Abstract
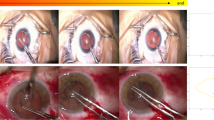
To increase the timeliness, objectivity, and efficiency in evaluating ophthalmology residents’ learning of cataract surgery, an automatic analysis system for cataract surgery videos is developed to assess performance, particularly in the capsulorhexis step on the Kitaro simulator. We utilize computer vision technologies to measure performance of this critical step including duration, size, centrality, circularity, as well as motion stability during the capsulorhexis procedure. Consequently, a grading mechanism is established based on either linear regression or non-linear classification via Support Vector Machine of those computed measures. Comparisons of expert graders to the computer vision-based approach have demonstrated the accuracy and consistency of the computerized technique.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kitaro kits from fci ophthalmics. http://www.fci-ophthalmics.com/blog/category/kitaro-kits/. Accessed 30 June 2014 (2011)
Ahad, M.A.: Motion history image. In: Motion history images for action recognition and understanding, pp. 31–76. Springer (2013)
Ahmidi, N., Ishii, M., Fichtinger, G., Gallia, G.L., Hager, G.D.: Anobjective and automated method for assessing surgical skill in endoscopic sinus surgery using eye-tracking and tool-motion data. In: International forum of allergy & rhinology, vol. 2, pp. 507–515. Wiley Online Library (2012)
Ballard, D.H.: Generalizing the hough transform to detect arbitrary shapes. Pattern Recognit. 13(2), 111–122 (1981)
Barron, J.L., Fleet, D.J., Beauchemin, S.S.: Performance of optical flow techniques. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 12(1), 43–77 (1994)
Bertalmio, M., Sapiro, G., Caselles, V., Ballester, C.: Image inpainting. In: Proceedings of the 27th annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques, pp. 417–424. ACM Press/Addison-Wesley Publishing Co. (2000)
Bhatia, B., Oates, T., Xiao, Y., Hu, P.: Real-time identification of operating room state from video. In: AAAI, pp. 1761–1766 (2007)
Black, M.J., Yacoob, Y.: Tracking and recognizing rigid and non-rigid facial motions using local parametric models of image motion. In: IEEE Proceedings, Fifth International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 374–381 (1995)
Blum, T., Feußner, H., Navab, N.: Modeling and segmentation of surgical workflow from laparoscopic video. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention-MICCAI 2010, pp. 400–407. Springer (2010)
Bouget, D., Lalys, F., Jannin, P., et al.: Surgical tools recognition and pupil segmentation for cataract surgical process modeling. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 173, 78–84 (2012)
Bradski, G.R., Davis, J.W.: Motion segmentation and pose recognition with motion history gradients. Mach. Vis. Appl. 13(3), 174–184 (2002)
Chanwimaluang, T., Fan, G.: An efficient blood vessel detection algorithm for retinal images using local entropy thresholding. In: IEEE Proceedings of the 2003 International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, 2003, ISCAS’03, vol. 5, pp. V-21 (2003)
Chutatape, O., Zheng, L., Krishnan, S.: Retinal blood vessel detection and tracking by matched gaussian and kalman filters. In: IEEE Proceedings of the 20th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 1998, vol. 6, pp. 3144–3149 (1998)
Cohen, J.: Weighted kappa: Nominal scale agreement provision for scaled disagreement or partial credit. Psychol. Bull. 70(4), 213 (1968)
Cortes, C., Vapnik, V.: Support vector machine. Mach. Learn. 20(3), 273–297 (1995)
Criminisi, A., Pérez, P., Toyama, K.: Region filling and object removal by exemplar-based image inpainting. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 13(9), 1200–1212 (2004)
Duan, F., Zhang, Y., Pongthanya, N., Watanabe, K., Yokoi, H., Arai, T.: Analyzing human skill through control trajectories and motion capture data. In: IEEE International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering, IEEE 2008. CASE 2008, pp. 454–459 (2008)
Duda, R.O., Hart, P.E.: Use of the hough transformation to detect lines and curves in pictures. Commun. ACM 15(1), 11–15 (1972)
Forgy, E.W.: Cluster analysis of multivariate data: efficiency versus interpretability of classifications. Biometrics 21, 768–769 (1965)
Hance, G.A., Umbaugh, S.E., Moss, R.H., Stoecker, W.V.: Unsupervised color image segmentation: with application to skin tumor borders. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 15(1), 104–111 (1996)
Horiguchi, M., Miyake, K., Ohta, I., Ito, Y.: Staining of the lens capsule for circular continuous capsulorrhexis in eyes with white cataract. Arch. Ophthalmol. 116(4), 535 (1998)
Horn, B.K., Schunck, B.G.: Determining optical flow. Artif. Intell. 17(1), 185–203 (1981)
Jiang, X., Mojon, D.: Adaptive local thresholding by verification-based multithreshold probing with application to vessel detection in retinal images. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 25(1), 131–137 (2003)
Jolliffe, I.: Principal component analysis. Wiley Online Library, New York (2005)
Kahol, K., Krishnan, N.C., Balasubramanian, V.N., Panchanathan, S., Smith, M., Ferrara, J.: Measuring movement expertise in surgical tasks. In: Proceedings of the 14th annual ACM international conference on Multimedia, pp. 719–722. ACM (2006)
Karkanis, S.A., Iakovidis, D.K., Maroulis, D.E., Karras, D.A., Tzivras, M.: Computer-aided tumor detection in endoscopic video using color wavelet features. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 7(3), 141–152 (2003)
Kershner, R.M.: Management of the small pupil for clear corneal cataract surgery. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 28(10), 1826–1831 (2002)
Khalifa, Y.M., Bogorad, D., Gibson, V., Peifer, J., Nussbaum, J.: Virtual reality in ophthalmology training. Surv. Ophthalmol. 51(3), 259–273 (2006)
Khalifa, Y.M., Hines, M.A., Gearinger, M.: The future of surgical assessment. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 96(8), 1145–1145 (2012)
Klank, U., Padoy, N., Feussner, H., Navab, N.: Automatic feature generation in endoscopic images. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 3(3–4), 331–339 (2008)
Kumar, R., Jog, A., Malpani, A., Vagvolgyi, B., Yuh, D., Nguyen, H., Hager, G., Chen, C.C.G.: Assessing system operation skills in robotic surgery trainees. Int. J. Med. Robot. Comput. Assist. Surg. 8(1), 118–124 (2012)
Lalys, F., Riffaud, L., Bouget, D., Jannin, P.: An application-dependent framework for the recognition of high-level surgical tasks in the or. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention-MICCAI 2011, pp. 331–338. Springer (2011)
Lalys, F., Riffaud, L., Bouget, D., Jannin, P.: A framework for the recognition of high-level surgical tasks from video images for cataract surgeries. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 59(4), 966–976 (2012)
Lalys, F., Riffaud, L., Morandi, X., Jannin, P.: Automatic phases recognition in pituitary surgeries by microscope images classification. In: Information Processing in Computer-Assisted Interventions, pp. 34–44. Springer (2010)
Lloyd, S.: Least squares quantization in pcm. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 28(2), 129–137 (1982)
Lo, B.P., Darzi, A., Yang, G.Z.: Episode classification for the analysis of tissue/instrument interaction with multiple visual cues. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention-MICCAI 2003, pp. 230–237. Springer (2003)
Müller, M.: Dynamic time warping. Information retrieval for music and motion pp. 69–84 (2007)
Neter, J., Wasserman, W., Kutner, M.H., et al.: Applied linear statistical models, vol. 4. Irwin Chicago (1996)
Padoy, N., Blum, T., Feussner, H., Berger, M.O., Navab, N.: On-line recognition of surgical activity for monitoring in the operating room. In: AAAI, pp. 1718–1724 (2008)
Reiley, C.E., Hager, G.D.: Decomposition of robotic surgical tasks: an analysis of subtasks and their correlation to skill. In: M2CAI Workshop, MICCAI (2009)
Reynolds, D.A.: Gaussian mixture models. (2009)
Rizon, M., Haniza, Y., Puteh, S., Yeon, A., Shakaff, M., Sugisaka, M., Sazali, Y., Karthigayan, M.: Object detection using circular hough transform. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2(12), 1606–1609 (2005)
Rosen, J., Solazzo, M., Hannaford, B., Sinanan, M.: Task decomposition of laparoscopic surgery for objective evaluation of surgical residents’ learning curve using hidden markov model. Comput. Aided Surg. 7(1), 49–61 (2002)
Shapiro, L.G., Stockman, G.C.: Computer vision, pp. 279–325 (2001)
Speidel, S., Sudra, G., Senemaud, J., Drentschew, M., Müller-stich, B., Gun, C., Dillmann, R.: Situation modeling and situation recognition for a context-aware augmented reality system. Progress. Biomed. Opt. Imaging 9(1), 35 (2008)
Suzuki, S., Harashima, F.: Skill evaluation from observation of discrete hand movements during console operation. J. Robot. 2010, 13 (2010)
Suzuki, S., Tomomatsu, N., Harashima, F., Furuta, K.: Skill evaluation based on state-transition model for human adaptive mechatronics (ham). In: IEEE 30th Annual Conference of IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, 2004. IECON 2004, vol. 1, pp. 641–646. (2004)
Thompson, B.: Canonical correlation analysis. Encyclopedia of statistics in behavioral science (2005)
Watanabe, K., Hokari, M.: Kinematical analysis and measurement of sports form. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part A Syst. Hum. 36(3), 549–557 (2006)
Zhang, Q., Li, B.: Relative hidden markov models for evaluating motion skill. In: 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) IEEE, pp. 548–555 (2013)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the Flaum Eye Institute, University of Rochester Medical Center. I would like to thank Dr. William Gensheimer for the expert’s grading and fruitful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, J., Luo, J., Soh, J.M. et al. A computer vision-based approach to grade simulated cataract surgeries. Machine Vision and Applications 26, 115–125 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-014-0646-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-014-0646-x