Abstract
Background
The effect of MDR1 C3435T single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in exon 26 on digoxin pharmacokinetics has recently been challenged.
Objective
To clarify the relationships between MDR1 genetic polymorphisms in exon 26 (C3435T) and 21 (G2677T/A) and digoxin pharmacokinetics.
Materials and methods
MDR1 genotypes for C3435T and G2677T/A SNPs were determined in 32 healthy subjects whose single oral dose digoxin pharmacokinetics had been measured over 48 h.
Results
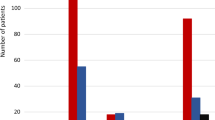
A significant relationship was observed between C3435T SNP and digoxin AUCs (p<0,05). Homozygous TT subjects had 20% higher digoxin plasma concentrations than CT and CC subjects and a trend for higher 48 h digoxin urinary recoveries (TT>CT>CC). Similar results, although not statistically significant, were observed from the MDR1 G2677T/A SNP.
Conclusions
Our results confirm that the MDR1 C3435T single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) significantly affects digoxin disposition kinetics, with homozygous TT subjects presenting the highest plasma concentrations.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fromm MF, Eichelbaum M (2002) The pharmacogenomics of human P-glycoprotein. In: Licinio J, Wong M-L (eds) Pharmacogenomics: the search for individualized therapies. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, pp 159–178
Hoffmeyer S, Burk O, von Richter O, Arnold HP, Brockmoller J, Johne A, et al (2000) Functional polymorphisms of the human multidrug-resistance gene: multiple sequence variations and correlation of one allele with P-glycoprotein expression and activity in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:3473–2378
Kim RB, Leake BF, Choo EF, Dresser GK, Kubba SV, Schwarz UI, et al (2001) Identification of functionally variant MDR1 alleles among European Americans and African Americans. Clin Pharmacol Ther 70:189–199
Drescher S, Schaeffeler E, Hitzl M, Hofmann U, Schwab M, Brinkmann U, et al (2002) MDR1 gene polymorphisms and disposition of the P-glycoprotein substrate fexofenadine. Br J Clin Pharmacol 53:526–534
Fellay J, Marzolini C, Meaden ER, Back DJ, Buclin T, Chave JP, et al (2002) Response to antiretroviral treatment in HIV-1-infected individuals with allelic variants of the multidrug resistance transporter 1: a pharmacogenetics study. Lancet 359:30–36
Ragueneau I, Poirier JM, Radembino N, Sao AB, Funck-Brentano C, Jaillon P (1999) Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic drug interactions between digoxin and macrogol 4000, a laxative polymer, in healthy volunteers. Br J Clin Pharmacol 48:453–456
Becquemont L, Verstuyft C, Kerb R, Brinkmann U, Lebot M, Jaillon P, et al (2001) Effect of grapefruit juice on digoxin pharmacokinetics in humans. Clin Pharmacol Ther 70:311–316
Verstuyft C, Strabach S, El Morabet H, Kerb R, Brinkmann U, Dubert l, et al (2003) Dipyridamole enhances digoxin bioavailability via P-glycoprootein inhibition. Clin Pharmacol Ther 73(1):51–60
Sakaeda T, Nakamura T, Horinouchi M, Kakumoto M, Ohmoto N, Sakai T, et al (2001) MDR1 genotype-related pharmacokinetics of digoxin after single oral administration in healthy Japanese subjects. Pharm Res 18:1400–1404
Johne A, Kopke K, Gerloff T, Mai I, Rietbrock S, Meisel C, et al (2002) Modulation of steady-state kinetics of digoxin by haplotypes of the P-glycoprotein MDR1 gene. Clin Pharmacol Ther 72:584–594
Kurata Y, Ieiri I, Kimura M, Morita T, Irie S, Urae A, et al (2002) Role of human MDR1 gene polymorphism in bioavailability and interaction of digoxin, a substrate of P-glycoprotein. Clin Pharmacol Ther 72:209–219
Bhardwaj RK, Gleser H, Becquemont L, Klotz U, Gupta SK, Fromm MF (2002) Piperine, a major constituent of black pepper, inhibits human P-glycoprotein and CYP3A4. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 302:645–650
Darbar D, Fromm MF, Dell'Orto S, Kim RB, Kroemer HK, Eichelbaum M, et al (1998) Modulation by dietary salt of verapamil disposition in humans. Circulation 98:2702–2708
Dresser G, Bailey D, Leake B, Schwarz U, Dawson P, Freeman D, et al (2002) Fruit juices inhibit organic anion transporting polypeptide-mediated drug uptake to decrease the oral availability of fexofenadine. Clin Pharmacol Ther 71:11–20
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by two grants from the Délégation Régionale de la Recherche Clinique d'Ile de France—Assistance Publique Hôpitaux de Paris (CRIC 2001 and CRIC 2000) and by the Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale and the Assistance Publique—Hôpitaux de Paris at the Clinical Investigation Center of Saint Antoine University Hospital and the Robert-Bosch Foundation, Stuttgart Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verstuyft, C., Schwab, M., Schaeffeler, E. et al. Digoxin pharmacokinetics and MDR1 genetic polymorphisms. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 58, 809–812 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-003-0567-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-003-0567-5