Abstract
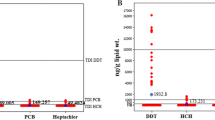
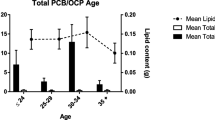
This study determined the concentrations of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins/dibenzofurans (PCDD/Fs), polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), organochlorine (OC) pesticides, and tris(4-chlorophenyl) methane (TCPMe) in human breast milk samples collected in 2003 from primipara mothers living in Penang, Malaysia. OCs were detected in all the samples analyzed with DDTs, hexachlorocyclohexane isomers (HCHs), and PCBs as the major contaminants followed by chlordane compounds (CHLs), hexachlorobenzene (HCB), and TCPMe. The residue levels of DDTs, HCHs, and CHLs were comparable to or higher than those in general populations of other countries, whereas PCBs and HCB were relatively low. In addition, dioxins and related compounds were also detected with a range of dioxin equivalent concentrations from 3.4 to 24 pg-TEQs/g lipid wt. Levels of toxic equivalents (TEQs) were slightly higher than those in other developing countries but still much lower than those of industrialized nations. One donor mother contained a high TEQs level, equal to the mean value in human breast milk from Japan, implying that some of the residents in Malaysia may be exposed to specific pollution sources of dioxins and related compounds. No association was observed between OCs concentrations and maternal characteristics, which might be related to a limited number of samples, narrow range of age of the donor mothers, and/or other external factors. The recently identified endocrine disrupter, TCPMe, was also detected in all human breast milk samples of this study. A significant positive correlation was observed between TCPMe and DDTs, suggesting that technical DDT might be a source of TCPMe in Malaysia. The present study provides a useful baseline for future studies on the accumulations of OCs in the general population of Malaysia.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abelsohn A, Gibson BL, Sanborn MD, Weir E (2002) Identifying and managing adverse environmental health effects: 5. Persistent organic pollutants. Can Med Assoc J 166:1549–1552
Albers JMC, Kreis IA, Liem AICD, van Zoonen P (1996) Factors that influence levels of contamination of human milk with poly-chlorinated organic compounds. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 30:285–291
Buser HR (1995) DDT, a potential source of environmental tris (chlorophenyl)methane and tris (chlorophenyl) methanol. Environ Sci Technol 29:2133–2139
Becher Q Skaare JU, Polder A, Sletten B, Rossland OJ, Hansen HK, Ptashekas J (1995) PCDDs, PCDFs, and PCBs in human milk from different parts of Norway and Lithuania. J Toxicol Environ Health 46:133–148
Cok I, Bilgili A, Ozdemir M, Ozbek H, Bilgili N, Burgaz S (1997) Organochlorine pesticides residues in human breast milk from agricultural regions of Turkey. 1995-1996. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 59:377–582
Dewailly E, Nantel A, Brunea S, Laliberte C, Perron L, Gingras S (1992) PCDDs, PCDFs and PCBs in Arctic Quebec: a preliminary assessment. Chemosphere 25:1245–1249
Falandysz J, Strandberg B, Strandberg L, Rappe C, Mizera T, Kalisinska E (1999) Tris(4-chlorophenyl)methane and tris(4-chlorophenyl)methanol in sediment and food webs from the Baltic south coast. Environ Sci Technol 33:517–521
Furst P, Furst C, Wilmers K (1994) Human milk as a bioindicator for body burden of PCDDs, PCDFs, organochlorine pesticides, and PCBs. Environ Health Perspect 102:187–193
Gladen BC, Monaghan SC, Lukyanova EM, Hulchiy OP, Shkyryak-Nuzhnyk ZA, Sericano JL, Little RE (1999) Organochlorine in breast milk from two cities in Ukraine. Environ Health Perspect 107: 459–462
Gonzalez MJ, Jimenez B, Hernandez LM, Gonnord MF (1996) Levels of PCDDs and PCDFs in human milk from populations in Madrid and Paris. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 56:197–204
Harris CA, O’Hagan S, Merson GHJ (1999) Organochlorine pesticide residues in human milk in the United Kingdom. Hum Exp Toxicol 18:602–606
Harris CA, Woolridge MW, Hay AWM (2001) Factors affecting the transfer of organochlorine pesticide residues to breastmilk. Chemosphere 43:243–256
Iida T, Hirakawa H, Matsueda T, Takenaka S, Nagayama J (1999) Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and related compounds in breast milk of Japanese primiparas and multiparas. Chemosphere 38: 2461–2466
Iwata H, Tanabe S, Sakai N, Tatsukawa R (1993) Distribution of persistent organochlorines in the oceanic air and surface seawater and the role of ocean on their global transport and fate. Environ Sci Technol 27: 1080–1098
Jarman WM, Simon M, Nostrom RJ, Bruns SA, Bacon CA, Simaret BRT, Riseborough RW (1992) Global distribution of tris(4-chlorophenyl)methanol in high trophic level birds and mammals. Environ Sci Technol 26:1770–1774
Kiviranta H, Purkunen R, Vartiainen T (1999) Levels and trends of PCDD/Fs and PCBs in human milk in Finland. Chemosphere 38:311–323
Konishi Y, Kuwabara K, Hori S (2001) Continuous surveillance of organochlorine compounds in human breast milk from 1972- to 1998 in Osaka, Japan. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 40:571–578
Kunisue T, Watanabe M, Someya M, Monirith I, Minh TB, Subramanian AN, Tana TS, Viet PH, Prudente M, Tanabe S (2002) PCDDs, PCDFs, PCBs and organochlorine insecticides in human breast milk collected from Asian developing countries: risk assessment for infants. Organohalogen Compound 58:285–287
Kunisue T, Someya M, Kayama F, Jin Y, Tanabe S (2004a) Persistent organochlorines in human breast milk collected from primiparae in Dalian and Shenyang. China. Environ Pollut 131:381–392
Kunisue T, Someya M, Monirith I, Watanabe M, Tana TS, Tanabe S (2004b) Occurrence of PCBs, organochlorine insecticides, tris(4-chlorophenyl)methane and tris(4-chlorophenyl)methanol in human breast milk collected from Cambodia. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 46:405–412
Lascombe I, Beffa D, Rüegg U, Tarradellas J, Wahli W (2000) Estrogenic activity assessment of environmental chemicals using in vitro assays: identification of two new estrogenic compounds. Environ Health Perspect 108: 621–629
Longnecker MP, Rogan WJ (2001) Persistent organic pollutants in children, Pediatr Res 50:322–323
Lonnerdal B (2000) Breast milk: a truly functional food. Nutrition 16:509–511
Minh TB, Watanabe M, Tanabe S, Miyazaki N, Jefferson TA, Prudente MS, Subramanian A, Karuppiah S (2000) Widespread contamination by tris(4-chlorophenyl)methane and tris(4-chlorophenyl)methanol in cetaceans from the North Pacific and Asian coastal waters. Environ Pollut 110:459–468
Minh TB, Watanabe M, Tanabe S, Yamada T, Hata J, Watanabe S (2001) Specific accumulation and elimination kinetics of tris(4-chlorophenyl)methane, tris(4-chlorophenyl)methanol, and other persistent organochlorines in humans from Japan. Environ Health Perspect 109:927–935
Minh NH, Minh TB, Watanabe M, Kunisue T, Monirith I, Tanabe S, Sakai S, Subramanian A, Sasikumar K, Viet PH, Buyen BC, Tana TS, Prudente MS (2003) Open dumping site in Asian developing countries: a potential source of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and polychlorinated dibenzofurans. Environ Sci Technol 37:1493–1502
Minh NH, Someya M, Minh TB, Kunisue K, Iwata H, Watanabe M, Tanabe S, Viet PH, Tuyen BC (2004). Persistent organochlorine residues in human breast milk from Hanoi and Hochiminh city, Vietnam: contamination, accumulation kinetics and risk assessment for infants. Environ Pollut 129:431–441
Monirith I, Ueno D, Takahashi S, Nakata H, Sudaryanto A, Subramanian A, Karuppiah S, Ismail A, Muchtar M, Zheng J, Richardson BJ, Prudente M, Hue ND, Tana TS, Tkalin AV, Tanabe S (2003) Asia-Pacific mussel watch: monitoring contamination of persistent organochlorine compounds in coastal waters of Asian countries. Mar Pollut Bull 46:281–300
Newsome WH, Ryan JJ (1999) Toxaphene and other chlorinated compounds in human milk from Northern and Southern Canada: a comparison. Chemosphere 39:519–526
Noren K, Meironyte D (2000) Certain organochlorine and organobromine contaminants in Swedish human milk in perspective of past 20-30 years. Chemosphere 40:1111–1123
Oostdam JV, Oilman A, Dewailly E, Usher P, Wheatley B, Kuhnlein H (1999) Human health implications of environmental contaminants in Arctic Canada: a review. Sci Total Environ 230:1–82
Othman AB, Balasubramanian K (2001) The FAO Programme for Community ICPM in Asia, Country report—Malaysia. Prepared for the meeting of the Programme Advisory Committee (PAC), Ayutthaya, Thailand, 2001. pp 1–11 November
Paumgartten FJR, Cruz CM, Chahoud I, Palavinskas R, Mathar W, (2000) PCDDs, PCDFs, PCB, and other organochlorine compounds in human milk from Rio de Janeiro. Braz Environ Res Sect A 83:293–291
Polder A, Odland JO, Tkachev A, Foreid S, Savinova TN, Skaare JU (2003) Geographic variation of chlorinated pesticides, toxaphenes and PCBs in human milk from sub-arctic locations in Russia. Sci Total Environ 306:179–195
Quinsey PM, Donohue DC, Ahokas JT (1995) Persistent of organochlorines in breast milk of women in Victoria-Australia. Food Chem Toxicol 33:49–56
Rahman MS, Montanarella L, Johansson B, Larsen BR (1993) Trace levels of tris(chlorophenyl)-methanol and -methane in human milk. Chemosphere 27:1487–1497
Sakai S, Hayakawa K, Takatsuki H, Kawakami I (2001) Dioxin-like PCBs released from waste incineration and their deposition flux. Environ Sci Technol 35:3601–3607
Schade G, Heinzow B (1998) Organochlorine pesticides and poly chlorinated biphenyls in human milk of mothers living in northern Germany: Current extent of contamination, time trend from 1986 to 1997 and factors that influence the levels of contamination. Sci Total Environ 215:31–39
Schecter A, Furst P, Furst C? Groebel W, Kolesnikov S, Savchenkov M, Beim A, Boldonov A, Trubitsan E, Vlasov B (1990) Levels of dioxins, dibenzofurans and other chlorinated xenobiotics in human milk from the Soviet Union. Chemosphere 20:927–934
Schoula R, Hajslova J, Bencko V, Pouska J, Holadova K, Vizek V (1996) Occurrence of persistent organochlorine contaminants in human milk collected in several regions of Czech Republic. Chemosphere 33:1485–1494
Schulz DE, Petrick G, Duinker JC (1989) Complete characterization of polychlorinated biphenyl congeners in commercial Aroclor and Clophen mixtures by multidimensional gas chromatography-electron capture detection. Environ Sci Technol 23:852–859
Uauy R, Peirano P (1999) Breast is best: human milk is the optimal food for brain development. Am J Clin Nutr 70:433–434
Van Leeuwen FXR, Feeley M, Schrenk D, Larsen JC, Farland W, Younes M (2000) Dioxins: WHO’s tolerable daily intake (TDI) revisited. Chemosphere 40:1095–1101
Van den Berg M, Birbaum I, Bosveld ATC, Brunstrom B, Cook P, Feeley M, Giesy JP, Hanberg A, Hasegawa R, Kennedy S W, Kubiak T, Larsen JC, Rolaf van Leeuwen FX, Liem AKD, Nolt C, Petersen RE, Poelinger L, Safe S, Schrenk D, Tillit D, Tysklind M, Younes M, Waem F, Zacharewski T (1998) Toxic equivalency factor (TEFs) for PCBs, PCDDs, PCDFs for humans and wildlife. Environ Health Perspect 106:775–792
Waliszewski SM, Aguirre AA, Infanzon RM, Silva CS, Siliceo J (2001) Organochlorine pesticide levels in maternal adipose tissue, maternal blood serum, umbilical blood serum and milk from inhabitants of Veracruz, Mexico. Arch Environ Contain Toxicol 40:432–438
Watanabe M, Niida M, Hashim H, Tanabe S (2003) Contamination by polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDDs) and dibenzofurans (PCDFs) in soils from dumping sites of municipal wastes in Malaysia. Presented in the PCB Symposium 2003 in Malaysia, February 24-15, 2003. http://www.tabemono.info/chosa/chikvukan/2003/2003/e_index.html
Wong CC, Leung KM, Poon BHT, Lan CY, Wong MH (2002) Organochlorine hydrocarbons in human breast milk collected in Hong Kong and Guangzhou. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 43:364–372
Zakaria Z, Heng LY, Abdullah P, Osman R, Din L (2003) The environmental contamination by Organochlorine insecticides of some agricultural areas in Malaysia. Mal J Chem 5:078–085
Acknowledgments
We thank the staff of Consumers’ Association of Penang, and Adventist Hospital Nursery, Malaysia for their assistance in sample collections. This study was supported by grants from the Japan Fund for Global Environment and “21st Century COE Program” from the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sudaryanto, A., Kunisue, T., Tanabe, S. et al. Persistent Organochlorine Compounds in Human Breast Milk from Mothers Living in Penang and Kedah, Malaysia. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 49, 429–437 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-004-0208-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-004-0208-8