Abstract
Rationale
Previous studies have demonstrated an association between genetic polymorphisms of the μ opioid receptor gene (OPRM1) and response to naltrexone treatment. The Asp40 variant genotype previously shown to be associated with naltrexone treatment response is known to be relatively common among Koreans.
Objectives
This study was conducted to prospectively investigate the relationship between genotype and response to open-label naltrexone treatment in Korean alcohol-dependent subjects.
Materials and methods
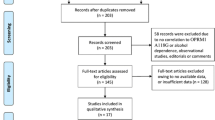
Sixty-three alcohol-dependent subjects were prescribed naltrexone for 12 weeks in combination with cognitive behavioral therapy. Thirty-two subjects were adherent, taking the medication at least 80% of the treatment days [16 Asn40 (A/A) patients and 16 Asp40 variant (A/G or G/G) patients].
Results
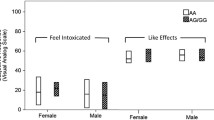
Subjects adherent to naltrexone treatment with one or two copies of the Asp40 allele took a significantly longer time than the Asn40 group to relapse (p = 0.014). Although not significant, the Asn40 group treated with naltrexone had a 10.6 times greater relapse rate than the Asp40 variant group. There was no significant difference between the Asn40 group and the Asp40 variant group treated with naltrexone in rates of abstinence.
Conclusions
These results demonstrating a higher therapeutic effect of naltrexone in Korean alcohol-dependent individuals with the Asp40 variant genotype than the Asn40 genotype are consistent with previous study results in individuals of European descent. This is the first study to examine the pharmacogenetics treatment response to naltrexone in non-European subjects.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association. DSM-IV (1994) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4th edn. American Psychiatric Press, Washington, DC
Anton RF, Moak DH, Latham PK, Waid LR, Malcolm RJ, Dias JK, Roberts JS (2001) Posttreatment results of combining naltrexone with cognitive-behavior therapy for the treatment for alcoholism. J Clin Psychopharmacol 21:72–77
Anton RF, Oroszi G, O’Malley S, Couper D, Swift R, Pettinati H, Goldman D (2008) An evaluation of mu-opioid receptor (OPRM1) as a predictor of naltrexone response in the treatment of alcohol dependence: results from the Combined Pharmacotherapies and Behavioral Interventions for Alcohol Dependence (COMBINE) study. Arch Gen Psychiatry 65:132–133
Bergen AW, Kokoszka J, Peterson R, Long JC, Virkkunen M, Linnoila M, Goldman D (1997) Mu opioid receptor gene variants: lack of associated with alcohol dependence. Mol Psychiatry 2:490–494
Bond C, LaForge KS, Tian M, Melia D, Zhang S, Borg L, Gong J, Schluger J, Strong JA, Leal SM, Tischfield JA, Kreek MJ, Yu L (1998) Single-nucleotide polymorphism in the human mu opioid receptor gene alters beta-endorphin binding and activity: possible implications for opiate addiction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:9608–9613
Chick J, Anton R, Checinski K, Croop R, Drummond DC, Farmer R, Labriola D, Marshall J, Moncrieff J, Morgan MY, Peters T, Ritson B (2000) A multicentre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of naltrexone in the treatment of alcohol dependence or abuse. Alcohol Alcohol 35:587–593
Chou WY, Yang LC, Lu HF, Ko JY, Wang CH, Lin SH, Lee TH, Concejero A, Hsu CJ (2006) Association of mu-opioid receptor gene polymorphism (A118G) with variations in morphine consumption for analgesia after total knee arthroplasty. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 50:787–792
De Witte (1996) The role of neurotransmitters in alcohol dependence: animal research.31(Suppl 1):13–16
Filbey FM, Ray L, Smolen A, Claus ED, Audette A, Hutchison KE (2008) Differential neuronal response to alcohol priming and alcohol taste cues is associated with DRD4 VNTR and OPRM1 genotypes. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 32:1113–1123
Gelernter J, Gueorguieva R, Kranzler HR, Zhang H, Cramer J, Rosenheck R, Krystal JH (2007) Opioid receptor gene (OPRM1, OPRK1, and OPRD1) variants and response to naltrexone treatment for alcohol dependence: results from the VA Cooperative Study. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 31:555–563
Gelernter J, Kranzler H, Cubells J (1999) Genetics of two mu opioid receptor gene (OPRM1) exon 1 polymorphisms: population studies, and allele frequencies in alcohol- and drug-dependence subjects. Mol Psychiatry 4:476–483
Gianoulakis C (1996) Implications of endogenous opioids and dopamine in alcoholism: human and basic science studies. Alcohol Alcohol 31(Suppl 1):33–42
Hernandez-Avila CA, Wand G, Luo X, Gelernter J, Kranzler HR (2003) Association between the cortisol response to opioid blockade and the Asn40Asp polymorphism at the mu-opioid receptor locus (OPRM1). Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 118:60–65
Kim SG, Kim CM, Kang DH, Kim YJ, Byun WT, Kim SY, Park JM, Kim MJ, Oslin DW (2004) Association of functional opioid receptor genotypes with alcohol dependence in Koreans. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 28:986–990
King AC, Volpicelli JR, Frazer A, O’Brien CP (1997) Effect of naltrexone on subjective alcohol response in subjects at high and low risk for future alcohol dependence. Psychopharmacology 129:15–22
Klepstad P, Rakvag TT, Kaasa S, Holthe M, Dale O, Borchgrevink PC, Baar C, Vikan T, Krokan HE, Skorpen F (2004) The 118 A > G polymorphism in the human mu-opioid receptor gene may increase morphine requirements in patients with pain caused by malignant disease. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 48:1232–1239
Kranzler H, Modesto-Lowe V, Van Kirk J (2000) Naltrexone vs. nefazadone for treatment of alcohol dependence. A placebo-controlled trial. Neuropsychopharmacology 22:493–503
Krystal JH, Cramer JA, Krol WF, Kirk GF, Rosenheck RA (2001) Veterans Affairs Naltrexone Cooperative Study 425 Group. Naltrexone in the treatment of alcohol dependence. N Engl J Med 345:1734–1739
Lahiri DK, Schnabel B (1993) DNA isolation by a rapid method from human blood samples: effects of MgCl2, EDTA, storage time, and temperature on DNA yield and quality. Biochem Genet 31:321–328
Lerman C, Wileyto EP, Patterson F, Rukstalis M, Audrain-McGovern J, Restine S, Shields PG, Kaufmann V, Redden D, Benowitz N, Berrettini WH (2003) The functional mu opioid receptor (OPRM1) Asn40Asp variant predicts short-term response to nicotine replacement therapy in a clinical trial. Pharmacogenomics J 4:184–192
Lotsch J, Skarke C, Grosch S, Darimont J, Schmidt H, Geisslinger G (2002) The polymorphism A118G of the human mu-opioid receptor gene decreases the pupil constrictory effect of morphine-6-glucuronide but not that of morphine. Pharmacogenetics 12:3–9
Lotsch J, Stuck B, Hummel T (2006) The human mu-opioid receptor gene polymorphism 118A > G decreases cortical activation in response to specific nociceptive stimulation. Behav Neurosci 120:1218–1224
Monterosso JR, Flannery BA, Pettinati HM, Oslin DW, Rukstalis M, O’Brien CP, Volpicelli JR (2001) Predicting treatment response to naltrexone: the influence of craving and family history. Am J Addict 10:258–269
Monti PM, Rohsenow DJ, Swift RM, Gulliver SB, Colby SM, Mueller TI, Brown RA, Gordon A, Abrams DB, Niaura RS, Asher MK (2001) Naltrexone and cue exposure with coping and communication skills training for alcoholics: treatment process and 1-year outcomes. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 25:1634–1647
Morris PL, Hopwood M, Whelan G, Gardiner J, Drummond E (2001) Naltrexone for alcohol dependence: a randomized controlled trial. Addiction 96:1565–1573
Munafo MR, Elliot KM, Murphy MF, Walton RT, Johnstone EC (2007) Association of the mu-opioid receptor gene with smoking cessation. Pharmacogenomics J 7:353–361
Murray C, Lopez AD (1996) The global burden of disease: a comprehensive assessment of mortality and disability from disease, injuries, and risk factors in 1990 and projected to 2020. Harvard University Press, Boston
Oertel BG, Schmidt R, Schneider A, Geisslinger G, Lotsch J (2006) The mu-opioid receptor gene polymorphism 118A>G depletes alfentanil-induced analgesia and protects against respiratory depression in homozygous carriers. Pharmacogenet Genomics 16:625–636
O’Malley SS, Jaffe AJ, Chang G, Schottenfeld RS, Meyer RE, Rounsaville B (1992) Naltrexone and coping skills therapy for alcohol dependence: a controlled study. Arch Gen Psychiatry 49:881–887
Ooteman W, Koeter MW, Verheul R, Schippers GM, van den Brink W (2007) The effect of naltrexone and acamprosate on cue-induced craving, autonomic nervous system and neuroendocrine reactions to alcohol-related cues in alcoholics. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 17:558–666
Oslin D, Liberto JG, O’Brein J, Krois S, Norbeck J (1997) Naltrexone as an adjunctive treatment for older patients with alcohol dependence. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 5:324–332
Oslin DW, Berrettini W, Kranzler HR, Pettinati H, Gelernter J, Volpicelli JR, O’Brien CP (2003) A functional polymorphism of the mu-opioid receptor gene is associated with naltrexone response in alcohol dependent patients. Neuropsychopharmaclolgy 28:1546–1552
Patel VA, Pohorecky LA (1989) Acute and chronic ethanol treatment on beta-endorphin and catecholamine levels. Alcohol 6:59–63
Ray LA, Hutchison KE (2004) A polymorphism of the mu-opioid receptor gene (OPRM1) and sensitivity to the effects of alcohol in humans. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 28:1789–1795
Ray LA, Hutchison KE (2007) Effects of naltrexone on alcohol sensitivity and genetic moderators of medication response: a double-blind placebo-controlled study. Arch Gen Psychiatry 64:1069–1077
Ray R, Jepson C, Patterson F, Strasser A, Rukstalis M, Perkins K, Lynch KG, O’Malley S, Berrettini WH, Lerman C (2006) Association of OPRM1 A118G variant with the relative reinforcing value of nicotine. Psychopharmacology 188:355–363
Rohsenow DJ, Miranda R Jr, McGeary JE, Monti PM (2007) Family history and antisocial traits moderate naltrexone’s effects on heavy drinking in alcoholics. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 15:272–281
Sander T, Gscheidel N, Wendel B, Samochowiec J, Smolka M, Rommelspacher H, Schmialt LG, Hoehe MR (1998) Human mu-opioid receptor variation and alcohol dependence. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 22:2108–2110
van den Wildenberg E, Wiers RW, Dessers J, Janssen RG, Lambrichs EH, Smeets HJ, van Breukelen GJ (2007) A functional polymorphism of the mu-opioid receptor gene (OPRM1) influences cue-induced craving for alcohol in male heavy drinkers. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 31:1–10
Volpicelli JR, O’Brein CP, Alterman AI, Hayashida M (1990) Naltrexone and the treatment of alcohol dependence: initial observations. In: Reid LD (ed) Opioids, bulimia and alcohol abuse & addiction. Springer, New York, pp 195–214
Volpicelli JR, Alterman AI, Hayashida M, O’Brien CP (1992) Naltrexone in the treatment of alcohol dependence. Arch Gen Psychiatry 49:876–880
Volpicelli JR, Watson NT, King AC, Sherman CE, O’Brien CP (1995) Effect of naltrexone on alcohol ‘high’ in alcoholics. Am J Psychiatry 152:613–615
Wand GS, McCaul M, Yang X, Reynolds J, Gotjen D, Lee S, Ali A (2002) The mu-opioid receptor gene polymorphism (A118G) alters HPA axis activation induced by opioid receptor blockade. Neuropsychopharmacology 26:106–114
Widdowson PS, Holman RB (1992) Ethanol-induced increase in endogenous dopamine release may involve endogenous opiates. J Neurochem 59:157–163
Wood PL (1982) Multiple opiate receptors: support for unique mu, delta and kappa sites. Neuropharmacology 21:487–497
Zhang Y, Wang D, Johnson AD, Papp AC, Sadee W (2005) Allelic expression imbalance of human mu opioid receptor (OPRM1) caused by variant A118G. J Biol Chem 280:32618–32624
Zhang D, Shao C, Shao M, Yan P, Wang Y, Liu Y, Liu W, Lin T, Xie Y, Zha Y, Lu D, Li Y, Jin L (2007) Effect of mu-opioid receptor gene polymorphisms on heroin-induced subjective responses in a Chinese population. Bio Psychiatry 61:1244–1251
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by Je-il Pharmaceutical Co., Seoul, South Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, SG., Kim, CM., Choi, SW. et al. A mu opioid receptor gene polymorphism (A118G) and naltrexone treatment response in adherent Korean alcohol-dependent patients. Psychopharmacology 201, 611–618 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-008-1330-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-008-1330-5