibit late stage HIV-1 replication by modulating integrase multimerization in the virions. Retrovirology 10:57
Jurado KA, Wang H, Slaughter A, Feng L, Kessl JJ, Koh Y, Wang W, Ballandras-Colas A, Patel PA, Fuchs JR, Kvaratskhelia M, Engelman A (2013) Allosteric integrase inhibitor potency is determined through the inhibition of HIV-1 particle maturation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:8690–8695
Gupta K, Brady T, Dyer BM, Malani N, Hwang Y, Male F, Nolte RT, Wang L, Velthuisen E, Jeffrey J, Van Duyne GD, Bushman FD (2014) Allosteric inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus integrase: late block during viral replication and abnormal multimerization involving specific protein domains. J Biol Chem 289:20477–20488
Sharma A, Slaughter A, Jena N, Feng L, Kessl JJ, Fadel HJ, Malani N, Male F, Wu L, Poeschla E, Bushman FD, Fuchs JR, Kvaratskhelia M (2014) A new class of multimerization selective inhibitors of HIV-1 integrase. PLoS Pathog 10:e1004171
van Gent DC, Elgersma Y, Bolk MWJ, Vink C, Plasterk RHA (1991) DNA binding properties of the integrase proteins of human immunodeficiency viruses types 1 and 2. Nucleic Acids Res 19:3821–3827
Engelman A, Bushman FD, Craigie R (1993) Identification of discrete functional domains of HIV-1 integrase and their organization within an active multimeric complex. EMBO J 12:3269–3275
Vincent KA, Ellison V, Chow SA, Brown PO (1993) Characterization of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase expressed in Escherichia coli and analysis of variants with amino-terminal mutations. J Virol 67:425–437
Taddeo B, Carlini F, Verani P, Engelman A (1996) Reversion of a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase mutant at a second site restores enzyme function and virus infectivity. J Virol 70:8277–8284
Hayouka Z, Rosenbluh J, Levin A, Loya S, Lebendiker M, Veprintsev D, Kotler M, Hizi A, Loyter A, Friedler A (2007) Inhibiting HIV-1 integrase by shifting its oligomerization equilibrium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:8316–8321
Hare S, Di Nunzio F, Labeja A, Wang J, Engelman A, Cherepanov P (2009) Structural basis for functional tetramerization of lentiviral integrase. PLoS Pathog 5:e1000515
Pandey KK, Bera S, Grandgenett DP (2011) The HIV-1 integrase monomer induces a specific interaction with LTR DNA for concerted integration. Biochemistry 50:9788–9796
Raghavendra NK, Engelman A (2007) LEDGF/p75 interferes with the formation of synaptic nucleoprotein complexes that catalyze full-site HIV-1 DNA integration in vitro: implications for the mechanism of viral cDNA integration. Virology 360:1–5
Kessl JJ, Li M, Ignatov M, Shkriabai N, Eidahl JO, Feng L, Musier-Forsyth K, Craigie R, Kvaratskhelia M (2011) FRET analysis reveals distinct conformations of IN tetramers in the presence of viral DNA or LEDGF/p75. Nucleic Acids Res 39:9009–9022
Feng L, Dharmarajan V, Serrao E, Hoyte A, Larue RC, Slaughter A, Sharma A, Plumb MR, Kessl JJ, Fuchs JR, Bushman FD, Engelman AN, Griffin PR, Kvaratskhelia M (2016) The competitive interplay between allosteric HIV-1 integrase inhibitor BI/D and LEDGF/p75 during the early stage of HIV-1 replication adversely affects inhibitor potency. ACS Chem Biol 11:1313–1321
Deng N, Hoyte A, Mansour YE, Mohamed MS, Fuchs JR, Engelman AN, Kvaratskhelia M, Levy R (2016) Allosteric HIV-1 integrase inhibitors promote aberrant protein multimerization by directly mediating inter-subunit interactions: structural and thermodynamic modeling studies. Protein Sci 25:1911–1917
Gupta K, Turkki V, Sherrill-Mix S, Hwang Y, Eilers G, Taylor L, McDanal C, Wang P, Temelkoff D, Nolte RT, Velthuisen E, Jeffrey J, Van Duyne GD, Bushman FD (2016) Structural basis for inhibitor-induced aggregation of HIV integrase. PLoS Biol 14:e1002584
Tsiang M, Jones GS, Niedziela-Majka A, Kan E, Lansdon EB, Huang W, Hung M, Samuel D, Novikov N, Xu Y, Mitchell M, Guo H, Babaoglu K, Liu X, Geleziunas R, Sakowicz R (2012) New class of HIV-1 integrase (IN) inhibitors with a dual mode of action. J Biol Chem 287:21189–21203
Fontana J, Jurado KA, Cheng N, Ly NL, Fuchs JR, Gorelick RJ, Engelman AN, Steven AC (2015) Distribution and redistribution of HIV-1 nucleocapsid protein in immature, mature, and integrase-inhibited virions: a role for integrase in maturation. J Virol 89:9765–9780
Engelman A (1999) In vivo analysis of retroviral integrase structure and function. Adv Virus Res 52:411–426
Engelman A (2011) Pleiotropic nature of HIV-1 integrase mutations. In: Neamati N (ed) HIV-1 integrase: mechanism and inhibitor design. Wiley, Hoboken, pp 67–81
Engelman A, Englund G, Orenstein JM, Martin MA, Craigie R (1995) Multiple effects of mutations in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase on viral replication. J Virol 69:2729–2736
Johnson BC, Métifiot M, Ferris A, Pommier Y, Hughes SH (2013) A homology model of HIV-1 integrase and analysis of mutations designed to test the model. J Mol Biol 425:2133–2146
Madison MK, Lawson DQ, Elliott J, Ozantürk AN, Koneru PC, Townsend D, Errando M, Kvaratskhelia M, Kutluay SB (2017) Allosteric HIV-1 integrase inhibitors lead to premature degradation of the viral RNA genome and integrase in target cells. J Virol 91:e00821–00817
Kessl JJ, Kutluay SB, Townsend D, Rebensburg S, Slaughter A, Larue RC, Shkriabai N, Bakouche N, Fuchs JR, Bieniasz PD, Kvaratskhelia M (2016) HIV-1 integrase binds the viral RNA genome and is essential during virion morphogenesis. Cell 166(1257–1268):e1212
Chun T-W, Stuyver L, Mizell SB, Ehler LA, Mican JAM, Baseler M, Lloyd AL, Nowak MA, Fauci AS (1997) Presence of an inducible HIV-1 latent reservoir during highly active antiretroviral therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:13193–13197
Chun TW, Fauci AS (2012) HIV reservoirs: pathogenesis and obstacles to viral eradication and cure. AIDS 26:1261–1268
Maldarelli F, Wu X, Su L, Simonetti FR, Shao W, Hill S, Spindler J, Ferris AL, Mellors JW, Kearney MF, Coffin JM, Hughes SH (2014) Specific HIV integration sites are linked to clonal expansion and persistence of infected cells. Science 345:179–183
Wagner TA, McLaughlin S, Garg K, Cheung CY, Larsen BB, Styrchak S, Huang HC, Edlefsen PT, Mullins JI, Frenkel LM (2014) Proliferation of cells with HIV integrated into cancer genes contributes to persistent infection. Science 345:570–573
Ho YC, Shan L, Hosmane NN, Wang J, Laskey SB, Rosenbloom DI, Lai J, Blankson JN, Siliciano JD, Siliciano RF (2013) Replication-competent noninduced proviruses in the latent reservoir increase barrier to HIV-1 cure. Cell 155:540–551
Cohn LB, Silva IT, Oliveira TY, Rosales RA, Parrish EH, Learn GH, Hahn BH, Czartoski JL, McElrath MJ, Lehmann C, Klein F, Caskey M, Walker BD, Siliciano JD, Siliciano RF, Jankovic M, Nussenzweig MC (2015) HIV-1 integration landscape during latent and active infection. Cell 160:420–432
Simonetti FR, Sobolewski MD, Fyne E, Shao W, Spindler J, Hattori J, Anderson EM, Watters SA, Hill S, Wu X, Wells D, Su L, Luke BT, Halvas EK, Besson G, Penrose KJ, Yang Z, Kwan RW, Van Waes C, Uldrick T, Citrin DE, Kovacs J, Polis MA, Rehm CA, Gorelick R, Piatak M, Keele BF, Kearney MF, Coffin JM, Hughes SH, Mellors JW, Maldarelli F (2016) Clonally expanded CD4+ T cells can produce infectious HIV-1 in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:1883–1888
Hughes SH, Coffin JM (2016) What integration sites tell us about HIV persistence. Cell Host Microbe 19:588–598
Darcis G, Van Driessche B, Van Lint C (2017) HIV latency: should we shock or lock? Trends Immunol 38:217–228
Chen HC, Martinez JP, Zorita E, Meyerhans A, Filion GJ (2017) Position effects influence HIV latency reversal. Nat Struct Mol Biol 24:47–54
Gres AT, Kirby KA, KewalRamani VN, Tanner JJ, Pornillos O, Sarafianos SG (2015) X-ray crystal structures of native HIV-1 capsid protein reveal conformational variability. Science 349:99–103
Acknowledgements
Work in the corresponding author’s laboratory is funded by Grants AI039394 and AI052014 from the US National Institutes of Health. The authors thank Vasudevan Achuthan, Gregory Bedwell, and Sooin Jang for their critical review of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Engelman, A.N., Singh, P.K. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of HIV-1 integration targeting. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 75, 2491–2507 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-018-2772-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-018-2772-5