Abstract
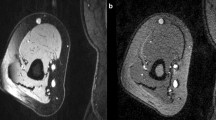
A contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography (CE-MRA) protocol for selective imaging of the entire upper extremity arterial and venous tree in a single exam has been developed. Twenty-five end-stage renal disease (ESRD) patients underwent CE-MRA and duplex ultrasonography (DUS) of the upper extremity prior to hemodialysis vascular access creation. Accuracy of CE-MRA arterial and venous diameter measurements were compared with DUS and intraoperative (IO) diameter measurements, the standard of reference. Upper extremity vasculature depiction was feasible with CE-MRA. CE-MRA forearm and upper arm arterial diameters were 2.94 ± 0.67 mm and 4.05 ± 0.84 mm, respectively. DUS arterial diameters were 2.80 ± 0.48 mm and 4.38 ± 1.24 mm; IO diameters were 3.00 ± 0.35 mm and 3.55 ± 0.51 mm. Forearm arterial diameters were accurately determined with both techniques. Both techniques overestimated upper arm arterial diameters significantly. Venous diameters were accurately determined with CE-MRA but not with DUS (forearm: CE-MRA: 2.64 ± 0.61 mm; DUS: 2.50 ± 0.44 mm, and IO: 3.40 ± 0.22 mm; upper arm: CE-MRA: 4.09 ± 0.71 mm; DUS: 3.02 ± 1.65 mm, and IO: 4.30 ± 0.78 mm). CE-MRA enables selective imaging of upper extremity vasculature in patients requiring hemodialysis access. Forearm arterial diameters can be assessed accurately by CE-MRA. Both CE-MRA and DUS slightly overestimate upper arm arterial diameters. In comparison to DUS, CE-MRA enables a more accurate determination of upper extremity venous diameters.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grassmann A, Gioberge S, Moeller S, Brown G (2005) ESRD patients in 2004: global overview of patient numbers, treatment modalities and associated trends. Nephrol Dial Transplant 20:2587–2593
Meichelboeck W (2005) ESRD 2005—a worldwide overview—facts, figures and trends. In: Mickley V (ed) 4th International Congress of the Vascular Access Society (VAS). Blood Purif 23:227–261
Robbin ML, Chamberlain NE, Lockhart ME, Gallichio MH, Young CJ, Deierhoi MH, Allon M (2002) Hemodialysis arteriovenous fistula maturity: US evaluation. Radiology 225:59–64
NKF-K/DOQI (2001) Clinical practice guidelines for vascular access: update 2000. Am J Kidney Dis 37(Suppl 1):S137–S181
Tordoir JH, Mickley V (2003) European guidelines for vascular access: clinical algorithms on vascular access for haemodialysis. Edtna Erca J 29:131–136
Robbin ML, Gallichio MH, Deierhoi MH, Young CJ, Weber TM, Allon M (2000) US vascular mapping before hemodialysis access placement. Radiology 217:83–88
Malovrh M (2002) Native arteriovenous fistula: preoperative evaluation. Am J Kidney Dis 39:1218–1225
Malovrh M (1998) Non-invasive evaluation of vessels by duplex sonography prior to construction of arteriovenous fistulas for haemodialysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 13:125–129
Silva MB Jr, Hobson RW 2nd, Pappas PJ, Jamil Z, Araki CT, Goldberg MC, Gwertzman G, Padberg FT Jr (1998) A strategy for increasing use of autogenous hemodialysis access procedures: impact of preoperative noninvasive evaluation. J Vasc Surg 27:302–307; discussion 307–308
Lemson MS, Leunissen KM, Tordoir JH (1998) Does pre-operative duplex examination improve patency rates of Brescia-Cimino fistulas? Nephrol Dial Transplant 13:1360–1361
Leblanc M, Saint-Sauveur E, Pichette V (2003) Native arterio-venous fistula for hemodialysis: What to expect early after creation? J Vasc Access 4:39–44
Mendes RR, Farber MA, Marston WA, Dinwiddie LC, Keagy BA, Burnham SJ (2002) Prediction of wrist arteriovenous fistula maturation with preoperative vein mapping with ultrasonography. J Vasc Surg 36:460–463
Tordoir JH, Rooyens P, Dammers R, van der Sande FM, de Haan M, Yo TI (2003) Prospective evaluation of failure modes in autogenous radiocephalic wrist access for haemodialysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 18:378–383
Wong V, Ward R, Taylor J, Selvakumar S, How TV, Bakran A (1996) Factors associated with early failure of arteriovenous fistulae for haemodialysis access. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 12:207–213
Brimble KS, Rabbat ChG, Treleaven DJ, Ingram AJ (2002) Utility of ultrasonographic venous assessment prior to forearm arteriovenous fistula creation. Clin Nephrol 58:122–127
Ascher E, Gade P, Hingorani A, Mazzariol F, Gunduz Y, Fodera M, Yorkovich W (2000) Changes in the practice of angioaccess surgery: impact of dialysis outcome and quality initiative recommendations. J Vasc Surg 31:84–92
Patel ST, Hughes J, Mills JL Sr (2003) Failure of arteriovenous fistula maturation: an unintended consequence of exceeding dialysis outcome quality Initiative guidelines for hemodialysis access. J Vasc Surg 38:439–445; discussion 445
Lockhart ME, Robbin ML, Allon M (2004) Preoperative sonographic radial artery evaluation and correlation with subsequent radiocephalic fistula outcome. J Ultrasound Med 23:161–168; quiz 169–171
Huber TS, Ozaki CK, Flynn TC, Lee WA, Berceli SA, Hirneise CM, Carlton LM, Carter JW, Ross EA, Seeger JM (2002) Prospective validation of an algorithm to maximize native arteriovenous fistulae for chronic hemodialysis access. J Vasc Surg 36:452–459
Miller PE, Tolwani A, Luscy CP, Deierhoi MH, Bailey R, Redden DT, Allon M (1999) Predictors of adequacy of arteriovenous fistulas in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int 56:275–280
Mihmanli I, Besirli K, Kurugoglu S, Atakir K, Haider S, Ogut G, Numan F, Canturk E, Sayin AG (2001) Cephalic vein and hemodialysis fistula: surgeon's observation versus color Doppler ultrasonographic findings. J Ultrasound Med 20:217–222
Allon M, Robbin ML (2002) Increasing arteriovenous fistulas in hemodialysis patients: problems and solutions. Kidney Int 62:1109–1124
Lemson MS, Zwiers I, Leunissen KML, Tordoir JHM (1999) Patient selection with preoperative duplex examination can improve patnecy rates of brescia-cimino fistulas. J Vasc Technol 23:115–119
Hoogeveen RM, Bakker CJ, Viergever MA (1998) Limits to the accuracy of vessel diameter measurement in MR angiography. J Magn Reson Imaging 8:1228–1235
Westenberg JJ, van der Geest RJ, Wasser MN, van der Linden EL, van Walsum T, van Assen HC, de Roos A, Vanderschoot J, Reiber JH (2000) Vessel diameter measurements in gadolinium contrast-enhanced three-dimensional MRA of peripheral arteries. Magn Reson Imaging 18:13–22
Katz ML, Comerota AJ, DeRojas J, Bowman G, Czeredarczuk M, White JV (1987) B-mode imaging to determine the suitability of arm veins for primary arteriovenous fistulae. J Vasc Technol 11:172–174
Bland JM (1987) An introduction to medical statistics, Oxford University Press, Oxford
Bland JM, Altman DG (1986) Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1:307–310
Yucel EK, Anderson CM, Edelman RR, Grist TM, Baum RA, Manning WJ, Culebras A, Pearce W (1999) AHA scientific statement. Magnetic resonance angiography: update on applications for extracranial arteries. Circulation 100:2284–2301
Willinek WA, von Falkenhausen M, Born M, Gieseke J, Holler T, Klockgether T, Textor HJ, Schild HH, Urbach H (2005) Noninvasive detection of steno-occlusive disease of the supra-aortic arteries with three-dimensional contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography: a prospective, intra-individual comparative analysis with digital subtraction angiography. Stroke 36:38–43
Willinek WA, Gieseke J, Conrad R, Strunk H, Hoogeveen R, von Falkenhausen M, Keller E, Urbach H, Kuhl CK, Schild HH (2002) Randomly segmented central k-space ordering in high-spatial-resolution contrast-enhanced MR angiography of the supraaortic arteries: initial experience. Radiology 225:583–588
Ruehm SG, Wiesner W, Debatin JF (2000) Pelvic and lower extremity veins: contrast-enhanced three-dimensional MR venography with a dedicated vascular coil-initial experience. Radiology 215:421–427
Ruehm SG, Zimny K, Debatin JF (2001) Direct contrast-enhanced 3D MR venography. Eur Radiol 11:102–112
Ruehm SG (2003) MR venography. Eur Radiol 13:229–230
Quinn SF, Sheley RC, Semonsen KG, Leonardo VJ, Kojima K, Szumowski J (1998) Aortic and lower-extremity arterial disease: evaluation with MR angiography versus conventional angiography. Radiology 206:693–701
Ho KY, Leiner T, de Haan MW, van Engelshoven JM (1999) Peripheral MR angiography. Eur Radiol 9:1765–1774
Leiner T, Kessels AG, Nelemans PJ, Vasbinder GB, de Haan MW, Kitslaar PE, Ho KY, Tordoir JH, van Engelshoven JM (2005) Peripheral arterial disease: comparison of color duplex US and contrast-enhanced MR angiography for diagnosis. Radiology 235:699–708
Goyen M, Barkhausen J, Kuehl H, Goehde SC, Kroger K, Bosk S, Debatin JF, Ruehm SG (2001) Contrast-enhanced 3D MR venography of central thoracic veins: preliminary experience. Rofo Fortschr Geb Rontgenstr Neuen Bildgeb Verfahr 173:356–361
Kroencke TJ, Taupitz M, Arnold R, Fritsche L, Hamm B (2001) Three-dimensional gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance venography in suspected thrombo-occlusive disease of the central chest veins. Chest 120:1570–1576
Shankar KR, Abernethy LJ, Das KS, Roche CJ, Pizer BL, Lloyd DA, Losty PD (2002) Magnetic resonance venography in assessing venous patency after multiple venous catheters. J Pediatr Surg 37:175–179
Wentz KU, Frohlich JM, von Weymarn C, Patak MA, Jenelten R, Zollikofer CL (2003) High-resolution magnetic resonance angiography of hands with timed arterial compression (tac-MRA). Lancet 361:49–50
Haire WD, Lynch TG, Lund GB, Lieberman RP, Edney JA (1991) Limitations of magnetic resonance imaging and ultrasound-directed (duplex) scanning in the diagnosis of subclavian vein thrombosis. J Vasc Surg 13:391–397
Ho VB, Prince MR, Dong Q (1999) Magnetic resonance imaging of the aorta and branch vessels. Coron Artery Dis 10:141–149
Laissy JP, Fernandez P, Karila-Cohen P, Delmas V, Dupuy E, Chillon S, Mignon F, Schouman-Claeys E (2003) Upper limb vein anatomy before hemodialysis fistula creation: cross-sectional anatomy using MR venography. Eur Radiol 13:256–261
Polak JF, Fox LA (1999) MR assessment of the extremity veins. Semin Ultrasound CT MR 20:36–46
Schuman ES, Quinn SF, Standage BA, Ragsdale JW, Demlow TA, Leonardo V, Sheley RC, Szumowski J, Ferris BL (1999) Magnetic resonce angiography in evaluation of central and peripheral vasculature prior to dialysis surgery. Vascular access for hemodialysis-VI. WL Gore—Precept Press, Chicago, pp 103–109
Shinde TS, Lee VS, Rofsky NM, Krinsky GA, Weinreb JC (1999) Three-dimensional gadolinium-enhanced MR venographic evaluation of patency of central veins in the thorax: initial experience. Radiology 213:555–560
Mihmanli I, Kantarci F (2004) MR venography needs to know where it stands for vascular mapping prior to fistula creation. Eur Radiol 14:1130–1131
Meaney JF (2003) Magnetic resonance angiography of the peripheral arteries: current status. Eur Radiol 13:836–852
Geoffroy O, Tassart M, Le Blanche AF, Khalil A, Duedal V, Rossert J, Bigot JM, Boudghene FP (2001) Upper extremity digital subtraction venography with gadoterate meglumine before fistula creation for hemodialysis. Kidney Int 59:1491–1497
Thomsen HS (2006) Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: a serious late adverse reaction to gadodiamide. Eur Radiol 16:2619–2621
Planken RN, Keuter XH, Hoeks AP, Kooman JP, van der Sande FM, Kessels AG, Leiner T, Tordoir JH (2006) Diameter measurements of the forearm cephalic vein prior to vascular access creation in end–stage renal disease patients: graduated pressure cuff versus tourniquet vessel dilatation. Nephrol Dial Transplant 21:802–806
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Planken, N.R., Tordoir, J.H., Duijm, L.E. et al. Magnetic resonance angiographic assessment of upper extremity vessels prior to vascular access surgery: feasibility and accuracy. Eur Radiol 18, 158–167 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-007-0714-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-007-0714-y