Abstract
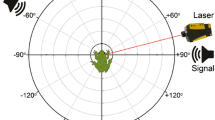
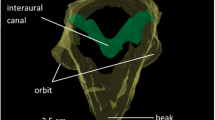
We studied the directional response of the coupled-eardrum system in the northern leopard frog, Rana pipiens pipiens. Eardrum behavior closely approximates a linear time-invariant system, with a highly correlated input–output relationship between the eardrum pressure difference and the eardrum velocity. Variations in the eardrum transfer function at frequencies below 800 Hz indicate the existence of an extratympanic sound transmission pathway which can interfere with eardrum motions. The eardrum velocity was shown to shift in phase as a function of sound incident angle, which was a direct result of the phase-shift of the eardrum pressure difference. We used two laser-Doppler vibrometers to measure the interaural vibration time difference (IVTD) and the interaural vibration amplitude difference (IVAD) between the motions of the two eardrums. The coupled-eardrum system enhanced the IVTD and IVAD by a factor of 3 and 3 dB, respectively, when compared to an isolated-eardrum system of the same size. Our findings are consistent with the time-delay sensitivity of other coupled-eardrum systems such as those found in crickets and flies.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IPD:
-
Interaural phase difference
- ITD:
-
Interaural time difference
- IID:
-
Interaural intensity difference
- IVAD:
-
Interaural vibration amplitude difference
- LTI:
-
Linear time-invariant
References
Aertsen AMHJ, Vlaming MSMG, Eggermont JJ, Johannesma PIM (1986) Directional hearing in the grassfrog (Rana temporaria L.). II. Acoustics and modelling of the auditory periphery. Hearing Res 21:17–40
Christensen-Dalsgaard J (2005) Directional hearing in nonmammalian tetrapods. In: Popper AN, Fay RR (eds) Sound source localization. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 67–123
Christensen-Dalsgaard J, Jørgensen MB (1996) Sound and vibration sensitivity of VIIIth nerve fibers in the grassfrog, Rana temporaria. J Comp Physiol A 179:437–445
Christensen-Dalsgaard J, Narins PM (1993) Sound and vibration sensitivity of VIIIth nerve fibers in the frogs Leptodactylus albilabris and Rana pipiens pipiens. J Comp Physiol A 172:653–662
Chung S-H, Pettigrew A, Anson M (1978) Dynamics of the amphibian middle ear. Nature 272:142–147
Ehret G, Tautz J, Schmitz B, Narins PM (1990) Hearing through the lungs: lung-eardrum transmission of sound in the frog Eleutherodactylus coqui. Naturwissenschaften 77:192–194
Ehret G, Keilwerth E, Kamada T (1994) The lung-eardrum pathway in three treefrog and four dendrobatid frog species: some properties of sound transmission. J Exp Biol 195:329–343
Feng AS (1980) Directional characteristics of the acoustic receiver of the leopard frog (Rana pipiens): a study of the eighth nerve auditory responses. J Acoust Soc Am 68:1107–1114
Feng AS, Capranica RR (1978) Sound localization in anurans II. Binaural interaction in superior olivary nucleus of the green treefrog (Hyla cinerea). J Neurophysiol 41:43–54
Feng AS, Shofner WP (1981) Peripheral basis of sound localization in anurans. Acoustic properties of the frog’s ear. Hearing Res 5:201–216
Feng AS, Gerhardt HC, Capranica RR (1976) Sound localization behavior of the green treefrog (Hyla cinerea) and the barking treefrog (H. gratiosa). J Comp Physiol A 107:241–252
Feng AS, Hall JC, Gooler DM (1990) Neural basis of sound pattern recognition in anurans. Progr Neurobiol 34:313–329
Fletcher NH, Thwaites S (1979) Physical models for the analysis of acoustical systems in biology. Q Rev Biophys 12:25–65
Gerhardt HC, Klump (1988) Phonotactic responses and selectivity of barking treefrogs (Hyla gratiosa) to chorus sounds. J Comp Physiol A 163:795–802
Gerhardt HC, Rheinlaender J (1980) Accuracy of sound localization in a miniature dendrobatid frog. Naturwissenschaften 67:362
Gourevitch G (1987) Binaural hearing in land mammals. In: Yost WA, Gourevitch G (eds) Directional hearing. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 226–246
Jørgensen MB (1991) Comparative studies of the biophysics of directional hearing in anurans. J Comp Physiol A 169:591–598
Jørgensen MB, Christensen-Dalsgaard J (1997a) Directionality of auditory nerve fiber responses to pure tone stimuli in the grassfrog, Rana temporaria. I. Spike rate responses. J Comp Physiol A 180:493–502
Jørgensen MB, Christensen-Dalsgaard J (1997b) Directionality of auditory nerve fiber responses to pure tone stimuli in the grassfrog, Rana temporaria. II. Spike timing. J Comp Physiol A 180:503–511
Jørgensen MB, Gerhardt HC (1991) Directional hearing in the gray treefrog Hyla versicolor: eardrum vibrations and phonotaxis. J Comp Physiol A 169:177–183
Jørgensen MB, Schmitz B, Christensen-Dalsgaard J (1991) Biophysics of directional hearing in the frog Eleutherodactylus coqui. J Comp Physiol A 168:223–232
Klump GM, Gerhardt HC (1989) Sound localization in the barking treefrog. Naturwissenschaften 76:35–37
Lombard RE, Straughan IR (1974) Functional aspects of anuran middle ear structures. J Exp Biol 61:71–93
Michelsen A, Löhe G (1995) Tuned directionalitiy in cricket ears. Nature 375:639
Michelsen A, Larsen ON (2004) Properties of pressure difference receiving ears. In: Abstract 7th Congress of the Int’l Soc Neuroethol Nyborg Denmark PO33
Michelsen A, Jørgensen M, Christensen-Dalsgaard J, Capranica RR (1986) Directional hearing of awake, unrestrained treefrogs. Naturwissenschaften 73:682
Narins PM, Lewis ER (1984) The vertebrate ear as an exquisite seismic sensor. J Acoust Soc Am 76:1384–1387
Narins PM, Ehret G, Tautz J (1988) Accessory pathway for sound transfer in a neotropical frog. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:1255–1265
Passmore NI, Capranica RR, Telford SR, Bishop PJ (1984) Phonotaxis in the painted reed frog (Hyperolius marmoratus). J Comp Physiol A 154:189–197
Pinder AC, Palmer AR (1983) Mechanical properties of the frog ear: vibration measurements under free-and closed-field acoustic conditions. Proc R Soc Lond B 219:371–396
Rheinlaender J, Klump G (1988) Behavioral aspects of sound localization. In: Fritzsch B, Ryan MJ, Wilczynski W, Hetherington TE, Walkowiak W (eds) The evolution of the amphibian auditory system. Wiley, New York, pp 297–305
Rheinlaender J, Gerhardt HC, Yager DD, Capranica RR (1979) Accuracy of phonotaxis by the green treefog (Hyla cinerea). J Comp Physiol A 133:247–255
Rheinlaender J, Walkowiak W, Gerhardt HC (1981) Directional hearing in the green treefrog: a variable mechanism? Naturwissenschaften 68:430–431
Robert D, Miles RN, Hoy RR (1996) Directional hearing by mechanical coupling in the parasitoid fly Ormia ochracea. J Comp Physiol A 179:29–44
Robert D, Miles RN, Hoy RR (1999) Tympanal hearing in the sarcophagid parasitoid fly Emblemasoma sp.: the biomechanics of directional hearing. J Exp Biol 202:1865–1876
Schmitz B, White TD, Narins PM (1992) Directionality of phase locking in auditory nerve fibers of the leopard frog Rana pipiens pipiens. J Comp Physiol A 170:589–604
Vlaming MSMG, Aertsen AMHJ, Epping WJM (1984) Directional hearing in the grass frog (Rana temporaria L.): I. Mechanical vibration of tympanic membrane. Hearing Res 14:191–201
Wang J, Ludwig TA, Narins PM (1996) Spatial and spectral dependence of the auditory periphery in the northern leopard frog. J Comp Physiol A 178:159–172
Wilczynski W, Resler C, Capranica RR (1987) Tympanic and extratympanic sound transmission in the leopard frog. J Comp Physiol A 161:659–669
Yu X, Lewis ER, Feld D (1991) Seismic and auditory tuning curves from bullfrog saccular and amphibian papillar axons. J Comp Physiol A 169:241–248
Acknowledgements
We thank Rick Klufas and Mike Eng for their help in machining various parts for this project, Margaret Kowalczyk for help in producing Figs. 5–7, and Urban Willi for helpful discussions. This work is supported by NIH Grant no. DC-00222 to PMN. The experiments comply with the “Principles of animal care”, publication No. 86–23, revised 1985 of the National Institute of Health, and also with the current laws of the United States of America.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ho, C.C.K., Narins, P.M. Directionality of the pressure-difference receiver ears in the northern leopard frog, Rana pipiens pipiens . J Comp Physiol A 192, 417–429 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-005-0080-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-005-0080-7