Abstract
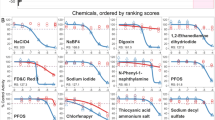
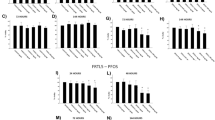
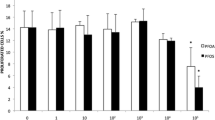
The Fischer rat thyroid follicular cell line (FRTL-5) endogenously expresses the sodium-iodide symporter (NIS) and has been used to identify environmental chemicals that perturb thyroid hormone homeostasis by disruption of NIS-mediated iodide uptake. Previously, a high-throughput radioactive iodide uptake (RAIU) screening assay incorporating the hNIS-HEK293T-EPA cell line was used to identify potential human NIS (hNIS) inhibitors in 1028 ToxCast Phase I (ph1_v2) and Phase II chemicals. In this study, the FRTL-5 cell line was evaluated and applied as a secondary RAIU assay coupled with cell viability assays to further prioritize highly active NIS inhibitors from the earlier screening. Assay validation with ten reference chemicals and performance assessment by chemical controls suggest the FRTL-5 based assays are robust and highly reproducible. Top-ranked chemicals from the ToxCast screening were then evaluated in both FRTL-5 and hNIS RAIU assays using newly sourced chemicals to strengthen the testing paradigm and to enable a rat vs. human species comparison. Eighteen of 29 test chemicals showed less than 1 order of magnitude difference in IC50 values between the two assays. Notably, two common perfluorinated compounds, perfluorooctanesulfonic acid (PFOS) and perfluorohexane sulfonate (PFHxS), demonstrated strong NIS inhibitory activity [IC50 − 6.45 (PFOS) and − 5.70 (PFHxS) log M in FRTL-5 RAIU assay]. In addition, several chemicals including etoxazole, methoxyfenozide, oxyfluorfen, triclocarban, mepanipyrim, and niclosamide also exhibited NIS inhibition with minimal cytotoxicity in both assays and are proposed for additional testing using short-term in vivo assays to characterize effects on thyroid hormone synthesis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambesi-Impiombato FS, Parks LA, Coon HG (1980) Culture of hormone-dependent functional epithelial cells from rat thyroids. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77(6):3455–3459
Barrientos A, Moraes CT (1999) Titrating the effects of mitochondrial complex I impairment in the cell physiology. J Biol Chem 274(23):16188–16197
Brucker-Davis F (1998) Effects of environmental synthetic chemicals on thyroid function. Thyroid 8(9):827–856. https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.1998.8.827
Capen CC, Martin SL (1989) The effects of xenobiotics on the structure and function of thyroid follicular and C-cells. Toxicol Pathol 17(2):266–293. https://doi.org/10.1177/019262338901700205
Carrasco N (1993) Iodide transport in the thyroid gland. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta BBA Rev Biomembr 1154(1):65–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-4157(93)90017-I
Chanda D, Krishna AV, Gupta PK et al (2008) Role of low ouabain-sensitive isoform of Na+–K+-ATPase in the regulation of basal tone and agonist-induced contractility in ovine pulmonary artery. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 52(2):167–175. https://doi.org/10.1097/FJC.0b013e31818127dd
Crofton KM (2008) Thyroid disrupting chemicals: mechanisms and mixtures. Int J Androl 31(2):209–223. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2605.2007.00857.x
Davies L, Morris LGT, Haymart M et al (2015) American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology Disease State Clinical Review: The Increasing Incidence Of Thyroid Cancer. Endocrine Practice 21(6):686–696. https://doi.org/10.4158/EP14466.DSCR
De Groef B, Decallonne BR, Van der Geyten S, Darras VM, Bouillon R (2006) Perchlorate versus other environmental sodium/iodide symporter inhibitors: potential thyroid-related health effects. Eur J Endocrinol Eur Feder Endocrine Soc 155(1):17–25. https://doi.org/10.1530/eje.1.02190
Di Bernardo J, Iosco C, Rhoden KJ (2011) Intracellular anion fluorescence assay for sodium/iodide symporter substrates. Anal Biochem 415(1):32–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2011.04.017
Dong H, Atlas E, Wade MG (2019) Development of a non-radioactive screening assay to detect chemicals disrupting the human sodium iodide symporter activity. Toxicol In Vitro 57:39–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2019.01.021
Escobar GMD, Obregon MJ, Rey FED (2004) Role of thyroid hormone during early brain development. Eur J Endocrinol 151(Suppl_3):U25–U37
Ferrari SM, Fallahi P, Antonelli A, Benvenga S (2017) Environmental issues in thyroid diseases. Front Endocrinol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2017.00050
Ghassabian A, Trasande L (2018) Disruption in thyroid signaling pathway: a mechanism for the effect of endocrine-disrupting chemicals on child neurodevelopment. Front Endocrinol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2018.00204
Gilbert ME, Zoeller R (2010) Thyroid hormone—impact on the developing brain: possible mechanisms of neurotoxicity neurotoxicology, vol 3. Informa Healthcare USA Inc, New York, pp 79–111
Gilbert ME, Hedge JM, Valentín-Blasini L et al (2013) An animal model of marginal iodine deficiency during development: the thyroid axis and neurodevelopmental outcome*. Toxicol Sci 132(1):177–195. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfs335
Haddow JE, Palomaki GE, Allan WC et al (1999) Maternal thyroid deficiency during pregnancy and subsequent neuropsychological development of the child. N Engl J Med 341(8):549–555. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm199908193410801
Hallinger DR, Murr AS, Buckalew AR, Simmons SO, Stoker TE, Laws SC (2017) Development of a screening approach to detect thyroid disrupting chemicals that inhibit the human sodium iodide symporter (NIS). Toxicol In Vitro 40:66–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2016.12.006
Hornung MW, Kosian PA, Haselman JT et al (2015) In vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo determination of thyroid hormone modulating activity of benzothiazoles. Toxicol Sci 146(2):254–264. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfv090
Hornung MW, Korte JJ, Olker JH et al (2018) Screening the ToxCast phase 1 chemical library for inhibition of deiodinase type 1 activity. Toxicol Sci 162(2):570–581. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfx279
Hurley PM (1998) Mode of carcinogenic action of pesticides inducing thyroid follicular cell tumors in rodents. Environ Health Perspect 106(8):437–445. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.98106437
Kaminsky SM, Levy O, Garry MT, Carrasco N (1991) Inhibition of the Na/I-symporter by harmaline and 3-amino-1-methyl-5H-pyrido(4,3-b)indole acetate in thyroid cells and membrane vesicles. Eur J Biochem FEBS 200(1):203–207
Kheradpisheh Z, Mirzaei M, Mahvi AH et al (2018) Impact of drinking water fluoride on human thyroid hormones: a case–control study. Sci Rep 8(1):2674. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-20696-4
Köhrle J (2008) Environment and endocrinology: the case of thyroidology. Ann Endocrinol 69(2):116–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ando.2008.02.008
Korevaar TIM, Medici M, Visser TJ, Peeters RP (2017) Thyroid disease in pregnancy: new insights in diagnosis and clinical management. Nat Rev Endocrinol 13:610. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2017.93
Lau C, Anitole K, Hodes C, Lai D, Pfahles-Hutchens A, Seed J (2007) Perfluoroalkyl acids: a review of monitoring and toxicological findings. Toxicol Sci 99(2):366–394. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfm128
Lecat-Guillet N, Merer G, Lopez R, Pourcher T, Rousseau B, Ambroise Y (2007) A 96-well automated radioiodide uptake assay for sodium/iodide symporter inhibitors. Assay Drug Dev Technol 5(4):535–540. https://doi.org/10.1089/adt.2007.068
Lecat-Guillet N, Merer G, Lopez R, Pourcher T, Rousseau B, Ambroise Y (2008) Small-molecule inhibitors of sodium iodide symporter function. Chembiochem Eur J Chem Biol 9(6):889–895. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.200700682
Lee S, Kim C, Youn H, Choi K (2017) Thyroid hormone disrupting potentials of bisphenol A and its analogues—in vitro comparison study employing rat pituitary (GH3) and thyroid follicular (FRTL-5) cells. Toxicol In Vitro 40:297–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2017.02.004
Lee J, Kim S, Park YJ, Moon H-B, Choi K (2018) Thyroid hormone-disrupting potentials of major benzophenones in two cell lines (GH3 and FRTL-5) and embryo-larval zebrafish. Environ Sci Technol 52(15):8858–8865. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b01796
Malin AJ, Riddell J, McCague H, Till C (2018) Fluoride exposure and thyroid function among adults living in Canada: effect modification by iodine status. Environ Int 121:667–674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.09.026
Moog NK, Entringer S, Heim C, Wadhwa PD, Kathmann N, Buss C (2017) Influence of maternal thyroid hormones during gestation on fetal brain development. Neuroscience 342:68–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.09.070
Murk AJ, Rijntjes E, Blaauboer BJ et al (2013) Mechanism-based testing strategy using in vitro approaches for identification of thyroid hormone disrupting chemicals. Toxicol In Vitro 27(4):1320–1346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2013.02.012
Navarro A, Bández MJ, Gómez C, Repetto MG, Boveris A (2010) Effects of rotenone and pyridaben on complex I electron transfer and on mitochondrial nitric oxide synthase functional activity. J Bioenerg Biomembr 42(5):405–412. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-010-9309-4
Noyes PD, Friedman KP, Browne P et al (2019) Evaluating chemicals for thyroid disruption: opportunities and challenges with in vitro testing and adverse outcome pathway approaches. Environ Health Perspect 127(9):095001. https://doi.org/10.1289/EHP5297
O’Shaughnessy KL, Kosian PA, Ford JL, Oshiro WM, Degitz SJ, Gilbert ME (2018) Developmental thyroid hormone insufficiency induces a cortical brain malformation and learning impairments: a cross-fostering study. Toxicol Sci 163(1):101–115. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfy016
Olker JH, Haselman JT, Kosian PA et al (2018a) Evaluating iodide recycling inhibition as a novel molecular initiating event for thyroid axis disruption in amphibians. Toxicol Sci 166(2):318–331. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfy203
Olker JH, Korte JJ, Denny JS et al (2018b) Screening the ToxCast phase 1, phase 2, and e1k chemical libraries for inhibitors of iodothyronine deiodinases. Toxicol Sci. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfy302
Paul KB, Hedge JM, Rotroff DM, Hornung MW, Crofton KM, Simmons SO (2014) Development of a thyroperoxidase inhibition assay for high-throughput screening. Chem Res Toxicol 27(3):387–399. https://doi.org/10.1021/tx400310w
Paul Friedman K, Watt ED, Hornung MW et al (2016) Tiered high-throughput screening approach to identify thyroperoxidase inhibitors within the ToxCast phase I and II chemical libraries. Toxicol Sci 151(1):160–180. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfw034
Radovic B, Schmutzler C, Kohrle J (2005) Xanthohumol stimulates iodide uptake in rat thyroid-derived FRTL-5 cells. Mol Nutr Food Res 49(9):832–836. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.200500053
OECD (2017) New scoping document on in vitro and ex vivo assays for the identification of modulators of thyroid hormone signalling. OECD Publishing, Paris
Tavares MA, Palma IDF, Medeiros HCD, Guelfi M, Santana AT, Mingatto FE (2015) Comparative effects of fipronil and its metabolites sulfone and desulfinyl on the isolated rat liver mitochondria. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 40(1):206–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2015.06.013
Taylor PN, Razvi S, Pearce SH, Dayan CM (2013) A review of the clinical consequences of variation in thyroid function within the reference range. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 98(9):3562–3571. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2013-1315
Thomas RS, Bahadori T, Buckley TJ et al (2019) The next generation blueprint of computational toxicology at the US Environmental Protection Agency. Toxicol Sci 169(2):317–332. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfz058
Waltz F, Pillette L, Ambroise Y (2010) A nonradioactive iodide uptake assay for sodium iodide symporter function. Anal Biochem 396(1):91–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2009.08.038
Wang J, Hallinger DR, Murr AS et al (2018) High-throughput screening and quantitative chemical ranking for sodium-iodide symporter inhibitors in ToxCast phase I chemical library. Environ Sci Technol 52(9):5417–5426. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b06145
Wang J, Hallinger DR, Murr AS et al (2019) High-throughput screening and chemotype-enrichment analysis of ToxCast phase II chemicals evaluated for human sodium-iodide symporter (NIS) inhibition. Environ Int 126:377–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.02.024
Weiss SJ, Philp NJ, Grollman EF (1984) Iodide transport in a continuous line of cultured cells from rat thyroid. Endocrinology 114(4):1190–1198. https://doi.org/10.1210/endo-114-4-1090
Wu Y, Beland FA, Fang J-L (2016) Effect of triclosan, triclocarban 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether, and bisphenol A on the iodide uptake, thyroid peroxidase activity, and expression of genes involved in thyroid hormone synthesis. Toxicol In Vitro 32(Supplement C):310–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2016.01.014
Xiong J, Tian L, Qiu Y et al (2018) Evaluation on the thyroid disrupting mechanism of malathion in Fischer rat thyroid follicular cell line FRTL-5. Drug Chem Toxicol 41(4):501–508. https://doi.org/10.1080/01480545.2017.1397162
Yen PM (2001) Physiological and molecular basis of thyroid hormone action. Physiol Rev 81(3):1097–1142. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.2001.81.3.1097
Zhang J-H, Chung TDY, Oldenburg KR (1999) A simple statistical parameter for use in evaluation and validation of high throughput screening assays. J Biomol Screen 4(2):67–73. https://doi.org/10.1177/108705719900400206
Zimmermann MB, Boelaert K (2015) Iodine deficiency and thyroid disorders. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 3(4):286–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(14)70225-6
Zuang V, Desprez B, Barroso J et al (2018) EURL ECVAM status report on the development, validation and regulatory acceptance of alternative methods and approaches (2018) Report EUR 29455 EN
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the Office of Research and Development, U.S. EPA, Washington, DC. The authors thank U.S. EPA scientists Andrew Johnstone, Hisham El-Masri, and DeAnna DeVane for their scientific and editorial contributions to this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The views expressed in this paper are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views or policies of the US Environmental Protection Agency.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buckalew, A.R., Wang, J., Murr, A.S. et al. Evaluation of potential sodium-iodide symporter (NIS) inhibitors using a secondary Fischer rat thyroid follicular cell (FRTL-5) radioactive iodide uptake (RAIU) assay. Arch Toxicol 94, 873–885 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-020-02664-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-020-02664-y