Abstract
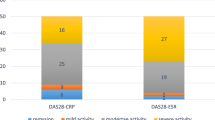
Antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptides (anti-CCP) are highly specific for the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) with a marginal increased prediction of the disease. In this study, we aimed to investigate the relation of the presence of anti-CCP with clinical manifestations and disease activity in a cohort of RA patients. A total of 61 RA patients were included in this study. Data of disease-related parameters such as duration of disease, medications, degree of pain (visual analog scale, VAS), disease activity score 28 (DAS-28) and health assessment questionnaire (HAQ) were recorded. Laboratory workup included erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), plasma C-reactive protein (CRP), rheumatoid factor (RF), anti-CCP, complete blood count and anemia parameters. Anti-CCP positivity was associated with higher scores of DAS-28, longer duration of morning stiffness, serum RF positivity and low levels of serum ferritin, while it was not associated with disease duration, VAS, HAQ, ESR, CRP and hemoglobin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee DM, Weinblatt ME (2001) Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 358:903–911
Hochberg MC (1993) Predicting the prognosis of patients with rheumatoid arthritis: is there a crystal ball? J Rheumatol 20:1265–1267
Turesson C, O’Fallon MW, Crowson CS, Gabriel SE, Matteson EL (2002) Occurrence of extra-articular disease manifestation is associated with excess mortality in a community-based cohort of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 29:62–67
Dörner T, Egerer K, Feist E, Burmester GR (2004) Rheumatoid factor revisited. Curr Opin Rheumatol 16:246–253
Nienhuis RL, Mandema E (1964) A new serum factor in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: the antiperinuclear factor. Ann Rheum Dis 23:302–305
Young BJ, Mallya RK, Leslie RD, Clark CJ, Hamblin TJ (1979) Anti-keratinantibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. Br Med J 2:97–99
Vossenaar ER, Despre′s N, Lapointe E, van der Heijden A, Lora M, Senshu T et al (2004) Rheumatoid arthritis specific anti-Sa antibodies target citrullinated vimentin. Arthritis Res Ther 6:R142–R150
Vossenaar ER, Radstake TR, van der Heijden A, van Mansum MA, Dieteren C, de Rooij DJ et al (2004) Expression and activity of citrullinating peptidylarginine deiminase enzymes in monocytes and macrophages. Ann Rheum Dis 63:373–381
Vossenaar ER, Zendman AJ, van Venrooij WJ, Pruijn GJ (2003) PAD, a growing family of citrullinating enzymes: genes, features and involvement in disease. Bioessays 25:1106–1118
Schellekens GA, de Jong BA, van den Hoogen FH, van de Putte LB, van Venrooij WJ (1998) Citrulline is an essential constituent of antigenic determinants recognized by rheumatoid arthritis-specific autoantibodies. J Clin Invest 101:273–281
Schellekens GA, Visser H, de Jong BA, van den Hoogen FH, Hazes JM, Breedveld FC et al (2000) The diagnostic properties of rheumatoid arthritis antibodies recognizing a cyclic citrullinated peptide. Arthritis Rheum 43:155–163
Zendman AJW, van Venrooij WJ, Pruijn GJM (2006) Use and significance of anti-CCP autoantibodies in rheumatoid arhritis. Rheumatology 45:20–25
Ates A, Karaaslan Y, Aksaray S (2006) Predictive value of autoantibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptide in patients with early arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 25:743–745
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, Healey LA, Kaplan SR, Liang MH, Luthra HS et al (1998) The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 31:315–324
Bizzaro N, Mazzanti G, Tonutti E, Villalta D, Tozzoli R (2001) Diagnostic accuracy of the anti-citrulline antibody assay for rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Chem 47(6):1089–1093
Nishimura K, Sugiyama D, Kogata Y, Tsuji G, Nakazawa T, Kawano S, Saigo K, Morinobu A, Koshiba M, Kuntz KM, Kamae I, Kumagai S (2007) Meta-analysis: diagnostic accuracy of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody and rheumatoid factor for rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Intern Med 146(11):797–808
Alexiou I, Germenis A, Ziogas A, Theodoridou K, Sakkas LI (2007) Diagnostic value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies in Greek patients with rheumatoid arthritis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 8:37
Nieto-Colonia AM, Santos WS, Keusseyan SP, Caldana W, Fernandes AR, Andrade LE (2008) Antibodies to citrullinated peptides are not associated with the rate of joint destruction in patients with a well-established diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Braz J Med Biol Res 41(3):188–192
Vittecoq O, Incaurgarat B, Jouen-Beades F, Legoedec J, Letourneur O, Rolland D, Gervasi G, Ménard JF, Gayet A, Fardellone P, Daragon A, Jolivet M, le Loët X, Tron F (2004) Autoantibodies recognizing citrullinated rat filaggrin in an ELISA using citrullinated and non-citrullinated recombinant proteins as antigens are highly diagnostic for rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol 135(1):173–180
Berglin E, Padyukov L, Sundin U, Hallmans G, Stenlund H, Van Venrooij WJ, Klareskog L, Dahlqvist SR (2004) A combination of autoantibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptide (CCP) and HLA-DRB1 locus antigens is strongly associated with future onset of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 6(4):R303–R308
Bukhari M, Thomson W, Naseem H, Bunn D, Silman A, Symmons D, Barton A (2007) The performance of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies in predicting the severity of radiologic damage in inflammatory polyarthritis: results from the Norfolk Arthritis Register. Arthritis Rheum 56(9):2929–2935
Kroot EJ, de Jong BA, van Leeuwen MA, Swinkels H, van den Hoogen FH, van’t Hof M, van de Putte LB, van Rijswijk MH, van Venrooij WJ, van Riel PL (2000) The prognostic value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in patients with recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 43(8):1831–1835
Agrawal S, Misra R, Aggarwal A (2007) Autoantibodies in rheumatoid arthritis: association with severity of disease in established RA. Clin Rheumatol 26(2):201–204
American College of Rheumatology Ad Hoc Committee on Clinical Guidelines (2002) Guidelines for the management of rheumatoid arthritis: 2002 update. Arthritis Rheum 46:328
Fries JF, Spitz PW, Young DY (1982) The dimensions of health outcomes: the health assessment questionnaire, disability, pain scales. J Rheumatol 9:789
Fries JF, Spitz PW, Kraines RG et al (1980) Measurement of patient outcome in arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 23:137
Lane SK, Gravel JW Jr (2002) Clinical utility of common serum rheumatologic tests. Am Fam Physician 65:1073
Donald F, Ward MM (1998) Evaluative laboratory testing practices of United States rheumatologists. Arthritis Rheum 41:725
Listing J, Rau R, Muller B, Berlin Collaborating Rheumatological Study Group et al (2000) HLA-DRB1 genes, rheumatoid factor, elevated C-reactive protein: independent risk factors of radiographic progression in early rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 27:2100
Wolfe F, Kleinheksel SM, Cathey MA et al (1988) The clinical value of the Stanford Health Assessment Questionnaire Functional Disability Index in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 15:1480
Bruce B, Fries JF (2003) The Stanford Health Assessment Questionnaire: a review of its history, issues, progress, documentation. J Rheumatol 30:167
Prevoo MLL, van’t Hof MA, Kuper HH, van de Putte LBA et al (1995) Modified disease activity scores that include twenty-eight-joint counts: development and validation in a prospective longitudinal study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 3:44
Papadopoulos NG, Tsiaousis GZ, Pavlitou-Tsiontsi A, Giannakou A, Galanopoulou VK (2008) Does the presence of anti-CCP autoantibodies and their serum levels influence the severity and activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients? Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 34(1):11–15
Inanc N, Dalkilic E, Kamali S, Kasapoglu-Günal E, Elbir Y, Direskeneli H, Inanc M (2007) Anti-CCP antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 26(1):17–23
Serdaroğlu M, Cakirbay H, Değer O, Cengiz S, Kul S (2008) The association of anti-CCP antibodies with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 28(10):965–970
Glasnović M, Bosnjak I, Vcev A, Soldo I, Glasnović-Horvatić E, Soldo-Butković S, Pavela J, Mićunović N (2007) Anti-citrullinated antibodies, radiological joint damages and their correlations with disease activity score (DAS28). Coll Antropol 31(1):345–348
Fitzsimons EJ, Houston T, Munro R, Sturrock RD, Speekenbrink AB, Brock JH (2002) Erythroblast iron metabolism and serum soluble transferrin receptor values in the anemia of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 47(2):166–171
Orbach H, Zandman-Goddard G, Amital H, Barak V, Szekanecz Z, Szucs G, Danko K, Nagy E, Csepany T, Carvalho JF, Doria A, Shoenfeld Y (2007) Novel biomarkers in autoimmune diseases: prolactin, ferritin, vitamin D, and TPA levels in autoimmune diseases. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1109:385–400
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Önder, B., Kurtaran, A., Kimyon, S. et al. Association of anti-CCP positivity with serum ferritin and DAS-28. Rheumatol Int 30, 223–227 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-009-0941-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-009-0941-4