Abstract
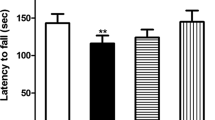
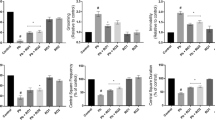
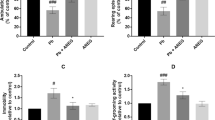
Lead poisoning has been extensively studied over the years. Many adverse physiological and behavioral impacts on the human body have been reported due to the entry of this heavy metal. It especially affects the neural development of children. The current study investigates the effect of lead exposure in young (1.5 months) and adult (10 months) male Fisher 344 rats. Five weeks of lead administration resulted in a profound change in the lead levels in the red blood cells (RBCs) of the young lead-exposed group (37.0 ± 4.47 μg/dl) compared to the control (<1 μg/dl) and adult (27.4 ± 8.38 μg/dl) lead-exposed groups. Therefore, this study confirms the fact that gastrointestinal absorption of lead in young is greater than that of adults. Furthermore, glutathione and glutathione disulfide (GSSG) levels in RBCs, liver, and brain tissues were measured to determine thiol status; malondialdehyde (MDA) levels of lipid peroxidation and catalase activity were measured to assess changes in oxidative stress parameters. Liver GSSG and MDA levels were significantly higher in the young lead-exposed group than those in the adult lead-exposed group. In RBCs and brains, however, adult lead-exposed animals have shown more elevated MDA levels than young animals exposed to the same lead treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 14 February 2002/Accepted: 6 August 2002
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aykin-Burns, N., Laegeler, A., Kellogg, G. et al. Oxidative Effects of Lead in Young and Adult Fisher 344 Rats. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 44, 0417–0420 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-002-2023-4
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-002-2023-4