Abstract
Objective
To compare image quality and noise of conventional unenhanced (CU) and virtual unenhanced (VU) images in patients who underwent hepatic dual energy computed tomography (DECT) and to assess potential radiation dose reduction.
Materials and methods
Forty consecutive patients were studied. Mean CU and VU image quality and noise were analyzed by two blinded radiologists using a five-point grade scale. The effective radiation dose of a triple-phase protocol (CU, arterial and DE portal phases) were compared with that of a dual-phase protocol (arterial and DE portal phases).
Results
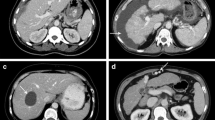
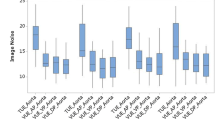
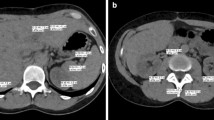
No significant difference in mean image quality was observed between VU (3.92 ± 0.85) and CU images (4.20 ± 0.72). A significant difference in mean image noise was observed between VU and CU (P < 0.01). The dose reduction achieved by omitting the unenhanced acquisition was 30.47 ± 7.07% (P < 0.01). In 6 patients, a complete VU liver image was not obtained.
Conclusions
VU images can be obtained with similar image quality as CU. This approach favors a reduction in patient’s radiation exposure. Nevertheless, a complete abdominal DECT is possible only in patients with a low body mass index, due technical limitations of the present DECT systems.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Johnson TR, Krauss B, Sedlmair M et al (2007) Material differentiation by dual energy CT: initial experience. Eur Radiol 17:1510–1517
Godoy MCB, Naidich DP, Marchiori E, Assadourian B, Leidecker C (2009) Basic principles and postprocessing techniques of dual-energy CT: illustrated by selected congenital abnormalities of the thorax. J Thorac Imaging 24:152–159
Graser A, Johnson TR, Chandarana H, Macari M (2009) Dual energy CT: preliminary observations and potential clinical applications in the abdomen. Eur Radiol 19:13–23
Hazirolan T, Akpinar B, Ünal S, Gümrük F, Haliloglu M, Alibek S (2008) Value of dual energy computed tomography for detection of myocardial iron deposition in thalassaemia patients: initial experience. Eur J Radiol 68:442–445
Uotani K, Watanabe Y, Higashi M, Nakazawa T, Kono AK, Hori Y, Fukuda T et al (2009) Dual-energy CT head bone and hard plaque removal for quantification of calcified carotid stenosis: utility and comparison with digital subtraction angiography. Eur Radiol 19:2060–2065
Chae EJ, Song JW, Seo JB et al (2008) Clinical utility of dual-energy CT in the evaluation of solitary pulmonary nodules: initial experience. Radiology 249:671–681
Yeh BM, Shepherd JA, Wang ZJ et al (2009) Dual-energy and low-kVp CT in the abdomen. AJR 193:47–54
Thieme SF, Becker CR, Hacker M, Nikolaou K, Reiser MF, Johnson TRC (2008) Dual energy CT for the assessment of lung perfusion – correlation to scintigraphy. Eur J Radiol 68:369–374
Scheffel H, Stolzmann P, Frauenfelder T et al (2007) Dual-energy contrast-enhanced computed tomography for the detection of urinary stone disease. Invest Radiol 42:823–829
Choi HK, Al-Arfaj A, Eftekhari A, Munk PL, Shojania K, Reid G, Nicolaou S (2009) Dual energy computed tomography in tophaceous gout. Ann Rheum Dis 68:1609–1612
Thomas C, Patschan O, Ketelsen D, Tsiflikas I, Reimann A, Brodoefel H, Buchgeister M et al (2009) Dual-energy CT for the characterization of urinary calculi: In vitro and in vivo evaluation of a low-dose scanning protocol Eur Radiol 19:1553–1559
Brown CL, Hartman RP, Dzyubak OP, Takahashi N, Kawashima A, McCollough CH et al (2009) Dual-energy CT iodine overlay technique for characterization of renal masses as cyst or solid: a phantom feasibility study. Eur Radiol 19:1289–1295
Ruzsics B, Lee H, Zwerner PL, Gebregziabher M, Costello P, Schoepf UJ (2008) Dual-energy CT of the heart for diagnosing coronary artery stenosis and myocardial ischemia - initial experience. Eur Radiol 18:2414–2424
Graser A, Johnson TR, Hecht EM, Becker CR, Leidecker C, Staehler M et al (2009) Dual-energy CT in patients suspected of having renal masses: can virtual nonenhanced images replace true nonenhanced images? Radiology 252:433–440
Chandarana H, Godoy MC, Vlahos I, Graser A, Babb J, Leidecker C, Macari M (2008) Abdominal aorta: evaluation with dual-source dual-energy multidetector CT after endovascular repair of aneurysms – initial observations. Radiology 249:692–700
Stolzmann P, Frauenfelder T, Pfammatter T, Peter N, Scheffel H, Lachat M et al (2008) Endoleaks after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: detection with dual-energy dual-source CT. Radiology 249:682–691
Ferda J, Novák M, Mírka H, Baxa J, Ferdová E, Bednárová A, Flohr T et al (2009) The assessment of intracranial bleeding with virtual unenhanced imaging by means of dual-energy CT angiography. Eur Radiol 19:2518–2522
Graser A, Wintersperger BJ, Suess C, Reiser MF, Becker CR (2006) Dose reduction and image quality in MDCT colonography using tube current modulation. AJR 187:695–701
Heiken JP, Brink JA, McClennan BL, Sagel SS et al (1995) Dynamic incremental CT: effect of volume and concentration of contrast material and patient weight on hepatic enhancement. Radiology 195:353–357
Brink JA, Heiken JP, Forman HP, Sagel SS et al (1995) Hepatic spiral CT: reduction of dose of intravenous contrast material. Radiology 197:83–88
Menzel H, Schibilla H, Teunen D (eds) (2000) European guidelines on quality criteria for computed tomography. Publication no. EUR 16262 EN. European Commission, Luxembourg, pp 735–738
Brenner DJ, Elliston CD (2004) Estimated radiation risks potentially associated with full-body CT screening. Radiology 232:735–738
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Cecco, C.N., Buffa, V., Fedeli, S. et al. Dual energy CT (DECT) of the liver: conventional versus virtual unenhanced images. Eur Radiol 20, 2870–2875 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-010-1874-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-010-1874-8