Abstract
Objectives
The objectives were to study the absorption kinetics and pharmacodynamics of two oral formulations of flecainide in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) and to assess the relationship between pharmacokinetic parameters and the efficacy in restoring sinus rhythm.
Methods
The data of 54 patients included in a randomised, open, parallel-group study were used. Patients received an oral solution containing 300 mg flecainide and 20 mg cisapride or three tablets each containing 100 mg flecainide. The pharmacokinetic profile of flecainide was fitted using a one-compartment model with lag-time and first-order absorption.
Results
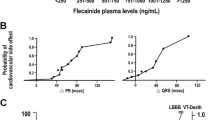
The tablets gave a maximum concentration (C max\ fit) of 0.43±0.14 mg/l at 2.37±1.20 h. The oral solution resulted in a much faster peak concentration at 1.05±0.71 h (P<0.0001). The C max\ fit of the oral solution of 0.60±0.17 mg/l was higher (P=0.0002) than that of the tablets, and interindividual variabilities of C max\ fit were 28% and 33%, respectively. The absorption rate constant (ka) of the oral solution was twofold larger (P<0.0001). A higher ka (P=0.04) and a duration of AF less than 24 h (P=0.006) increased the probability of cardioversion. If atrial fibrillation lasted less than 24 h, only ka (P=0.016) was obtained as a significant variable in multivariate analysis. The linear models of QRS interval changes versus flecainide concentrations of both formulations had similar slopes with similar interindividual variabilities.
Conclusions
The probability of cardioversion after an oral loading dose of flecainide in patients with AF is dependent on ka. Rapid loading of the effect compartment, i.e. the atria, appears to be critical to reach cardioversion. Higher flecainide serum concentrations and a more rapid absorption does not increase interindividual variability of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, which is important when safety is considered.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Suttorp MJ, Kingma JH, Lie-A-Huen L, Mast EG (1989) Intravenous flecainide versus verapamil for acute conversion of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation or flutter to sinus rhythm. Am J Cardiol 63:693–696
Suttorp MJ, Kingma JH, Jessurun ER, Lie-A-Huen L, Van Hemel NM, Lie KI (1990) The value of class Ic antiarrhythmic drugs for acute conversion of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation to sinus rhythm. J Am Coll Cardiol 16:1722–1727
Margolis B, De Silva RA, Lown B (1980) Episodic drug treatment in the management of paroxysmal arrhythmia. Am J Cardiol 45:621–626
Lie-A-Huen L, Kingma JH (1992) Episodic treatment of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. In: Kingma JH, Van Hemel NM, Lie KI (ed) Atrial fibrillation, a treatable disease? Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 149–157
Fuster V, Rydén LE, Asinger RW, Cannom DS, Crijns HJ, Frye RL, Halperin JL, Kay GN, Klein WW, Levy S, McNamara RL, Prytowsky EN, Wann LS, Wyse DG (2001) ACC/AHA/ESC guidelines for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the European Society of Cardiology Committee for Practice Guidelines and Policy Conferences. Eur Heart J 22:1852–1923
Hamer AWF, Tanasescu DE, Marks JW, Peter T, Waxman AD, Mandel WJ (1987) Failure of episodic high-dose oral verapamil therapy to convert supraventricular tachycardia: a study of plasma verapamil levels and gastric motility. Am Heart J 114:334–342
Salerno DM, Granrud G, Sharkey P, Krejci J, Larson T, Erlien D, Berry D, Hodges M (1986) Pharmacodynamics and side effects of flecainide acetate. Clin Pharmacol Ther 40:101–107
Van Gelder IC, Brüggeman J, Crijns HJGM (1998) Current treatment recommendations in antiarrhythmic therapy. Drugs 55:331–346
Lie-A-Huen L, Stuurman RM, IJdenberg FN, Kingma JH, Meijer DKF (1989) High performance liquid chromatographic assay of flecainide and its enantiomers in serum. Ther Drug Monit 6:708–712
Proost JH (1985) Wagner’s exact Loo-Riegelman equation: the need for a criterion to choose between the linear and logarithmic trapezoidal rule. J Pharm Sci 74:793–794
Lie-A-Huen L, Proost JH, Kingma JH, Meijer DKF (1990) Absorption kinetics of oral and rectal flecainide in healthy subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 38:595–598
Proost JH (1987) Critical evaluation of the determination of bioavailability by numerical deconvolution. Thesis, University of Groningen, The Netherlands
Chennavasin P, Brater DC (1982) Aminoglycoside dosage adjustment in renal failure: a hand-held calculator program. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 22:91–94
Press WH, Flennery BP, Teukolsky SA, Vetterling WT (1986) Numerical recipes. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Mentré F, Gomeni R (1995) A two-step iterative algorithm for estimation in nonlinear mixed-effect models with an evaluation in population pharmacokinetics. J Biopharm Stat 5:141–158
Bennett JE, Wakefield JC (1996) A comparison of a Bayesian population method with two methods as implemented in commercially available software. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 24:403–432
Baeyens R, Reyntjens A, Verlinden M (1984) Cisapride accelerates gastric emptying and mouth-to-caecum transit of a barium meal. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 27:315–318
Kresvsky B, Malmud LS, Maurer AH, Somers MB, Siegel JA, Fisher RS (1987) The effect of oral cisapride on colonic transit. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1:293–304
Deneer VHM, Lie-A-Huen L, Kingma JH, Proost JH, Kelder JC, Brouwers JRBJ (1998) Absorption kinetics of oral sotalol combined with cisapride and sublingual sotalol in healthy subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol 45:485–490
Rowbothan DJ, Milligan K, McHugh P (1991) Effect of single doses of cisapride and ranitidine administered simultaneously on plasma concentrations of cisapride and ranitidine. Br J Anaesth 67:302–305
Bateman DN (1986) The action of cisapride on gastric emptying and the pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of oral diazepam. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 30:205–208
Kirch W, Janisch HD, Ohnhaus EE, Van Peer A (1989) Cisapride-cimetidine interaction: enhanced cisapride bioavailability and accelerated cimetidine absorption. Ther Drug Monit 11:411–414
Rowbothan DJ, Parnacott S, Nimmo WS (1992) No effect of cisapride on paracetamol absorption after oral simultaneous administration. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 42:235–236
World Health Organisation (1998) Cisapride: new contraindications. WHO Drug information 12:236
Funck-Brentano C, Becquemont L, Kroemer HK, Buhl K, Knebel NG, Eichelbaum M, Jaillon P (1994) Variable disposition kinetics and electrocardiographic effects of flecainide during repeated dosing in humans: contribution of genetic factors, dose-dependent clearance and interaction with amiodarone. Clin Pharmacol Ther 55:256–269
Mikus G, Gross AS, Beckmann J, Hertrampf R, Gundert-Remy U, Eichelbaum M (1989) The influence of the sparteine/debrisoquin phenotype on the disposition of flecainide. Clin Pharmacol Ther 45:562–576
Crijns HJGM, Van Wijk LM, Van Gilst WH, Kingma JH, Van Gelder IC, Lie KI (1988) Acute conversion of atrial fibrillation to sinus rhythm: clinical efficacy of flecainide acetate. Comparison of two regimes. Eur Heart J 9:634–638
Padrini R, Piovan D, Busa M, Al-Bunni M, Maiolino P, Ferrari M (1993) Pharmacodynamic variability of flecainide assessed by QRS changes. Clin Pharmacol Ther 53:59–64
Boriani G, Capucci A, Strocchi E, Cavilla R, Santarelli A, Biffi M, Maganai B (1993) Flecainide acetate: concentration-response relationships for antiarrhythmic and electrocardiographic effects. Int J Clin Pharm Res XIII:211–219
Capucci A, Lenzi T, Boriani G, Trisolino G, Binetti N, Cavazza M, Fontana G, Magnani B (1992) Effectiveness of loading oral flecainide for converting recent-onset atrial fibrillation to sinus rhythm in patients without organic heart disease or with only systemic hypertension. Am J Cardiol 70:69–72
Capucci A, Boriani G, Botto GL, Lenzi T, Rubino I, Falcone C, Trisolino G, Della Casa S, Binetti N, Cavazza M, Sanguinetti M, Magnani B (1994) Conversion of recent onset atrial fibrillation by a single oral loading dose of propafenone or flecainide. Am J Cardiol 74:503–505
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deneer, V.H.M., Lie-A-Huen, L., Kingma, J.H. et al. Absorption kinetics and pharmacodynamics of two oral dosage forms of flecainide in patients with an episode of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 60, 693–701 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-004-0831-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-004-0831-3