Abstract
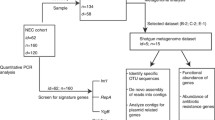
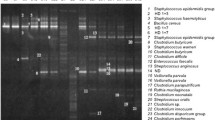
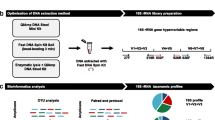
Different factors are known to influence the early gut colonization in newborns, among them the perinatal use of antibiotics. On the other hand, the effect on the baby of the administration of antibiotics to the mother during labor, referred to as intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis (IAP), has received less attention, although routinely used in group B Streptococcus positive women to prevent the infection in newborns. In this work, the fecal microbiota of neonates born to mothers receiving IAP and of control subjects were compared taking advantage for the first time of high-throughput DNA sequencing technology. Seven different 16S rDNA hypervariable regions (V2, V3, V4, V6 + V7, V8, and V9) were amplified and sequenced using the Ion Torrent Personal Genome Machine. The results obtained showed significant differences in the microbial composition of newborns born to mothers who had received IAP, with a lower abundance of Actinobacteria and Bacteroidetes as well as an overrepresentation of Proteobacteria. Considering that the seven hypervariable regions showed different discriminant ability in the taxonomic identification, further analyses were performed on the V4 region evidencing in IAP infants a reduced microbial richness and biodiversity, as well as a lower number of bacterial families with a predominance of Enterobacteriaceae members. In addition, this analysis pointed out a significant reduction in Bifidobacterium spp. strains. The reduced abundance of these beneficial microorganisms, together with the increased amount of potentially pathogenic bacteria, may suggest that IAP infants are more exposed to gastrointestinal or generally health disorders later in age.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahamsson TL, Jakobsson HE, Andersson AF, Björkst B, Engstrand L, Jenmalm MC (2012) Low diversity of the gut microbiota in infants with atopic eczema. J Allergy Clin Immunol 129:434–440
Albanese D, Fontana P, De Filippo C, Cavalieri D, Donati C (2015) MICCA: a complete and accurate software for taxonomic profiling of metagenomic data. Sci Rep 5:9743
Aloisio I, Mazzola G, Corvaglia LT, Tonti G, Faldella G, Biavati B, Di Gioia D (2014) Influence of intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis against group B Streptococcus on the early newborn gut composition and evaluation of the anti-streptococcus activity of Bifidobacterium strains. Appl Microbiol and Biotechnol 98:6051–6060
Al-Taiar A, Hammoud M, Thalib L, Isaacs D (2011) Pattern and etiology of culture-proven early onset neonatal sepsis: a five year prospective study. Int J Infec Diseases 15:631–634
Azad MB, Konya T, Maughan H, Guttman DS, Field CJ, Radha Chari RS, Sears MR, Becker AB, Scott JA, Kozyrskyj AL (2013) Gut microbiota of healty Canadian infants: profiles by mode of delivery and infant diet at 4 months. CMAJ 185:385–394
Azad MB, Konya T, Guttman DS, Field CJ, Sears MR, HayGlass KT, Mandhane PJ, Turvey SE, Subbarao P, Becker AB, Scott JA, Kozyrskyj AL (2015) Infant gut microbiota and food sensitization: associations in the first year of life. Clin Exp Allergy 45:632–643
Barriuso J, Valverde JR, Mellado RP (2011) Estimation of bacterial diversity using next generation sequencing of 16S rDNA: a comparison of different workflows. BMC Bioinformatics 12:473
Bezirtzoglou E (1997) The intestinal microflora during the first weeks of life. Anaerobe 3:173–177
Biagi E, Candela M, Centanni M, Consolandi C, Rampelli S, Turroni S, Severgnini M, Peano C, Ghezzo A, Scurti M, Salvioli S, Franceschi C, Brigidi P (2014) Gut microbiome in down syndrome. PLoS one 9:e112023
Cai L, Ye L, Tong AH, Lok S, Zhang T (2013) Biased diversity metrics revealed by bacterial 16 s pyrotags derived from different primer sets. PLoS one 8:e53649
Caporaso JG, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, DeSantis TZ, Anderson GL, Knight R (2010) PyNAST: a flexible tool for aligning sequences to a template alignment. Bioinformatics 26:266–267
Claesson MJ, Wang Q, O’Sullivan O, Greene-Diniz R, Cole JR, Ross RP, O’Toole PW (2010) Comparison of two next-generation sequencing technologies for resolving highly complex microbiota composition using tandem variable 16S rRNA gene regions. Nucleic Acids Res 38:e200
Dareng EO, Ma B, Famooto AO, Akarolo-Anthony SN, Offiong RA, Olaniyan O, Dakum PS, Wheeler CM, Fadrosh D, Yang H, Gajer P, Brotman RM, Ravel J, Adebamowo CA (2015) Prevalent high-risk HPV infection and vaginal microbiota in Nigerian women. Epidemiol Infect 11:1–15
De Filippo C, Cavalieri D, Di Paola M, Ramazzotti M, Poullet JB, Massart S, Collini S, Pieraccini G, Lionetti P (2010) Impact of diet in shaping gut microbiota revealed by a comparative study in children from Europe and rural Africa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:14691–14696
de Weerth C, Fuentes S, Puylaert P, de Vos WM (2013) Intestinal microbiota of infants with colic: development and specific signatures. Pediatrics 131:e550–e558
Di Gioia D, Aloisio I, Mazzola G, Biavati B (2014) Bifidobacteria: their impact on gut microbiota composition and their applications as probiotics in infants. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:563–577
Fouhy F, Ross RP, Fitzgerald G, Stanton C, Cotter P (2012) Composition of the early intestinal microbiota, knowledge, knowledge gaps and the use of high-throughput sequencing to address these gaps. Gut Microbes 3:203–220
Francino MP (2014) Early development of the gut microbiota and immune health. Pathogens 4:769–790
Hong S, Bunge J, Leslin C, Jeon S, Epstein SS (2009) Polymerase chain reaction primers miss half of rRNA microbial diversity. ISME J 3:1365–1373
Huda MN, Lewis Z, Kalanetra KM, Rashid M, Ahmad SM, Raqib R, Qadri F, Underwood MA, Mills DA, Stephensen CB (2014) Stool microbiota and vaccine responses of infants. Pediatrics 134:e362–e372
Jost T, Lacroix C, Braegger CP, Chassard C (2012) New insights in gut microbiota establishment in healthy breast fed neonates. PLoS one 7:e44595
Jost T, Lacroix C, Braegger CP, Rochat F, Chassard C (2014) Vertical mother-neonate transfer of maternal gut bacteria via breastfeeding. Environ Microbiol 16:2891–2904
Kennedy N, Walker A, Berry S, Duncan S, Farquarson F, Louis P, Thompson T, Ahmad T, Satsangi J, Flint H, Parkhill J, Lee C, Hold G (2014) The impact of different DNA extraction kits and laboratories upon the assessment of human gut microbiota composition by 16S rRNA gene sequencing. PLoS one 9:e88982
Keski-Nisula L, Kyynäräinen HR, Kärkkäinen U, Karhukorpi J, Heinonen S, Pekkanen J (2013) Maternal intrapartum antibiotics and decreased vertical transmission of Lactobacillus to neonates during birth. Acta Paediatr 102:480–485
Koenig JE, Scalfone N, FrickerAD SJ, Knight R, Angenent LT, Ruth EL (2011) Succession of microbial consortia in the developing infant gut microbiome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:4578–4585
Kumar PS, Brooker MR, Dowd SE, Camerlengo T (2011) Target region selection is a critical determinant of community fingerprints generated by 16S pyrosequencing. PLoS one 6:e20956
Makino H, Martin R, Ishikawa E, Gawad A, Kubota H, Sakai T, Oishi K, Tanaka R, Ben-Amor K, Knol J, Kushiro A (2015) Multilocus sequence typing of bifidobacterial strains from infant’s faeces and human milk: are bifidobacteria being sustainably shared during breastfeeding? Benef Microbes 6:563–572
Mao DP, Zhou Q, Chen CY, Quan ZX (2012) Coverage evaluation of universal bacterial primers using the metagenomic datasets. BMC Microbiol 12:66
Martin M (2011) Cut adapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMB Net J 17:10–12
Mejía-León ME, Petrosino JF, Ajami NJ, Domínguez-Bello MG, de la Barca AMC (2014) Fecal microbiota imbalance in Mexican children with type 1 diabetes. Sci Rep 4:e3814
Milani C, Hevia A, Foroni E, Duranti S, Turroni F (2013) Assessing the fecal microbiota: An optimized ion torrent 16S rRNA Gene-Based Analysis protocol. PLoS one 8:e68739
Polz MF, Cavanaugh CM (1998) Bias in template-to-product ratios in multitemplate PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:3724–3730
Price MN, Dehal PS, Arkin AP (2010) FastTree 2 – approximately maximum-likelihood trees for large alignments. PLoS one 5:e9490
Qin J, Li R, Raes J, Arumugam M, Burgdorf KS, Manichanh C, Nielsen T, Pons N, Levenez F, Yamada T, Mende DR, Li J, Xu J, Li S, Li D, Cao J, Wang B, Liang H, Zheng H, Xie Y, Tap J, Lepage P, Bertalan M, Batto JM, Hansen T, Le Paslier D, Linneberg A, Nielsen HB, Pelletier E, Renault P, Sicheritz-Ponten T, Turner K, Zhu H, Yu C, Li S, Jian M, Zhou Y, Li Y, Zhang X, Li S, Qin N, Yang H, Wang J, Brunak S, Doré J, Guarner F, Kristiansen K, Pedersen O, Parkhill J, Weissenbach J, MetaHIT Consortium, Bork P, Ehrlich SD, Wang J (2010) A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 464:59–65
Reysenbach AL, Giver LJ, Wickham GS, Pace NR (1992) Differential amplification of rRNA genes by polymerase chain reaction. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:3417–3418
Rodríguez JM, Murphy K, Stanton C, Ross RP, Kober OI, Juge N, Avershina E, Rudi K, Narbad A, Jenmalm MC, Marchesi JR, Collado MC (2015) The composition of the gut microbiota throughout life, with an emphasis on early life. Microb Ecol Health Dis 26:26050
Schloss PD, Gevers D, Westcott SL (2011) Reducing the effects of PCR amplification and sequencing artifacts on 16S rRNA-based studies. PLoS one 6:e27310
Sipos R, Szekely AJ, Palatinszky M, Revesz S, Marialigeti K, Nikolausz M (2007) Effect of primer mismatch, annealing temperature and PCR cycle number on 16S rRNA gene-targetting bacterial community analysis. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 60:341–350
Smith S, Vigilant L, Morin PA (2002) The effects of sequence length and oligonucleotide mismatches on 5′ exonuclease assay efficiency. Nucleic Acids Res 30:e111
Soergel DA, Dey N, Knight R, Brenner SE (2012) Selection of primers for optimal taxonomic classification of environmental 16S rRNA gene sequences. ISME J 6:1440–1444
Sundarakrishnan B, Pushpanathan M, Jayashree S, Rajendhran J, Sakthivel N, Jayachandran S, Gunasekaran P (2012) Assessment of microbial richness in pelagic sediment of andaman sea by bacterial tag encoded FLX titanium amplicon pyrosequencing (bTEFAP). Indian J Microbiol 52:544–550
Suzuki M, Rappe MS, Giovannoni SJ (1998) Kinetic bias in estimates of coastal picoplankton community structure obtained by measurements of small-subunit rRNA gene PCR amplicon length heterogeneity. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:4522–4529
Turroni F, Peano C, Pass DA, Foroni E, Severgnini M, Claesson MJ, Kerr C, Hourihane J, Murray D, Fuligni F, Gueimonde M, Margolles A, De Bellis G, O’Toole PW, van Sinderen D, Marchesi JR, Ventura M (2012) Diversity of bifidobacteria within the infant gut microbiota. PLoS one 7:e36957
Verani J, McGee L, Schrag S (2010) Prevention of perinatal group B streptococcal disease. Revised guidelines from CDC. MMWR Recomm Rep 59:1–32
Wagner Mackenzie B, Waite DW, Taylor MW (2015) Evaluating variation in human gut microbiota profiles due to DNA extraction method and inter-subject differences. Front Microbiol 6:e130
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole RJ (2007) Naïve bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:5261–5267
Yan ZL, Zheng XW, Han BZ, Han JS, Nout MJ, Chen JY (2013) Monitoring the ecology of Bacillus during daqu incubation, a fermentation starter, using culture-dependent and culture-independent methods. J Microbiol Biotechnol 23:614–622
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Life Technologies (Thermo Fisher Scientific) for the valuable support to our work. A special acknowledgment is for Dr. Raffaldi Fabio for his excellent technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The study was approved by the local ethics committee as indicated in the text.
Funding
This study was funding by the University of Bologna, Fundamental Research Oriented Program (grant number J61J10000790001).
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
“Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.”
Additional information
Irene Aloisio and Andrea Quagliariello contributed equally
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 49 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aloisio, I., Quagliariello, A., De Fanti, S. et al. Evaluation of the effects of intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis on newborn intestinal microbiota using a sequencing approach targeted to multi hypervariable 16S rDNA regions. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 5537–5546 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7410-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7410-2