Abstract
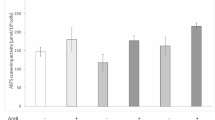
Cisplatin is one of the most potent chemotherapeutic antitumor drugs used in the treatment of a wide range of solid tumors. Its primary dose-limiting side effect is nephrotoxicity. The organic anion transporter 5 (Oat5) is exclusively localized in the kidney. Oat5 urinary excretion was recently proposed as a potential early biomarker of acute kidney injury (AKI). The aim of this study was to evaluate Oat5 renal expression and its urinary excretion in rats exposed to different doses of cisplatin, in comparison with traditional markers of renal injury, like renal histology, creatinine and urea plasma levels, creatinine clearance, protein and glucose urinary levels and urinary alkaline phosphatase (AP) activity. Male Wistar rats were treated with a single injection of cisplatin at different doses of 1, 2, 5 and 10 mg/kg b.w., i.p. (Cis1, Cis2, Cis5 and Cis10, n = 4, respectively) and experiments were carried out 48 h after cisplatin administration. The renal expression of Oat5 was evaluated by immunohistochemistry and Western blotting. Oat5 abundance, AP activity, creatinine, glucose and proteins were assayed in urine. Creatinine clearance and creatinine and urea plasma levels were also evaluated. In this experimental model, plasma urea and creatinine levels, creatinine clearance, AP urinary activity and protein and glucose urinary levels were significantly modified only at the highest cisplatin dose of 10 mg/kg b.w., i.p., as compared to control rats. In contrast, Oat5 urinary abundance was increased in a dose-related manner after the administration of cisplatin. Oat5 urinary abundance was elevated at a dose as low as 1 mg/kg b.w., i.p., implying renal perturbation, when no modifications of traditional markers of renal injury are yet observed. Oat5 renal expression was decreased in a dose-related manner, both in homogenates and apical membranes from cisplatin-treated kidneys. The increase in urinary Oat5 excretion might explain the decrease in the amount of Oat5 molecules in the renal tubule cells. Hence, the preclinical animal results showed in this work propose that Oat5 urinary excretion might potentially serve as a non-invasive early biomarker of cisplatin-induced AKI.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aleksunes LM, Augustine LM, Scheffer GL, Cherrington NJ, Manautou JE (2008) Renal xenobiotic transporters are differentially expressed in mice following cisplatin treatment. Toxicology 250:82–88
Ali BH, Al Moundhri MS, Tag Eldin M, Nemmar A, Tanira MO (2007) The ameliorative effect of cysteine prodrug L-2-oxothiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 21:547–553
Anzai N, Jutabha P, Enomoto A, Yokoyama H, Nonoguchi H, Hirata T, Shiraya K, He X, Cha SH, Takeda M, Miyazaki H, Sakatada T, Tomita K, Igarashi T, Kanai Y, Endou H (2005) Functional characterization of rat organic anion transporter 5 (Slc22a19) at the apical membrane of renal proximal tubules. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 315:534–544
Anzai N, Kanai Y, Endou H (2006) Organic anion transporter family: current knowledge. J Pharmacol Sci 100:411–426
Arjumand W, Seth A, Sultana S (2011) Rutin attenuates cisplatin induced renal inflammation and apoptosis by reducing NFκB, TNF-α and caspase-3 expression in wistar rats. Food Chem Toxicol 49:2013–2021
Bearcroft CP, Domizio P, Mourad FH, André EA, Farthing MJ (1999) Cisplatin impairs fluid and electrolyte absorption in rat small intestine: a role for 5-hydroxytryptamine. Gut 44:174–179
Brandoni A, Anzai N, Kanai Y, Endou H, Torres AM (2006) Renal elimination of p aminohippurate (PAH) in response to three days of biliary obstruction in the rat. The role of OAT1 and OAT3. Biochim Biophys Acta 1762:673–682
Breljak D, Ljubojevic M, Balen D, Zlender V, Brzica H, Micek V, Kusan M, Anzai N, Sabolic I (2010) Renal expression of organic anion transporter Oat5 in rats and mice exhibits the female-dominant sex differences. Histol Histopathol 25:1385–1402
Bulacio R, Hazelhoff MH, Torres AM (2012) Renal expression and function of Oat1 and Oat3 in rats with vascular calcification. Pharmacology 90:66–77
Burckhardt G (2012) Drug transport by organic anion transporters (OATs). Pharmacol Ther 136:106–130
Camano S, Lazaro A, Moreno-Gordaliza E, Torres AM, de Lucas C, Humanes B, Lazaro JA, Milagros Gomez-Gomez M, Bosca L, Tejedor A (2010) Cilastatin attenuates cisplatin-induced proximal tubular cell damage. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 334:419–429
Chatamra K, Daniel PM, Lam DK (1984) The effects of fasting on core temperature, blood glucose and body and organ weights in rats. Q J Exp Physiol 69:541–545
Claassen V (1994) Neglected factors in pharmacology and neuroscience research. Biopharmaceutics, Animals Characteristics, Maintenance, Testing Conditions. Elsevier, Amsterdam, In, pp 290–320
Di Giusto G, Torres AM (2010) Organic anion transporter 5 renal expression and urinary excretion in rats exposed to mercuric chloride: a potential biomarker of mercury-induced nephropathy. Arch Toxicol 84:741–749
Di Giusto G, Anzai N, Endou H, Torres AM (2009) Oat5 and NaDC1 protein abundance in kidney and urine after renal ischemic reperfusion injury. J Histochem Cytochem 57:17–27
Dobyan DC, Levi J, Jacobs C, Kosek J, Weiner MW (1980) Mechanism of cis-platinum nephrotoxicity: II. Morphologic observations. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 213:551–556
dos Santos NA, Martins NM, Curti C, Pires Bianchi M, dos Santos AC (2007) Dimethylthiourea protects against mitochondrial oxidative damage induced by cisplatin in liver of rats. Chem Biol Interact 170:177–186
du Cheyron D, Daubin C, Poggioli J, Ramakers M, Houillier P, Charbonneau P, Paillard M (2003) Urinary measurement of Na+/H+ exchanger isoform 3 (NHE3) protein as new marker of tubule injury in critically ill patients with ARF. Am J Kidney Dis 42:497–506
Ferguson MA, Vaidya VS, Bonventre JV (2008) Biomarkers of nephrotoxic acute kidney injury. Toxicology 245:182–193
Fliser D, Novak J, Thongboonkerd V, Argilés A, Jankowski V, Girolami MA, Jankowski J, Mischak H (2007) Advances in urinary proteome analysis and biomarker discovery. J Am Soc Nephrol 18:1057–1071
Heiene R, Moe L, Mølmen G (2001) Calculation of urinary enzyme excretion, with renal structure and function in dogs with pyometra. Res Vet Sci 70:129–137
Hosohata K, Ando H, Fujimura A (2012) Urinary vanin-1 as a novel biomarker for early detection of drug-induced acute kidney injury. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 341:656–662
Ivanišević I, Peco-Antić A, Vuličević I, Hercog D, Milovanović V, Kotur-Stevuljević J, Stefanović A, Kocev N (2013) L-FABP can be an early marker of acute kidney injury in children. Pediatr Nephrol 28:963–969
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Miller RP, Tadagavadi RK, Ramesh G, Reeves WB (2010) Mechanisms of cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Toxins 2:2490–2518
Muraki K, Koyama R, Honma Y, Yagishita S, Shukuya T, Ohashi R, Takahashi F, Kido K, Iwakami S, Sasaki S, Iwase A, Takahashi K (2012) Hydration with magnesium and mannitol without furosemide prevents the nephrotoxicity induced by cisplatin and pemetrexed in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Dis 4:562–568
Pinches M, Betts C, Bickerton S, Burdett L, Thomas H, Derbyshire N, Jones HB, Moores M (2012a) Evaluation of novel renal biomarkers with a cisplatin model of kidney injury: gender and dosage differences. Toxicol Pathol 40:522–533
Pinches MD, Betts CJ, Bickerton SJ, Beattie L, Burdett LD, Thomas HT, Derbyshire NA, Moores M (2012b) Evaluation of novel urinary renal biomarkers with a cisplatin model of kidney injury: effects of collection period. Toxicol Pathol 40:534–540
Pinches MD, Betts CJ, Bickerton SJ, Beattie L, Burdett LD, Thomas HT, Derbyshire NA, Moores M, Price SA (2012c) Evaluation of novel urinary renal biomarkers: biological variation and reference change values. Toxicol Pathol 40:541–549
Rifai N, Gillette MA, Carr SA (2006) Protein biomarker discovery and validation: the long and uncertain path to clinical utility. Nat Biotechnol 24:971–983
Sinha V, Vence LM, Salahudeen AK (2013) Urinary tubular protein-based biomarkers in the rodent model of cisplatin nephrotoxicity: a comparative analysis of serum creatinine, renal histology, and urinary KIM-1, NGAL, and NAG in the initiation, maintenance, and recovery phases of acute kidney injury. J Investig Med 61:1–5
Star RA (1998) Treatment of acute renal failure. Kidney Int 54:1817–1831
Taguchi T, Nazneen A, Abid MR, Razzaque MS (2005) Cisplatin-associated nephrotoxicity and pathological events. Contrib Nephrol 148:107–121
Tiseo M, Martelli O, Mancuso A, Sormani MP, Bruzzi P, Di Salvia R, De Marinis F, Ardizzoni A (2007) Short hydration regimen and nephrotoxicity of intermediate to high-dose cisplatin-based chemotherapy for outpatient treatment in lung cancer and mesothelioma. Tumori 93:138–144
Uchino S, Kellum JA, Bellomo R, Doig GS, Morimatsu H, Morgera S, Schetz M, Tan I, Bouman C, Macedo E, Gibney N, Tolwani A, Ronco C (2005) Acute renal failure in critically ill patients: a multinational, multicenter study. JAMA 294:813–818
Uehara T, Yamate J, Torii M, Maruyama T (2011) Comparative nephrotoxicity of cisplatin and nedaplatin: mechanisms and histopathological characteristics. J Toxicol Pathol 24:87–94
Umenishi F, Summer SN, Cadnapaphornchai M, Shrier RW (2002) Comparison of three methods to quantify urinary aquaporin-2 protein. Kidney Int 62:2288–2293
Vadiei K, Siddik ZH, Khokhar AR, Al-Baker S, Sampedro F, Perez-Soler R (1992) Pharmacokinetics of liposome-entrapped cis-bis-neodecanoato-trans-R, R-1,2-diamino-cyclohexane platinum(II) and cisplatin given i.v. and i.p. in the rat. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 30:365–369
Vaidya VS, Waikar SS, Ferguson MA, Collings FB, Sunderland K, Gioules C, Bradwin G, Matsouaka R, Betensky RA, Curhan GC, Bonventre JV (2008) Urinary biomarkers for sensitive and specific detection of acute kidney injury in humans. Clin Transl Sci 1:200–208
Vermeulen JK, de Vries A, Schlingmann F, Remie R (1997) Food deprivation: common sense or nonsense? Anim Technol 48:45–54
Yao X, Panichpisal K, Kurtzman N, Nugent K (2007) Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: a review. Am J Med Sci 334:115–124
Yokoo S, Yonezawa A, Masuda S, Fukatsu A, Katsura T, Inui K (2007) Differential contribution of organic cation transporters, OCT2 and MATE1, in platinum agent-induced nephrotoxicity. Biochem Pharmacol 74:477–487
Yonezawa A, Masuda S, Nishihara K, Yano I, Katsura T, Inui K (2005) Association between tubular toxicity of cisplatin and expression of organic cation transporter rOCT2 (Slc22a2) in the rat. Biochem Pharmacol 70:1823–1831
Youngblood GL, Sweet DH (2004) Identification and functional assessment of the novel murine organic anion transporter Oat5 (Slc22a19) expressed in kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 287:F236–F244
Zhou H, Pisitkun T, Aponte A, Yuen PS, Hoffert JD, Yasuda H, Hu X, Chawla L, Shen RF, Knepper MA, Star RA (2006a) Exosomal fetuin-A identified by proteomics: a novel urinary biomarker for detecting acute kidney injury. Kidney Int 70:1847–1857
Zhou H, Yuen PS, Pisitkun T, Gonzales PA, Yasuda H, Dear JW, Gross P, Knepper MA, Star RA (2006b) Collection, storage, preservation, and normalization of human urinary exosomes for biomarker discovery. Kidney Int 69:1471–1476
Zhou H, Cheruvanky A, Hu X, Matsumoto T, Hiramatsu N, Cho ME, Berger A, Leelahavanichkul A, Doi K, Chawla LS, Illei GG, Kopp JB, Balow JE, Austin HA 3rd, Yuen PS, Star RA (2008) Urinary exosomal transcription factors, a new class of biomarkers for renal disease. Kidney Int 74:613–621
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the following grants: Fondo para la Investigación Científica y Tecnológica (FONCYT), Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET), Universidad Nacional de Rosario (UNR), Secretaría de Estado de Ciencia, and Tecnología e Innovación de Santa Fe (SECTeI). The authors thank Prof. H. Endou and Prof. N. Anzai (Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Kyorin University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan) for kindly providing Oat5-specific antibodies and Mrs Alejandra Martínez (Area Morfología, Facultad de Ciencias Bioquímicas y Farmacéuticas, U.N.R.) for her collaboration in the present work. The authors also thank Wiener Lab Argentina for analytical kits.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bulacio, R.P., Torres, A.M. Organic anion transporter 5 (Oat5) renal expression and urinary excretion in rats treated with cisplatin: a potential biomarker of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Arch Toxicol 87, 1953–1962 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-013-1062-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-013-1062-0