Abstract
Objective
Systemic leukocyte activation is claimed to trigger inflammatory response and remote organ dysfunction in acute pancreatitis. Chemokines are inflammatory mediators with potent leukocyte-activating properties and have been shown to be involved in the pathophysiological process of experimental acute pancreatitis. However, as little is known about their role in human disease we investigated local and systemic concentrations of different CC-chemokine members in patients with acute pancreatitis.
Patients and methods
We included 68 patients with acute pancreatitis in the present study. Local complications in terms of necrosis were present in 37 (54%) patients of whom 21 (57%) developed pancreatic infections. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), macrophage inflammatory protein-1α (MIP-1α) and macrophage inflammatory protein-1β (MIP-1β) concentrations were measured daily over 2 weeks after study inclusion by ELISA in sera and lesser sac aspirates.
Results
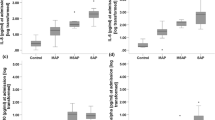
MCP-1 serum concentrations showed a dramatic increase in patients who developed local complications and/or remote organ failure. Herein, a close correlation was found between the severity of remote organ failure and the degree of MCP-1 elevation. Multiple regression analysis identified pancreatic infections as well as renal and cardiocirculatory failure as independent variables associated with enhanced systemic MCP-1 release. MIP-1α levels remained unaffected by local complications and showed a significant increase only; if multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) developed or patients subsequently died. In contrast, MIP-1β concentrations correlated with neither the presence nor the severity of any complication. Compared with systemic concentrations, local lesser sac aspirates revealed significantly higher levels of MCP-1, whereas MIP-1α and MIP-1β were not different.
Conclusions
Complicated acute pancreatitis is associated with significantly elevated local and systemic concentrations of the CC-chemokine MCP-1. Our results suggest that, among the CC-chemokine members investigated, MCP-1 might play a pivotal role in the pathological mechanism of complicated acute pancreatitis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beger HG, Bittner R, Block S, Büchler M (1986) Bacterial contamination of pancreatic necrosis. Gastroenterology 49:433–438
Isenmann R, Rau B, Beger HG (1999) Bacterial infection and extent of necrosis are determinants of organ failure in patients with acute necrotising pancreatitis. Br J Surg 86:1020–1024
Tran DD, Cuesta MA, Schneider AJ, Wesdorp RI (1993) Prevalence and prediction of multiple organ system failure and mortality in acute pancreatitis. J Crit Care 8:145–153
Tenner S, Sica G, Hughes M, Noordhoek E, Feng S, Zinner M, Banks PA (1997) Relationship of necrosis to organ failure in severe acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 113:899–903
Banerjee AK, Kaul A, Bache E, Doran J, Nicholson ML (1994) Multicentre audit of death from acute pancreatitis. Br J Surg 81:1541
Rinderknecht H (1994) Genetic determinants of mortality in acute necrotizing pancreatitis. Int J Pancreatol 16:11–15
Inoue S, Nakao A, Kishimoto W, Murakami H, Harada A, Nonami T, Takagi H (1996) LFA–1 (CD11a/CD18) and ICAM–1 (CD54) antibodies attenuate superoxide anion release from polymorphonuclear leukocytes in rats with experimental acute pancreatitis. Pancreas 12:183–188
Rau B, Poch B, Gansauge F, Bauer A, Nüssler AK, Nevalainen T, Schoenberg MH, Beger HG (2000) Pathophysiological role of oxygen free radicals in acute pancreatitis: initiating event or mediator of tissue damage? Ann Surg 231:352–360
Norman J (1998) The role of cytokines in the pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis. Am J Surg 175:76–83
Brady M, Christmas S, Sutton R, Neoptolemos J, Slavin J (1999) Cytokines and acute pancreatitis. Baillieres Clin Gastroenterol 13:265–289
Rollins BJ (1997) Chemokines. Blood 90:909–928
Premark BA, Schall TJ (1996) Chemokine receptors: gateway to inflammation and infection. Nat Med 11:1174–1178
Murphy PM (1994) The molecular biology of leukocyte chemoattractant receptors. Ann Rev Immunol 12:593–633
Grady T, Liang P, Ernst SA, Logsdon CD (1997) Chemokine gene expression in rat pancreatic acinar cells is an early event associated with acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 113:1966–1975
Bhatia M, Brady M, Christmas S, Neoptolemos JP, Slavin J (1999) Effect of caerulein on chemokine production from cultured rat pancreatic acini (abstract). Pancreas 19:415
Yang BM, Demaine AG, Kingsnorth A (2000) Chemokines MCP-1 and RANTES in isolated rat pancreatic acinar cells treated with CCK and ethanol in vitro. Pancreas 21:22–31
Bhatia M, Brady M, Zagorski J, Christmas SE, Campbell F, Neoptolemos JP, Slavin J (2000) Treatment with neutralizing antibody against cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant (CINC) protects rats against acute pancreatitis associated lung injury. Gut 47:838–844
Gerard C, Frossard JL, Bhatia M, Saluja A, Gerard NP, Lu B, Steer ML (1997) Trageted disruption of the β–chemokine receptor CCR-1 protects against pancreatitis associated lung injury. J Clin Invest 100:2022–2027
Shokui S, Bhatia M, Brady M, Christmas S, Neoptolemos JP, Slavin J (2000) Plasma levels of the CXC-chemokines ENA-78 and GRO-α are elevated in severe pancreatitis (abstract). Digestion 61:284
Rau B, Steinbach G, Gansauge F, Mayer J, Grunert A, Beger HG (1997) The potential role of procalcitonin and interleukin-8 in the prediction of infected necrosis in acute pancreatitis. Gut 41:832–840
Schoonjans F, Zalata A, Depuydt CE, Comhaire FH (1995) MedCalc: a new computer program for medical statistics. Comp Meth Prog Biomed 48:257–262
Wang X, Andersson R, Soltesz V, Leveau P, Ihse I (1996) Gut origin sepsis, macrophage function and oxygen extraction associated with acute pancreatitis in the rat. World J Surg 20:299–307
Andersson R, Deng XM, Wang XD (1997) Role of macrophage overactivation in the development of acute pancreatitis injury in rats. Br J Surg 84:775–780
Yang J, Denham W, Tracey KJ, Wang H, Kramer AA, Salhab KF, Norman J (1998) The physiologic consequences of macrophage pacification during severe acute pancreatitis. Shock 10:169–175
Yang J, Denham W, Carter G, Tracey KJ, Norman J (1998) Macrophage pacification reduces rodent pancreatitis-induced hepatocellular injury through down-regulation of hepatic tumor necrosis factor α and interleukin-1β. Hepatology 28:1282–1288
Yamaguchi Y, Okabe K, Liang J, Matsumura F, Akizuki E, Matsuda T, Ohshiro H, Nakano S, Ishihara K, Ogawa M (1999) The novel carboxamide derivate IS–741 reduces neutrophil chemoattractant production by bronchoalveolar macrophages in rats with cerulein-induced pancreatitis complicated by sepsis. Digestion 60:152–160
Fink GW, Norman J (1996) Intrapancreatic interleukin-1 beta gene expression by specific leukocyte populations during acute pancreatitis. J Surg Res 63:369–373
Denham W, Norman J (1999) The potential role of therapeutic cytokine manipulations in acute pancreatitis. Surg Clin North Am 79:767–781
Jiang Y, Beller DI, Frendl G, Graves DT (1992) Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 regulates adhesion molecule expression and cytokine production in human monocytes. J Immunol 148:2423–2428
Boring L, Gosling J, Chensue SW, Kunkel SL, Farese RV, Broxmeyer HE, Charo IF (1997) Impaired monocyte migration and reduced type 1 (Th1) cytokine responses in CC-chemokine receptor-2 knockout mice. J Clin Invest 100:2552–2561
Lu B, Rutledge BJ, Gu L, Fiorillo J, Lukacs NW, Kunkel SL, North R, Gerard C, Rollins BJ (1997) Abnormalities in monocyte recruitment and cytokine expression in monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 deficient mice. J Exp Med 187:601–608
Capelli A, Di Stefano A, Gnemmi I, Balbo P, Cerutti CG, Balbi B, Lusuardi M, Donner CF (1999) Increased MCP-1 and MIP-1β in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of chronic bronchitis. Eur Respir J 14:160–165
Fisher NC, Neil DAH, Williams A, Adams DH (1999) Serum concentrations and peripheral secretion of the beta chemokines monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 and macrophage inflammatory protein 1α in alcoholic liver disease. Gut 45:416–420
Uguccioni M, Gionchetti P, Robbiani DF, Rizzello F, Peruzzo S, Campieri M, Baggiolini M (1999) Increased expression of IP-10, IL-8, MCP-1 and MCP-3 in ulcerative colitis. Am J Pathol 155:331–336
Saurer L, Reber P, Schaffner T, Büchler MW, Buri C, Kappeler A, Walz A, Friess H, Mueller C (2000) Differential expression of chemokines in normal pancreas and chronic pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 118:356–367
Acknowledgements
This work was, in part, supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, grant SFB/A6 to B. Rau.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rau, B., Baumgart, K., Krüger, C.M. et al. CC-chemokine activation in acute pancreatitis: enhanced release of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in patients with local and systemic complications. Intensive Care Med 29, 622–629 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-003-1668-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-003-1668-4