Abstract
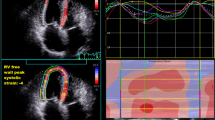
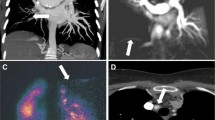
Differentiation between different forms of pulmonary hypertension (PH) is essential for correct disease management. The goal of this study was to elucidate the clinical impact of high spatial resolution MR angiography (SR-MRA) and time-resolved MRA (TR-MRA) to differentiate between patients with chronic thromboembolic PH (CTEPH) and idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH). Ten PH patients and five volunteers were examined. Twenty TR-MRA data sets (TA 1.5 s) and SR-MRA (TA 23 s) were acquired. TR-MRA data sets were subtracted as angiography and perfusion images. Evaluation comprised analysis of vascular pathologies on a segmental basis, detection of perfusion defects, and bronchial arteries by two readers in consensus. Technical evaluation comprised evaluation of image quality, signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) measurements, and contrast-media passage time. Visualization of the pulmonary arteries was possible down to a subsegmental (SR-MRA) and to a segmental (TR-MRA) level. SR-MRA outperformed TR-MRA in direct visualization of intravascular changes. Patients with IPAH predominantly showed tortuous pulmonary arteries while in CTEPH wall irregularities and abnormal proximal-to-distal tapering was found. Perfusion images showed a diffuse pattern in IPAH and focal defects in CTEPH. TR-MRA and SR-MRA resulted in the same final diagnosis. Both MRA techniques allowed for differentiation between IPAH and CTEPH. Therefore, TR-MRA can be used in the clinical setting, especially in dyspneic patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barst RJ, McGoon M, Torbicki A, Sitbon O, Krowka MJ, Olschewski H, Gaine S (2004) Diagnosis and differential assessment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol 43:40S–47S
Bouchard A, Higgins CB, Byrd BF III, Amparo EG, Osaki L, Axelrod R (1985) Magnetic resonance imaging in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am J Cardiol 56:938–942
van Beek EJ, Wild JM, Fink C, Moody AR, Kauczor HU, Oudkerk M (2003) MRI for the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism. J Magn Reson Imaging 18:627–640
Ley S, Kauczor HU, Heussel CP, Kramm T, Mayer E, Thelen M, Kreitner KF (2003) Value of contrast-enhanced MR angiography and helical CT angiography in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Eur Radiol 13:2365–2371
Bergin CJ, Hauschildt J, Rios G, Belezzuoli EV, Huynh T, Channick RN (1997) Accuracy of MR angiography compared with radionuclide scanning in identifying the cause of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am J Roentgenol 168:1549–1555
Fink C, Ley S, Puderbach M, Plathow C, Bock M, Kauczor HU (2004) 3D pulmonary perfusion MRI and MR angiography of pulmonary embolism in pigs after a single injection of a blood pool MR contrast agent. Eur Radiol 14:1291–1296
Fink C, Risse F, Buhmann R, Ley S, Meyer FJ, Plathow C, Puderbach M, Kauczor HU (2004) Quantitative analysis of pulmonary perfusion using time-resolved parallel 3D MRI-initial results. Fortschr Röntgenstr 176:170–174
Shors SM, Cotts WG, Pavlovic-Surjancev B, Francois CJ, Gheorghiade M, Finn JP (2003) Heart failure: evaluation of cardiopulmonary transit times with time-resolved MR angiography. Radiology 229:743–748
Fink C, Bock M, Kroeker R, Requardt M, Ley S, Kauczor H-U (2004) Contrast-enhanced MRA with elliptic-centric view ordering and view sharing: theoretical considerations and application in patients with cardiopulmonary disease. Proc Int Soc Mag Reson Med 11:6
Kreitner KF, Ley S, Kauczor HU, Mayer E, Kramm T, Pitton MB, Krummenauer F, Thelen M (2004) Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: pre- and postoperative assessment with breath-hold MR imaging techniques. Radiology 232:535–543
Goyen M, Ruehm SG, Debatin JF (2000) MR-angiography the role of contrast agents. Eur J Radiol 34:247–256
Kreitner K-F, Ley S, Kauczor H-U, Kalden P, Pitton MB, Mayer E, Laub G, Thelen M (2000) Assessment of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension by three-dimensional contrast-enhanced MR angiography-comparison with selective intraarterial DSA. Fortschr Röntgenstr 172:1–6
Fink C, Bock M, Puderbach M, Schmähl A, Delorme S (2003) Partially parallel three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging for the assessment of lung perfusion-initial results. Invest Radiol 38:482–488
Nikolaou K, Schoenberg S, Attenberger U, Nittka M, Behr J, Reiser M (2003) High-resolution MRA and fast perfusion imaging using integrated parallel acquisition techniques (iPAT) in the diagnosis of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Proc Int Soc Mag Reson Med 11:1370
Kauczor H-U, Schwickert HC, Mayer E, Schweden F, Schild HH, Thelen M (1994) Spiral CT of bronchial arteries in chronic thromboembolism. J Comput Assist Tomogr 18:855–861
Torheim G, Amundsen T, Rinck PA, Haraldseth O, Sebastiani G (2001) Analysis of contrast-enhanced dynamic MR images of the lung. J Magn Reson Imaging 13:577–587
Zheng J, Leawoods JC, Nolte M, Yablonskiy DA, Woodard PK, Laub G, Gropler RJ, Conradi MS (2002) Combined MR proton lung perfusion/angiography and helium ventilation: potential for detecting pulmonary emboli and ventilation defects. Magn Reson Med 47:433–438
Oudkerk M, van Beek EJ, Wielopolski P, van Ooijen PM, Brouwers-Kuyper EM, Bongaerts AH, Berghout A (2002) Comparison of contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography and conventional pulmonary angiography for the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism: a prospective study. Lancet 359:1643–1647
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the valuable help of S. Yubai and K. Knauer in performing the examinations. This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Grant FOR 474).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ley, S., Fink, C., Zaporozhan, J. et al. Value of high spatial and high temporal resolution magnetic resonance angiography for differentiation between idiopathic and thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: initial results. Eur Radiol 15, 2256–2263 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-005-2792-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-005-2792-z