Abstract
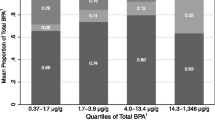
Bisphenol A (BPA) is a widely used industrial chemical in the manufacturing of polycarbonate plastic bottles, food and beverage can linings, thermal receipts, and dental sealants. Animal and human studies suggest that BPA may disrupt normal hormonal function and hence, potentially, have negative effects on the human health. While total BPA is frequently reported, it is recognized that free BPA is the biologically active form and is rarely reported in the literature. The objective of this study was to develop a sensitive and improved method for the measurement of free and total BPA in human urine. Use of a labeled conjugated BPA (bisphenol A-d6 β-d-glucuronide) allowed for the optimization of the enzymatic reaction and permitted an accurate determination of the conjugated BPA concentration in urine samples. In addition, a 13C12-BPA internal standard was used to account for the analytical recoveries and performance of the isotope dilution method. Solid-phase extraction (SPE) combined with derivatization and analysis using a triple quadrupole GC-EI/MS/MS system achieved very low method detection limit of 0.027 ng/mL. BPA concentrations were measured in urine samples collected during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy in 36 Canadian women. Total maternal BPA concentrations in urine samples ranged from not detected to 9.40 ng/mL (median, 1.21 ng/mL), and free BPA concentrations ranged from not detected to 0.950 ng/mL (median, 0.185 ng/mL). Eighty-six percent of the women had detectable levels of conjugated BPA, whereas only 22 % had detectable levels of free BPA in their urine. BPA levels measured in this study agreed well with data reported internationally.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
United States Environmental Protection Agency (2013) Bisphenol A (BPA) action plan summary. http://www.epa.gov/opptintr/existingchemicals/pubs/actionplans/bpa.html.
Calafat AM, Ye X, Wong LY, Reidy JA, Needham LL (2008) Exposure of the U.S. population to bisphenol A and 4-tertiary-octylphenol: 2003–2004. Environ Health Perspect 116(1):39–44. doi:10.1289/ehp.10753
Melzer D, Rice NE, Lewis C, Henley WE, Galloway TS (2010) Association of urinary bisphenol a concentration with heart disease: evidence from NHANES 2003/06. PLoS One 5(1):e8673
Lang IA, Galloway TS, Scarlett A, Henley WE, Depledge M, Wallace RB, Melzer D (2008) Association of urinary bisphenol A concentration with medical disorders and laboratory abnormalities in adults. JAMA 300(11):1303–1310
Hengstler JG, Foth H, Gebel T, Kramer PJ, Lilienblum W, Schweinfurth H, Völkel W, Wollin KM, Gundert-Remy U (2011) Critical evaluation of key evidence on the human health hazards of exposure to bisphenol A. Crit Rev Toxicol 41(4):263–291
Völkel W, Colnot T, Csanády GA, Filser JG, Dekant W (2002) Metabolism and kinetics of bisphenol a in humans at low doses following oral administration. Chem Res Toxicol 15(10):1281–1287
Tominaga T, Negishi T, Hirooka H, Miyachi A, Inoue A, Hayasaka I, Yoshikawa Y (2006) Toxicokinetics of bisphenol A in rats, monkeys and chimpanzees by the LC-MS/MS method. Toxicology 226(2–3):208–217
Fernandez MF, Arrebola JP, Taoufiki J, Navalon A, Ballesteros O, Pulgar R, Vilchez JL, Olea N (2007) Bisphenol-A and chlorinated derivatives in adipose tissue of women. Reprod Toxicol 24(2):259–264
Stahlhut RW, Welshons WV, Swan SH (2009) Bisphenol A data in NHANES suggest longer than expected half-life, substantial nonfood exposure, or both. Environ Health Perspect 117(5):784–789
Ouchi K, Watanabe S (2002) Measurement of bisphenol A in human urine using liquid chromatography with multi-channel coulometric electrochemical detection. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 780(2):365–370
Kim YH, Kim CS, Park S, Han SY, Pyo MY, Yang M (2003) Gender differences in the levels of bisphenol A metabolites in urine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 312(2):441–448
He Y, Miao M, Herrinton LJ, Wu C, Yuan W, Zhou Z, Li DK (2009) Bisphenol A levels in blood and urine in a Chinese population and the personal factors affecting the levels. Environ Res 109(5):629–633
Li X, Ying G-G, Zhao J-L, Chen Z-F, Lai H-J, Su H-C (2013) 4-Nonylphenol, bisphenol-A and triclosan levels in human urine of children and students in China, and the effects of drinking these bottled materials on the levels. Environ Int 52(0):81–86. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2011.03.026
Brock JW, Yoshimura Y, Barr JR, Maggio VL, Graiser SR, Nakazawa H, Needham LL (2001) Measurement of bisphenol A levels in human urine. J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol 11(4):323–328. doi:10.1038/sj.jea.7500174
Markham DA, Waechter JM Jr, Wimber M, Rao N, Connolly P, Chuang JC, Hentges S, Shiotsuka RN, Dimond S, Chappelle AH (2010) Development of a method for the determination of bisphenol A at trace concentrations in human blood and urine and elucidation of factors influencing method accuracy and sensitivity. J Anal Toxicol 34(6):293–303
Ye X, Pierik FH, Hauser R, Duty S, Angerer J, Park MM, Burdorf A, Hofman A, Jaddoe VW, Mackenbach JP, Steegers EA, Tiemeier H, Longnecker MP (2008) Urinary metabolite concentrations of organophosphorous pesticides, bisphenol A, and phthalates among pregnant women in Rotterdam, the Netherlands: the Generation R study. Environ Res 108(2):260–267
Ye X, Pierik FH, Angerer J, Meltzer HM, Jaddoe VW, Tiemeier H, Hoppin JA, Longnecker MP (2009) Levels of metabolites of organophosphate pesticides, phthalates, and bisphenol A in pooled urine specimens from pregnant women participating in the Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study (MoBa). Int J Hyg Environ Health 212(5):481–491
Kawaguchi M, Inoue K, Yoshimura M, Ito R, Sakui N, Okanouchi N, Nakazawa H (2004) Determination of bisphenol A in river water and body fluid samples by stir bar sorptive extraction with in situ derivatization and thermal desorption-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 805(1):41–48. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2004.02.005
Kawaguchi M, Sakui N, Okanouchi N, Ito R, Saito K, Izumi S, Makino T, Nakazawa H (2005) Stir bar sorptive extraction with in situ derivatization and thermal desorption-gas chromatography–mass spectrometry for measurement of phenolic xenoestrogens in human urine samples. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 820(1):49–57
Kawaguchi M, Ito R, Okanouchi N, Saito K, Nakazawa H (2008) Miniaturized hollow fiber assisted liquid-phase microextraction with in situ derivatization and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry for analysis of bisphenol A in human urine sample. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 870(1):98–102
Fukata H, Miyagawa H, Yamazaki N, Mori C (2006) Comparison of ELISA- and LC-MS-based methodologies for the exposure assessment of bisphenol A. Toxicol Mech Methods 16(8):427–430. doi:10.1080/15376520600697404
Dekant W, Volkel W (2008) Human exposure to bisphenol A by biomonitoring: methods, results and assessment of environmental exposures. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 228(1):114–134
Vandenberg LN, Chahoud I, Heindel JJ, Padmanabhan V, Paumgartten FJ, Schoenfelder G (2010) Urinary, circulating, and tissue biomonitoring studies indicate widespread exposure to bisphenol A. Environ Health Perspect 118(8):1055–1070. doi:10.1289/ehp.0901716
Matthews JB, Twomey K, Zacharewski TR (2001) In vitro and in vivo interactions of bisphenol A and its metabolite, bisphenol A glucuronide, with estrogen receptors α and β. Chem Res Toxicol 14(2):149–157
Shimizu M, Ohta K, Matsumoto Y, Fukuoka M, Ohno Y, Ozawa S (2002) Sulfation of bisphenol A abolished its estrogenicity based on proliferation and gene expression in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Toxicol in Vitro 16(5):549–556
Fox SD, Falk RT, Veenstra TD, Issaq HJ (2011) Quantitation of free and total bisphenol A in human urine using liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Sep Sci 34(11):1268–1274
Ye X, Kuklenyik Z, Needham LL, Calafat AM (2005) Quantification of urinary conjugates of bisphenol A, 2,5-dichlorophenol, and 2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzophenone in humans by online solid phase extraction-high performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 383(4):638–644. doi:10.1007/s00216-005-0019-4
Volkel W, Bittner N, Dekant W (2005) Quantitation of bisphenol A and bisphenol A glucuronide in biological samples by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Drug Metab Dispos 33(11):1748–1757
Volkel W, Kiranoglu M, Fromme H (2008) Determination of free and total bisphenol A in human urine to assess daily uptake as a basis for a valid risk assessment. Toxicol Lett 179(3):155–162
Cunha SC, Fernandes JO (2010) Quantification of free and total bisphenol A and bisphenol B in human urine by dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction (DLLME) and heart-cutting multidimensional gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (MD-GC/MS). Talanta 83(1):117–125
Volkel W, Kiranoglu M, Fromme H (2011) Determination of free and total bisphenol A in urine of infants. Environ Res 111(1):143–148
Lacroix MZ, Puel S, Collet SH, Corbel T, Picard-Hagen N, Toutain P, Viguie C, Gayrard V (2011) Simultaneous quantification of bisphenol A and its glucuronide metabolite (BPA-G) in plasma and urine: applicability to toxicokinetic investigations. Talanta 85(4):2053–2059
Kubwabo C, Kosarac I, Stewart B, Gauthier BR, Lalonde K, Lalonde PJ (2009) Migration of bisphenol A from plastic baby bottles, baby bottle liners and reusable polycarbonate drinking bottles. Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess 26(6):928–937
Stottmeister E, Heemken OP, Hendel P, Donnevert G, Frey S, Allmendinger H, Sawal G, Jandel B, Geiss S, Donau R, Koch A, Heinz I, Ottaviani M, Veschetti E, Hartl W, Kubwabo C, Benthe C, Tobinski V, Woldmann H, Spilker R (2009) Interlaboratory trial on the analysis of alkylphenols, alkylphenol ethoxylates, and bisphenol A in water samples according to ISO/CD 18857-2. Anal Chem 81(16):6765–6773. doi:10.1021/ac900813m
United States Environmental Protection Agency (1986) Part 136—Guidelines establishing test procedures for the analysis of pollutants. http://dnr.wi.gov/regulations/labcert/documents/guidance/-LODguide.pdf)
Kang JH, Katayama Y, Kondo F (2006) Biodegradation or metabolism of bisphenol A: from microorganisms to mammals. Toxicology 217(2–3):81–90. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2005.10.001
Bai X, Shi H, Ye Z, Sun Q, Wang Q, Wang Z (2013) Degradation of bisphenol A by microorganisms immobilized on polyvinyl alcohol microspheres. Front Environ Sci Eng 1–7
Flint S, Markle T, Thompson S, Wallace E (2012) Bisphenol A exposure, effects, and policy: a wildlife perspective. J Environ Manag 104:19–34. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2012.03.021
Lindblom E, Press-Kristensen K, Vanrolleghem PA, Mikkelsen PS, Henze M (2009) Dynamic experiments with high bisphenol-A concentrations modelled with an ASM model extended to include a separate XOC degrading microorganism. Water Res 43(13):3169–3176. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2009.04.030
Welshons WV, Nagel SC, vom Saal FS (2006) Large effects from small exposures. III. Endocrine mechanisms mediating effects of bisphenol A at levels of human exposure. Endocrinology 147(6 Suppl):S56–S69. doi:10.1210/en.2005-1159
Richter CA, Birnbaum LS, Farabollini F, Newbold RR, Rubin BS, Talsness CE, Vandenbergh JG, Walser-Kuntz DR, Vom Saal FS (2007) In vivo effects of bisphenol A in laboratory rodent studies. Reprod Toxicol 24(2):199–224. doi:10.1016/j.reprotox.2007.06.004
Vandenberg LN, Maffini MV, Sonnenschein C, Rubin BS, Soto AM (2009) Bisphenol-A and the great divide: a review of controversies in the field of endocrine disruption. Endocr Rev 30(1):75–95. doi:10.1210/er.2008-0021
Woodruff TJ, Zota AR, Schwartz JM (2011) Environmental chemicals in pregnant women in the United States: NHANES 2003-2004. Environ Health Perspect 119(6):878–885. doi:10.1289/ehp.1002727
Quiros-Alcala L, Eskenazi B, Bradman A, Ye X, Calafat AM, Harley K (2013) Determinants of urinary bisphenol A concentrations in Mexican/Mexican-American pregnant women. Environ Int 59C:152–160. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2013.05.016
Barr DB, Wilder LC, Caudill SP, Gonzalez AJ, Needham LL, Pirkle JL (2005) Urinary creatinine concentrations in the U.S. population: implications for urinary biologic monitoring measurements. Environ Health Perspect 113(2):192–200
Cantonwine D, Meeker JD, Hu H, Sanchez BN, Lamadrid-Figueroa H, Mercado-Garcia A, Fortenberry GZ, Calafat AM, Tellez-Rojo MM (2010) Bisphenol a exposure in Mexico City and risk of prematurity: a pilot nested case control study. Environ Health 9:62. doi:10.1186/1476-069X-9-62
Philippat C, Mortamais M, Chevrier C, Petit C, Calafat AM, Ye X, Silva MJ, Brambilla C, Pin I, Charles MA, Cordier S, Slama R (2012) Exposure to phthalates and phenols during pregnancy and offspring size at birth. Environ Health Perspect 120(3):464–470. doi:10.1289/ehp.1103634
Casas M, Valvi D, Luque N, Ballesteros-Gomez A, Carsin AE, Fernandez MF, Koch HM, Mendez MA, Sunyer J, Rubio S, Vrijheid M (2013) Dietary and sociodemographic determinants of bisphenol A urine concentrations in pregnant women and children. Environ Int 56:10–18. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2013.02.014
Braun JM, Kalkbrenner AE, Calafat AM, Bernert JT, Ye X, Silva MJ, Barr DB, Sathyanarayana S, Lanphear BP (2011) Variability and predictors of urinary bisphenol A concentrations during pregnancy. Environ Health Perspect 119(1):131–137. doi:10.1289/ehp.1002366
Braun JM, Kalkbrenner AE, Calafat AM, Yolton K, Ye X, Dietrich KN, Lanphear BP (2011) Impact of early-life bisphenol A exposure on behavior and executive function in children. Pediatrics 128(5):873–882. doi:10.1542/peds.2011-1335
Donohue KM, Miller RL, Perzanowski MS, Just AC, Hoepner LA, Arunajadai S, Canfield S, Resnick D, Calafat AM, Perera FP, Whyatt RM (2013) Prenatal and postnatal bisphenol A exposure and asthma development among inner-city children. J Allergy Clin Immunol 131(3):736–742. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2012.12.1573
Martina CA, Weiss B, Swan SH (2012) Lifestyle behaviors associated with exposures to endocrine disruptors. Neurotoxicology 33(6):1427–1433. doi:10.1016/j.neuro.2012.05.016
Meeker JD, Cantonwine DE, Rivera-Gonzalez LO, Ferguson KK, Mukherjee B, Calafat AM, Ye X, Anzalota Del Toro LV, Crespo-Hernandez N, Jimenez-Velez B, Alshawabkeh AN, Cordero JF (2013) Distribution, variability, and predictors of urinary concentrations of phenols and parabens among pregnant women in Puerto Rico. Environ Sci Technol 47(7):3439–3447. doi:10.1021/es400510g
Kosarac I, Kubwabo C, Lalonde K, Foster W (2012) A novel method for the quantitative determination of free and conjugated bisphenol A in human maternal and umbilical cord blood serum using a two-step solid phase extraction and gas chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 898:90–94. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2012.04.023
Philippat C, Wolff MS, Calafat AM, Ye X, Bausell R, Meadows M, Stone J, Slama R, Engel SM (2013) Prenatal exposure to environmental phenols: concentrations in amniotic fluid and variability in urinary concentrations during pregnancy. Environ Health Perspect 121(10):1225–1231. doi:10.1289/ehp.1206335
Chevrier J, Gunier RB, Bradman A, Holland NT, Calafat AM, Eskenazi B, Harley KG (2013) Maternal urinary bisphenol a during pregnancy and maternal and neonatal thyroid function in the CHAMACOS study. Environ Health Perspect 121(1):138–144. doi:10.1289/ehp.1205092
Harley KG, Aguilar Schall R, Chevrier J, Tyler K, Aguirre H, Bradman A, Holland NT, Lustig RH, Calafat AM, Eskenazi B (2013) Prenatal and postnatal bisphenol A exposure and body mass index in childhood in the CHAMACOS cohort. Environ Health Perspect 121(4):514–520. doi:10.1289/ehp.1205548, 520e511-516
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Canada’s Chemicals Management Plan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kubwabo, C., Kosarac, I., Lalonde, K. et al. Quantitative determination of free and total bisphenol A in human urine using labeled BPA glucuronide and isotope dilution mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 406, 4381–4392 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-014-7829-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-014-7829-1