Abstract.
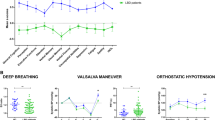
Rationale: Though reboxetine, a selective noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor, causes autonomic and cognitive adverse events there is a paucity of appropriately designed studies on the cognitive and autonomic effects of the drug in the literature. Objective: To compare the effects of reboxetine on cognitive and autonomic functions with those of placebo in healthy humans. Method: A randomised, double-blind, crossover study of 12 healthy male volunteers aged 25 (21–27; median, range) years. Subjects orally received 4 mg reboxetine and placebo twice daily for periods of 14 days each with at least 14 days in between. Vasoconstrictory response of cutaneous vessels (VR) and skin conductance response (SCR) following sudden deep breath were employed as parameters for autonomic function. Quantitative EEG (qEEG) and psychometric tests served as parameters for cognitive function. Results: Reboxetine decreased SCR and prolonged the dilation phase of VR (P<0.05). It did not affect cognitive functions such as flicker fusion frequency, choice reaction, memory and psychomotor coordination but increased slow beta (beta1) power density in the qEEG. Tiredness (n=12), dry mouth (n=9), delayed urination (n=3) and constipation (n=1) were noted with reboxetine. Conclusion: Sustained peripheral and/or central sympathetic activation accounts for the prolongation of VR. The decrease of SCR and typical side effects suggest a relevant antimuscarinic drug action. Chronic administration of reboxetine at therapeutic doses causes autonomic dysfunction and subjective sedation but does not impair cognitive and psychomotor abilities in healthy humans.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siepmann, .M., Mück-Weymann, .M., Joraschky, .P. et al. The effects of reboxetine on autonomic and cognitive functions in healthy volunteers. Psychopharmacology 157, 202–207 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130100791
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130100791