Abstract
Introduction
Pyogenic intraventricular empyema (PIE) is a potentially fatal CNS infection. However, it is sometimes difficult to diagnose PIE on the basis of clinical and conventional MRI findings. Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) has been accepted as a useful MR sequence for the diagnosis of various intracranial infections. The purpose of this study was to determine the DWI characteristics of PIE and the role of DWI in the diagnosis of PIE.
Methods
Eight patients with PIE underwent MRI including DWI. We assessed the presence and signal characteristics of PIE. In seven patients, the signal intensities of the PIE and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) were measured and the contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) percentage was calculated. ADC values of the PIE, CSF, and white matter were also determined.
Results
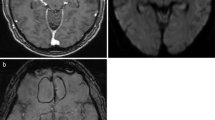
PIE was detected in all patients by DWI, in five (63%) by FLAIR imaging, and in two (25%) by T1- and T2-weighted imaging. The CNR percentages of the PIEs in relation to the CSF were highest for DWI, followed by FLAIR, T1-, and T2-weighted imaging. There were statistically significant differences between the images of each sequence. In all patients, PIE showed hyperintensities on DWI and hypointensities to the CSF and hypo- or isointensities to the white matter on ADC maps. The ADC values (mean±SD) of the PIE, CSF, and white matter were 0.60±0.27, 2.81±0.04, and 0.79±0.08 (×10−3 mm2/s). There was a statistically significant difference between PIE and the CSF.
Conclusion
PIE shows a bright intensity on DWI, and DWI is a sensitive MR sequence for the diagnosis of PIE.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pezzullo JA, Tung GA, Mudigonda S, Rogg JM (2003) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of pyogenic ventriculitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 180:71–75
Fukui MB, Williams RL, Mudigonda S (2001) CT and MR imaging features of pyogenic ventriculitis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1510–1516
Salmon J (1972) Ventriculitis complicating meningitis. Am J Dis Child 124:35–40
Kanamalla US, Ibarra RA, Jinkins JR (2000) Imaging of cranial meningitis and ventriculitis. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 10:309–331
Barloon TJ, Yuh WT, Knepper LE, Biller J, Ryals TJ, Sato Y (1990) Cerebral ventriculitis: MR findings. J Comput Assist Tomogr 14:272–275
Guo AC, Provenzale JM, Cruz LCH Jr, Petrella JR (2001) Cerebral abscesses: investigation using apparent diffusion coefficient maps. Neuroradiology 43:370–374
Ketelslegers E, Duprez T, Ghariani S, Thauvoy C, Cosnard G (2000) Time dependence of serial diffusion-weighted imaging features in a case of pyogenic brain abscess. J Comput Assist Tomogr 24(3):478–481
Noguchi K, Watanabe N, Nagayoshi T, Kanazawa T, Toyoshima S, Shimizu M et al (1999) Role of diffusion-weighted echo-planar MRI in distinguishing between brain abscess and tumour: a preliminary report. Neuroradiology 41:171–174
Tsuchiya K, Osawa A, Katase S, Fujikawa A, Hachiya J, Aoki S (2003) Diffusion-weighted MRI of subdural and epidural empyemas. Neuroradiology 45:220–223
Wong AM, Zimmerman RA, Simon EM, Pollock AN, Bilaniuk LT (2004) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of subdural empyemas in children. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1016–1021
Rana S, Albayram S, Lin DD, Yousem DM (2002) Diffusion-weighted imaging and apparent diffusion coefficient maps in a case of intracerebral abscess with ventricular extension. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:109–112
Fujikawa A, Tsuchiya K, Honya K, Nitatori T (2006) Comparison of MRI sequences to detect ventriculitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 187:1048–1053
Noguchi K, Ogawa T, Inugami A, Toyoshima H, Sugawara S, Hatazawa J et al (1995) Acute subarachnoid hemorrhage: MR imaging with fluid-attenuated inversion recovery pulse sequences. Radiology 196:773–777
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, KT., Choi, D.S., Ryoo, J.W. et al. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of pyogenic intraventricular empyema. Neuroradiology 49, 813–818 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-007-0264-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-007-0264-7