Abstract
Rationale
Disturbances in critical cognitive processes, such as working memory, are now regarded as core features of schizophrenia, but available pharmacological treatments produce little or no improvement in these cognitive deficits. Although other explanations are possible, these cognitive deficits appear to reflect a disturbance in executive control, the processes that facilitate complex information processing and behavior and that include context representation and maintenance, functions dependent on the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC). Studies in non-human primates indicate that normal working memory function depends upon appropriate GABA neurotransmission in the DLPFC, and alterations in markers of GABA neurotransmission are well documented in the DLPFC of subjects with schizophrenia.
Objectives
Thus, the purpose of this paper is to review the nature of the altered GABA neurotransmission in the DLPFC in schizophrenia, and to consider how these findings might inform the search for new treatments for cognitive dysfunction in this illness.
Results and conclusions
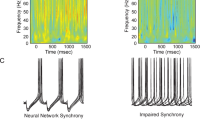
Postmortem studies suggest that markers of reduced GABA neurotransmission in schizophrenia may be selective for, or at least particularly prominent in, the subclass of GABA neurons, chandelier cells, that provide inhibitory input to the axon initial segment of populations of pyramidal neurons. Given the critical role that chandelier cells play in synchronizing the activity of pyramidal neurons, the pharmacological amelioration of this deficit may be particularly effective in normalizing the neural network activity required for working memory function. Because GABAA receptors containing the a2 subunit are selectively localized to the axon initial segment of pyramidal cells, and appear to be markedly up-regulated in schizophrenia, treatment with novel benzodiazepine-like agents with selective activity at GABAA receptors containing the a2 subunit may be effective adjuvant agents for improving working memory function in schizophrenia.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbarian S, Kim JJ, Potkin SG, Hagman JO, Tafazzoli A, Bunney JrWE, Jones EG (1995) Gene expression for glutamic acid decarboxylase is reduced without loss of neurons in prefrontal cortex of schizophrenics. Arch Gen Psychiatry 52:258–266
Anderson SA, Classey JD, Condé F, Lund JS, Lewis DA (1995) Synchronous development of pyramidal neuron dendritic spines and parvalbumin-immunoreactive chandelier neuron axon terminals in layer III of monkey prefrontal cortex. Neuroscience 67:7–22
Anderson SA, Eisenstat DD, Shi L, Rubenstein JLR (1997) Interneuron migration from basal forebrain to neocortex: dependence on Dlx genes. Science 278:474–476
Andreasen NC, Rezai R, Alliger R, Swayze VW, II, Flaum M, Kirchner P, Cohen G, O’Leary DS (1992) Hypofrontality in neuroleptic-naive patients and in patients with chronic schizophrenia: assessment with xenon 133 single-photon emission computed tomography and the Tower of London. Arch Gen Psychiatry 49:943–958
Barnard EA, Skolnick P, Olsen RW, Mohler H, Sieghart W, Biggio G, Braestrup C, Bateson AN, Langer SZ (1998) International Union of Pharmacology. XV. Subtypes of gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptors: classification on the basis of subunit structure and receptor function. Pharmacol Rev 50:291–313
Beasley CL, Zhang ZJ, Patten I, Reynolds GP (2002) Selective deficits in prefrontal cortical GABAergic neurons in schizophrenia defined by the presence of calcium-binding proteins. Biol Psychiatry 52:708–715
Ben-Ari Y (2002) Excitatory actions of GABA during development: The nature of the nurture. Nat Rev Neurosci 3:728–739
Benes FM, McSparren J, Bird ED, SanGiovanni JP, Vincent SL (1991) Deficits in small interneurons in prefrontal and cingulate cortices of schizophrenic and schizoaffective patients. Arch Gen Psychiatry 48:996–1001
Benes FM, Snyder-Marie A, Vincent S, Khan Y (1996) Up-regulation of GABA-A receptor binding on neurons of the prefrontal cortex in schizophrenic subjects. Neuroscience 75:1021–1031
Blum BP, Mann JJ (2002) The GABAergic system in schizophrenia. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 5:159–179
Botvinick MM, Braver TS, Barch DM, Carter CS, Cohen JD (2001) Conflict monitoring and cognitive control. Psychol Rev 108:624–652
Brunig I, Scotti E, Sidler C, Fritschy JM (2002) Intact sorting, targeting, and clustering of gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptor subtypes in hippocampal neurons in vitro. J Comp Neurol 443:43–55
Buchsbaum M (1990) The frontal lobes, basal ganglia and temporal lobes as sites for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 16:379–389
Callicott JH, Tallent K, Bertolino A, Ransey N, Santha A, Knable M, Coppola R, Goldberg T, Mattay V, van Gelderen P, Frank JA, Moonen CTW, Weinberger DR (1998) fMRI brain mapping in psychiatry. Neuropsychopharmacology 18:186–196
Callicott JH, Mattay VS, Bertolino A, Finn K, Coppola R, Frank JA, Goldberg TE, Weinberger DR (1999) Physiological characteristics of capacity constraints in working memory as revealed by functional MRI. Cereb Cortex 9:20–26
Callicott JH, Bertolino A, Mattay VS, Langheim FJP, Duyn J, Coppola R, Goldberg TE, Weinberger DR (2000) Physiological dysfunction of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia revisited. Cereb Cortex 10:1078–1092
Carpenter WT Jr, Buchanan RW, Kirkpatrick B, Breier AF (1999) Diazepam treatment of early signs of exacerbation in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 156:299–303
Carter CS, Robertson L, Chaderjian M, Celaya L, Nardahl T (1992) Attentional asymmetry in schizophrenia: controlled and automatic processes. Biol Psychiatry 31:909–918
Carter CS, Robertson L, Nordhal TE, Kraft L, Chaderjian M, Oshora-Celaya L (1996) Spatial working memory deficits and their relationship to negative symptoms in unmedicated schizophrenic patients. Biol Psychiatry 40:930–932
Carter CS, Perlstein W, Ganguli R, Brar J, Mintun M, Cohen JD (1998) Functional hypofrontality and working memory dysfunction in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 155:1285–1287
Carter CS, Botvinick M, Cohen JD (1999) The contribution of the anterior cingulate cortex to executive processes in cognition. Rev Neurosci 10:49–57
Cobb SR, Buhl EH, Halasy K, Paulsen O, Somogyi P (1995) Synchronization of neuronal activity in hippocampus by individual GABAergic interneurons. Nature 378:75–78
Cohen JD, Botvinick M, Carter CS (2002) Anterior cingulate and prefrontal cortex: who’s in control. Nat Neurosci 3:421–423
Collinson N, Kuenzi FM, Jarolimek W, Maubach KA, Cothliff R, Sur C, Smith A, Otu FM, Howell O, Atack JR, McKernan RM, Seabrook GR, Dawson GR, Whiting PJ, Rosahl TW (2002) Enhanced learning and memory and altered GABAergic synaptic transmission in mice lacking the α5 subunit of the GABAA receptor. J Neurosci 22:5572–5580
Condé F, Lund JS, Jacobowitz DM, Baimbridge KG, Lewis DA (1994) Local circuit neurons immunoreactive for calretinin, calbindin D-28 k, or parvalbumin in monkey prefrontal cortex: distribution and morphology. J Comp Neurol 341:95–116
Cornblatt BA, Lenzenweger MF, Erlenmeyer-Kimling L (1989) The continuous performance test, identical pairs version: II. Contrasting attention profiles in schizophrenic and depressed patients. Psychiatry Res 29:65–85
Crestani F, Keist R, Fritschy J-M, Benke D, Vogt K, Prut L, Blüthman H, Möhler H, Rudolph U (2002) Trace fear conditioning involves hippocampal α5 GABAA receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:8980–8985
Cruz DA, Eggan SM, Lewis DA (2003) Postnatal development of pre- and post-synaptic GABA markers at chandelier cell inputs to pyramidal neurons in monkey prefrontal cortex. J Comp Neurol 465:385–400
DeFelipe J (1997) Types of neurons, synaptic connections and chemical characteristics of cells immunoreactive for calbindin-D28K, parvalbumin and calretinin in the neocortex. J Chem Neuroanat 14:1–19
DeFelipe J, del Carmen Gonzalez-Albo M (1998) Chandelier cell axons are immunoreactive for GAT-1 in the human neocortex. NeuroReport 9:467–470
DeFelipe J, Hendry SHC, Jones EG (1989) Visualization of chandelier cell axons by parvalbumin immunoreactivity in monkey cerebral cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:2093–2097
Elvevåg B, Goldberg TE (2000) Cognitive impairment in schizophrenia is the core of the disorder. Crit Rev Neurobiol 14:1–21
Erickson SL, Lewis DA (2002) Postnatal development of parvalbumin- and GABA transporter-immunoreactive axon terminals in monkey prefrontal cortex. J Comp Neurol 448:186–202
Fritschy J-M, Mohler H (1995) GABAA-receptor heterogeneity in the adult rat brain: differential regional and cellular distribution of seven major subunits. J Comp Neurol 359:154–194
Fritschy J-M, Weinman O, Wenzel A, Benke D (1998) Synapse-specific localization of NMDA and GABAA receptor subunits revealed by antigen-retrieval immunohistochemistry. J Comp Neurol 390:194–210
Gabbott PLA, Bacon SJ (1996) Local circuit neurons in the medial prefrontal cortex (areas 24a,b,c, 25 and 32) in the monkey: II. Quantitative areal and laminar distributions. J Comp Neurol 364:609–636
Gabbott PLA, Dickie BGM, Vaid RR, Headlam AJM, Bacon SJ (1997) Local-circuit neurones in the medial prefrontal cortex (areas 25, 32 and 24b) in the rat: Morphology and quantitative distribution. J Comp Neurol 377:465–499
Gold JM, Carpenter C, Randolph C, Goldberg TE, Weinberger DR (1997) Auditory working memory and Wisconsin Card Sorting Test performance in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 54:159–165
Green MF (1996) What are the functional consequences of neurocognitive deficits in schizophrenia? Am J Psychiatry 153:321–330
Green MF (1998) Schizophrenia from a neurocognitive perspective: probing the impenetrable darkness. Allyn and Bacon, Boston, Mass.
Guidotti A, Auta J, Davis JM, Gerevini VD, Dwivedi Y, Grayson DR, Impagnatiello F, Pandey G, Pesold C, Sharma R, Uzunov D, Costa E (2000) Decrease in reelin and glutamic acid decarboxylase67 (GAD67) expression in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 57:1061–1069
Gulledge AT, Stuart GJ (2003) Excitatory actions of GABA in the cortex. Neuron 37:299–309
Gur RC, Gur RE (1995) Hypofrontality in schizophrenia: RIP. Lancet 345:1383–1384
Hakak Y, Walker JR, Li C, Wong WH, Davis KL, Buxbaum JD, Haroutunian V, Fienberg AA (2001) Genome-wide expression analysis reveals dysregulation of myelination-related genes in chronic schizophrenia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:4746–4751
Harvey PD, Howanitz E, Parrella M, White L, Davidson M, Mohs RC, Hoblyn J, Davis KL (1998) Symptoms, cognitive functioning, and adaptive skills in geriatric patients with lifelong schizophrenia: a comparison across treatment sites. Am J Psychiatry 155:1080–1086
Hashimoto T, Volk DW, Eggan SM, Mirnics K, Pierri JN, Sun Z, Sampson AR, Lewis DA (2003) Gene expression deficits in a subclass of GABA neurons in the prefrontal cortex of subjects with schizophrenia. J Neurosci 23:6315–6326
Kawaguchi Y, Kubota Y (1993) Correlation of physiological subgroupings of nonpyramidal cells with parvalbumin- and calbindinD28k-immunoreactive neurons in layer V of rat frontal cortex. J Neurophysiol 70:387–396
Keefe RSE, Roitman SEL, Harvey PD, Blum CS, DuPre RL, Prieto DM, Davidson D, Davis KL (1995) A pen-and-paper human analogue of a monkey prefrontal cortex activation task: spatial working memory in patients with schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 17:25–33
Klausberger T, Magill PJ, Marton LF, Roberts JDB, Cobden PM, Buzsaki G, Somogyi P (2003) Brain-state- and cell-type specific firing of hippocampal interneurons in vivo. Nature 421:844–848
Krimer LS, Goldman-Rakic PS (2001) Prefrontal microcircuits: membrane properties and excitatory input of local, medium, and wide arbor neurons. J Neurosci 21:3788–3796
Letinic K, Zoncu R, Rakic P (2002) Origin of GABAergic neurons in the human neocortex. Nature 417:645–649
Lewis DA, Lund JS (1990) Heterogeneity of chandelier neurons in monkey neocortex: corticotropin-releasing factor and parvalbumin immunoreactive populations. J Comp Neurol 293:599–615
Lewis DA, Pierri JN, Volk DW, Melchitzky DS, Woo T-U (1999) Altered GABA neurotransmission and prefrontal cortical dysfunction in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 46:616–626
Loup F, Weinmann O, Yonekawa Y, Aguzzi A, Wieser H-G, Fritschy J-M (1998) A highly sensitive immunofluorescence procedure for analyzing the subcellular distribution of GABAA receptor subunits in the human brain. J Histochem Cytochem 46:1129–1139
Löw K, Crestani F, Keist R, Benke D, Brünig I, Benson JA, Fritschy J-M, Rülicke T, Bluethmann H, Möhler H, Rudolph U (2000) Molecular and neuronal substrate for the selective attenuation of anxiety. Science 290:131–134
Manoach DS, Press DZ, Thangaraj V, Searl MM, Goff DC, Halpern E, Saper CB, Warach S (1999) Schizophrenic subjects activate dorsolateral prefrontal cortex during a working memory task, as measured by fMRI. Biol Psychiatry 45:1128–1137
McKernan RM, Rosahl TW, Reynolds DS, Sur C, Wafford KA, Atack JR, Farrar S, Myers J, Cook G, Ferris P, Garrett L, Bristow L, Marshall G, Macaulay A, Brown N, Howell O, Moore KM, Carling RW, Street LJ, Castro JL, Ragan CI, Dawson GR, Whiting PJ (2000) Sedative but not anxiolytic properties of benzodiazepines are mediated by the GABAA receptor α1 subtype. Nat Neurosci 3:587–592
Melchitzky DS, Lewis DA (2003) Pyramidal neuron local axon terminlas in monkey prefrontal cortex: Differential targeting of subclasses of GABA neurons. Cereb Cortex 13:452–460
Melchitzky DS, Sesack SR, Lewis DA (1999) Parvalbumin-immunoreactive axon terminals in macaque monkey and human prefrontal cortex: Laminar, regional and target specificity of type I and type II synapses. J Comp Neurol 408:11–22
Melchitzky DS, Gonzalez-Burgos G, Barrionuevo G, Lewis DA (2001) Synaptic targets of the intrinsic axon collaterals of supragranular pyramidal neurons in monkey prefrontal cortex. J Comp Neurol 430:209–221
Mirnics K, Middleton FA, Marquez A, Lewis DA, Levitt P (2000) Molecular characterization of schizophrenia viewed by microarray analysis of gene expression in prefrontal cortex. Neuron 28:53–67
Mirsky AF (1969) Neuropsychological bases of schizophrenia. Annu Rev Psychol 20:321–348
Neuchterlein KH, Dawson ME (1984) Information processing and attentional functioning in the developmental course of schizophrenia disorders. Schizophr Bull 10:160–203
Nusser Z, Sieghart W, Benke D, Fritschy J-M, Somogyi P (1996) Differential synaptic localization of two major γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor α subunits on hippocampal pyramidal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:11939–11944
Park S, Holzman PS (1992) Schizophrenics show spatial working memory deficits. Arch Gen Psychiatry 49:975–982
Peters A (1984) Chandelier cells. In: Jones EG, Peters A (eds) Cerebral cortex, vol 1. Plenum Press, New York, pp 361–380
Pierri JN, Chaudry AS, Woo T-U, Lewis DA (1999) Alterations in chandelier neuron axon terminals in the prefrontal cortex of schizophrenic subjects. Am J Psychiatry 156:1709–1719
Posner MI, Di Girolamo GJ (1998) The attentive brain. MIT Press, Cambridge
Pouille F, Scanziani M (2001) Enforcement of temporal fidelity in pyramidal cells by somatic feed-forward inhibition. Science 293:1159–1163
Rao SG, Williams GV, Goldman-Rakic PS (1999) Isodirectional tuning of adjacent interneurons and pyramidal cells during working memory: evidence for microcolumnar organization in PFC. J Neurophysiol 81:1903–1916
Rao SG, Williams GV, Goldman-Rakic PS (2000) Destruction and creation of spatial tuning by disinhibition: GABAA blockade of prefrontal cortical neurons engaged by working memory. J Neurosci 20:485–494
Rudolph U, Crestani F, Benke D, Brünig I, Benson JA, Fritschy J-M, Martin JR, Bluethmann H, Möhler H (1999) Benzodiazepine actions mediated by specific γ-aminobutyric acidA receptor subtypes. Nature 401:796–800
Shallice T (1988) From neuropsychology to mental structure. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Shu Y, Hasenstaub A, McCormick DA (2003) Turning on and off recurrent balanced cortical activity. Nature 423:288–293
Spencer KM, Nestor PG, Salisbury DF, Shenton ME, McCarley RW (2003) Abnormal neural synchrony in schizophrenia. J Neurosci 23:7407–7411
Tallon-Baudry C, Bertrand O, Peronnet F, Pernier J (1998) Induced gamma-band activity during the delay of a visual short-term memory task in humans. J Neurosci 18:4244–4254
Taylor SF (1996) Cerebral blood flow activation and functional lesions in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 19:129–140
Vawter MP, Crook JM, Hyde TM, Kleinman JE, Weinberger DR, Becker KG, Freed WJ (2002) Microarray analysis of gene expression in the prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia: a preliminary study. Schizophr Res 58:11–20
Volk DW, Lewis DA (2002) Impaired prefrontal inhibition in schizophrenia: relevance for cognitive dysfunction. Physiol Behav 77:501–505
Volk DW, Austin MC, Pierri JN, Sampson AR, Lewis DA (2000) Decreased GAD67 mRNA expression in a subset of prefrontal cortical GABA neurons in subjects with schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 57:237–245
Volk DW, Austin MC, Pierri JN, Sampson AR, Lewis DA (2001) GABA transporter-1 mRNA in the prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia: decreased expression in a subset of neurons. Am J Psychiatry 158:256–265
Volk DW, Pierri JN, Fritschy J-M, Auh S, Sampson AR, Lewis DA (2002) Reciprocal alterations in pre- and postsynaptic inhibitory markers at chandelier cell inputs to pyramidal neurons in schizophrenia. Cereb Cortex 12:1063–1070
Weinberger DR, Gallhofer B (1997) Cognitive dysfunction in schizophrenia. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 12S:29–36
Weinberger DR, Berman KF, Zec RF (1986) Physiologic dysfunction of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia. I. Regional cerebral blood flow evidence. Arch Gen Psychiatry 43:114–124
Weinberger DR, Berman KF, Illowsky BP (1988) Physiological dysfunction of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia: III. A new cohort and evidence for a monoaminergic mechanism. Arch Gen Psychiatry 45:609–615
Weinberger DR, Egan MF, Bertolino A, Callicott JH, Mattay VS, Lipska BK, Berman KF, Goldberg TE (2001) Prefrontal neurons and the genetics of schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 50:825–844
Wilson FA, O Scalaidhe SP, Goldman-Rakic PS (1994) Functional synergism between putative gamma-aminobutyrate-containing neurons and pyramidal neurons in prefrontal cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:4009–4013
Wolkowitz OM, Pickar D (1991) Benzodiazepines in the treatment of schizophrenia: a review and reappraisal. Am J Psychiatry 148:714–726
Woo T-U, Miller JL, Lewis DA (1997) Parvalbumin-containing cortical neurons in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 154:1013–1015
Woo T-U, Whitehead RE, Melchitzky DS, Lewis DA (1998) A subclass of prefrontal gamma-aminobutyric acid axon terminals are selectively altered in schizophrenia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:5341–5346
Xu Q, de la Cruz E, Anderson SA (2003) Cortical interneuron fate determination: diverse sources for distinct subtypes? Cereb Cortex 13:670–676
Acknowledgments
Work by the authors cited in this manuscript was supported by USPHS grants MH51234, MH43784 and MH45156.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lewis, D.A., Volk, D.W. & Hashimoto, T. Selective alterations in prefrontal cortical GABA neurotransmission in schizophrenia: a novel target for the treatment of working memory dysfunction. Psychopharmacology 174, 143–150 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-003-1673-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-003-1673-x